Introduction:
Imagine a landmass nearly three times the size of New York City, or as large as the state of Delaware, entirely composed of ice. That’s the awe-inspiring scale of Iceberg A23a, the world’s largest iceberg. This frozen behemoth has captured the attention of scientists and the public alike as it embarks on an unpredictable journey.
Iceberg A23a on the Move, the world’s largest iceberg, is a force of nature demanding our attention. Imagine a colossal fragment of ice nearly three times the size of New York City or the entire state of Delaware. That’s the incredible scale of A23a, which has broken free from Antarctica’s icy grip and has set off on an unpredictable journey.
What is an iceberg?
Icebergs are massive chunks of freshwater ice that have broken off (or “calved”) from glaciers or ice shelves and float freely in open water. They form over extended periods as snow accumulates and compresses into glacial ice, a process that can take centuries.

The Fascination with A23a
Iceberg A23a is remarkable not only for its sheer size but also for its recent movement. For 35 years, the iceberg remained grounded in Antarctica’s Weddell Sea. Recent shifts in ocean currents and temperature have now set A23a adrift. Scientists are closely monitoring the Iceberg A23a on the Move, eager to understand where its path will lead and what impact it might have on the delicate ocean ecosystem.
- Natural vs. Concerning: While the calving of icebergs is natural, these events’ increasing frequency and scale raise alarm. A23a is a poignant example of ice loss from Antarctica’s massive ice shelves.
- Ice Shelves as Buffers: Ice shelves act as barriers, slowing the flow of glaciers from the land into the ocean. When ice shelves weaken and collapse, this flow is unrestricted, directly contributing to rising sea levels.
- The Bigger Picture: While a single iceberg like A23a won’t dramatically impact sea levels (the ice was already floating), its story underscores the larger issue of accelerating ice loss from Antarctica, which has long-term consequences for coastal communities worldwide.
Iceberg A23a: A Brief History
Iceberg A23a has a compelling story that adds to the fascination surrounding this icy giant. Here’s a deeper dive into its origins and journey:
◉ The Birth of a Behemoth:
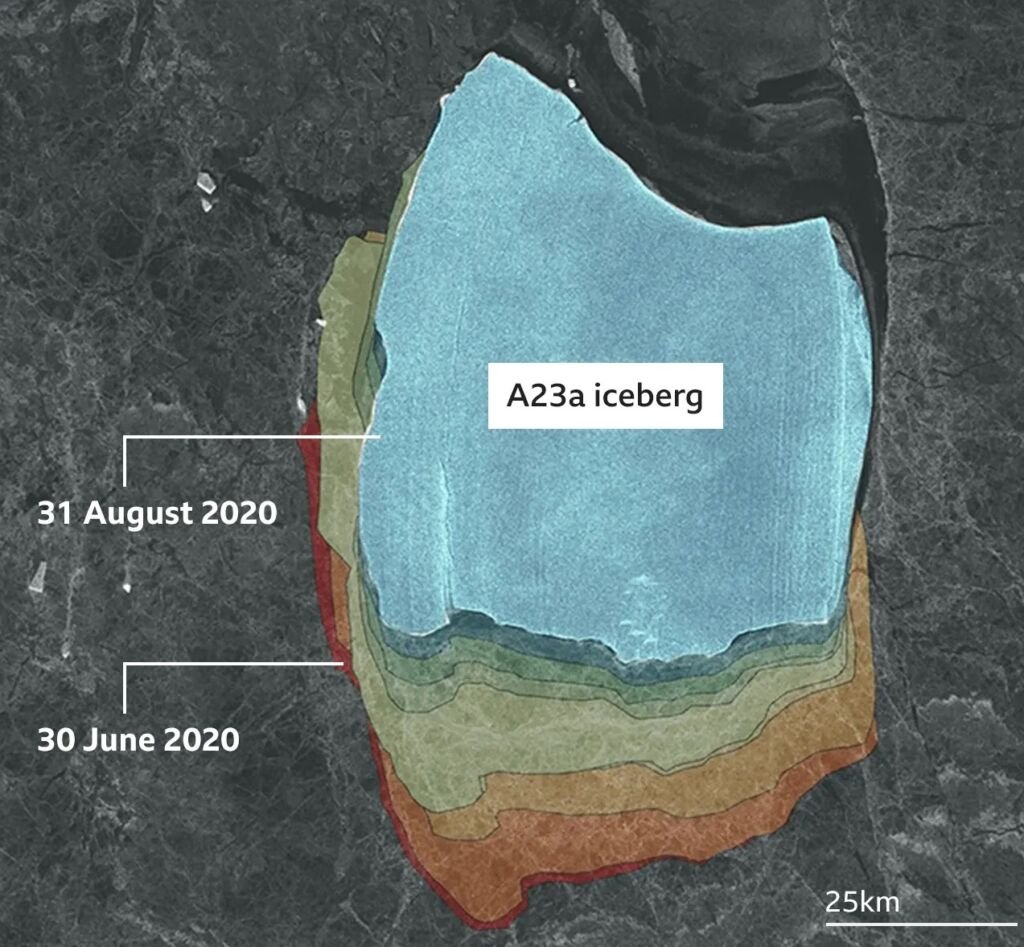
1986, a monumental calving event took place along Antarctica’s Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf. Given the designation Iceberg A23a, this colossal chunk of ice was born.
◉ A Grounded Giant:
Unlike many icebergs that begin drifting with ocean currents, A23a didn’t budge immediately. Wedged against the shallow seabed of the Weddell Sea, the iceberg remained stationary for an astonishing 35 years.
◉ Forces of Nature at Play:
Several factors likely contributed to A23a’s sudden movement in recent years:
- Shifting Currents: Changes in ocean circulation patterns can dislodge grounded icebergs, setting them on a new trajectory.
- Warmer Waters: Rising ocean temperatures can destabilize ice shelves, prompting more frequent calving events and weakening the grip of existing icebergs.
◉ A Record Breaker?
While Iceberg A23a is currently the world’s largest, it’s not unprecedented. Several historical records point to even more giant icebergs:
- B-15: Calved from Antarctica’s Ross Ice Shelf in 2000, B-15 held the world’s largest iceberg title for many years.
- Before Satellites: Accurate records of iceberg size became possible with satellite monitoring. Even more immense icebergs likely roamed the oceans in the past.
◉ The Continuing Saga of Iceberg A23a on the Move:
Scientists are eagerly tracking A23a’s path. Will it head for the warmer waters of the Southern Ocean, where it will break apart and melt more quickly? Will it become grounded once more? The answers will illuminate A23a’s fate and the complex dynamics of our changing polar regions. The story of this Iceberg on the Move captivates scientists and reminds us of the colossal forces at work in our world.
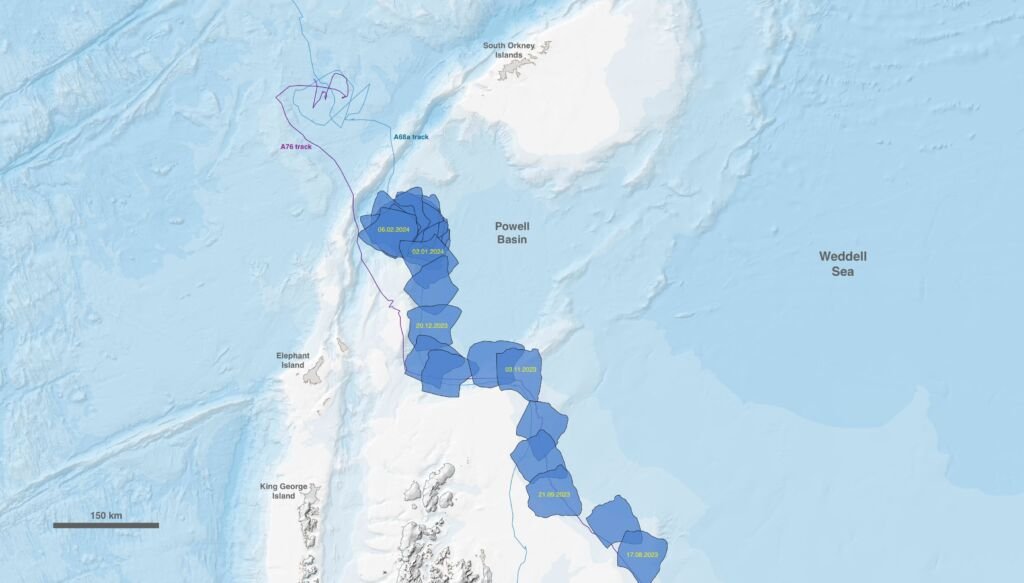
Where is Iceberg A23a Now?
After decades of remaining stationary, Iceberg A23a on the Move is rapidly shifting its position. Understanding its current location and trajectory is crucial in predicting its future and potential impact.
📣 Double-whammy iceberg news this morning:
— British Antarctic Survey 🐧 (@BAS_News) November 24, 2023
1️⃣ The largest iceberg, A23a, is on the move!
Here's its journey out of the Weddell Sea after being grounded on the sea floor after calving in August 1986.
Copernicus Sentinel-1 imagery, Google Earth Engine 👇 pic.twitter.com/KseKTD1Wrg
◉ Beyond the Antarctic Peninsula:
As of late 2023, A23a has drifted past the northern part of the Antarctic Peninsula and entered the open waters of the Southern Ocean. To visualize this, imagine the Antarctic Peninsula as a finger pointing northward – A23a has rounded that fingertip and is now venturing into the larger expanse of the ocean.
◉ The Path of Iceberg Alley:
Icebergs released from Antarctica commonly embark on a trajectory known as “Iceberg Alley.” This route follows the powerful Antarctic Circumpolar Current, which encircles the continent eastward. As A23a has broken free from its grounding, it’s been swept further east into this well-traveled icy highway.
◉ Forces Determining A23a's Drift:
A23a’s movement is primarily influenced by two significant factors:
- Ocean Currents: The strong flow of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current acts as a driving force, propelling the iceberg along its eastward path.
- Winds: Prevailing winds in the Southern Ocean can push against the exposed iceberg areas, adding to its movement and potentially altering its course.
◉ The Unpredictable Path Ahead:
With such dynamic forces at play, the exact destination of Iceberg A23a on the Move remains to be determined. A few likely scenarios for the iceberg’s journey include:
- Continued eastward drift in the Southern Ocean. Following Iceberg Alley’s path, A23a could travel vast distances.
- Grounding: Icebergs can find new resting points along their path, getting caught on shallow ocean features.
- Breaking apart: Due to its enormous size, A23a is subject to internal stresses and the impact of waves, leading to fracturing into smaller icebergs.
Regardless of the outcome, Iceberg A23a on the Move offers a valuable opportunity to study the lifecycle of these iconic icy behemoths, which provide insight into Antarctica’s ice dynamics and their potential responses to climate change.
Potential Destinations and Hazards
As Iceberg A23a on the Move navigates the currents of the Southern Ocean, its path poses some potential hazards, primarily as it draws nearer to certain crucial habitats.
◉ South Georgia Island: A Fragile Haven:
◉ Wildlife Oasis:
South Georgia Island is a remote sub-Antarctic gem with marine and terrestrial life. It’s a critical breeding ground for millions of penguins (including king penguins), seals, albatrosses, and other unique species.
◉ The A23a Threat:
The most significant hazard A23a poses to South Georgia Island is the grounding potential. If the iceberg becomes lodged in the shallow waters surrounding the island, it could:
- Disrupt food chains: Block foraging routes for penguins and seals, hindering their feeding ability and impacting populations.
- Damage seabed ecosystems: Crush delicate seafloor habitats as the iceberg grounds and potentially scrapes along the bottom.
- Release freshwater: Upon melting, A23a releases vast amounts of freshwater into the environment, disrupting the delicate balance of salinity around the island and potentially negatively affecting marine life.
◉ Likelihood of Grounding at South Georgia Island:
The exact trajectory of Iceberg A23a on the Move remains unpredictable. However, scientists note that grounding at South Georgia Island is a definite possibility. Historical records show past icebergs of similar scale have become stuck near the island. Ocean currents are a significant factor – if A23a veers slightly north, the risk of it colliding with South Georgia rises dramatically.
◉ Open Ocean Possibilities:
Should A23a successfully navigate past South Georgia and remain in open water, a different set of scenarios and issues will unfold:
- Gradual Melting: Warmer waters would accelerate A23a’s melting process. However, due to its massive size, complete disappearance could take years, possibly even decades.
- Location: Depending on currents and winds, the melting iceberg could travel considerable distances, potentially approaching shipping lanes.
- Breakup & Smaller Hazards: As A23a melts, the risk of fracturing into smaller yet still sizable icebergs increases. These fragments would create navigation hazards and pose significant threats to ecosystems if they drift toward islands or coastlines.
◉ A32a's Impact Beyond Its Path:
Whether Iceberg A23a on the Move grounds or continues its oceanic trek, its impact reaches far beyond its direct path:
- Freshwater Injection: As the iceberg melts, it releases massive freshwater into the ocean, disrupting marine currents and potentially impacting regional weather patterns.
- Nutrient Release: Icebergs store dust and minerals collected as part of glaciers. These released nutrients nourish phytoplankton, the base of the ocean food chain, with ripple effects throughout the ecosystem.
◉ Beyond South Georgia:
While South Georgia Island garners immediate concern, A23a’s route could disrupt other ecological areas or create hazards to shipping lanes should it continue eastward in the Southern Ocean. However, due to its enormous size, it’s more likely that Iceberg A23a on the Move will break apart before causing damage beyond its immediate vicinity. Close monitoring remains crucial to track its path and any potential threats.
Iceberg A23a on the Move has captured the world’s attention, representing nature’s powerful and sometimes unpredictable forces. Whether it wreaks havoc on island ecosystems or gradually dissolves into the ocean’s vastness, A23a is a powerful reminder of the dynamic changes occurring in our polar regions.
Scientific Implications
Beyond its immediate journey, Iceberg A23a on the Move raises significant scientific questions and underlines urgent concerns about climate change and its effects on our planet.
◉ Melting and Sea Level Rise

- Natural vs. Concerning: While the calving of icebergs is natural, these events’ increasing frequency and scale raise alarm. A23a is a poignant example of ice loss from Antarctica’s massive ice shelves.
- Ice Shelves as Buffers: Ice shelves act as barriers, slowing the flow of glaciers from the land into the ocean. When ice shelves weaken and collapse, this flow is unrestricted, directly contributing to rising sea levels.
- The Bigger Picture: While a single iceberg like A23a won’t dramatically impact sea levels (the ice was already floating), its story underscores the larger issue of accelerating ice loss from Antarctica, which has long-term consequences for coastal communities worldwide.
◉ Monitoring and Research
To better understand the behavior of icebergs and their relationship to broader climate systems, scientists employ a range of tracking and data collection methods:
- Satellite Monitoring: Satellites equipped with advanced imaging systems provide regular updates on the location, size, and movement of icebergs like A23a. This data is crucial for tracking its trajectory and analyzing how it may change shape due to melting or fracturing.
- Field Studies: When accessible, research teams may visit grounded icebergs to study their composition and structure directly. This offers valuable insights into the iceberg’s origins and deterioration processes.
- Data Collected: Key measurements from iceberg studies include:
- Size and Shape: How quickly is the iceberg melting or breaking apart?
- Drift Patterns: Does its movement align with predicted currents and wind patterns?
- Ocean Conditions: How do temperature and salinity around the iceberg impact its behaviour?
- Biological Activity: Do icebergs act as temporary micro-ecosystems for marine life?
◉ Data's Importance for Understanding Climate Change
Analyzing Iceberg A23a on the Move, in conjunction with data from other icebergs and the broader Antarctic ice sheet, provides scientists with essential clues about:
- Ice Shelf Stability: Assessing ice shelf weaknesses and the potential for future large-scale calving events.
- Ocean Circulation: Understanding how icebergs move and melt influences ocean circulation models, which is crucial for predicting large-scale climate patterns.
- Ecosystem Shifts: Observing the interaction between icebergs and marine life reveals potential impacts on food chains and biodiversity due to climate change.
- Sea Level Projections: Tracking ice flow from land into the ocean allows scientists to improve sea-level rise projections and inform climate adaptation strategies.
Iceberg A23a on the Move is more than a spectacle; it is a tangible symbol of the complex changes in our polar regions. The scientific endeavors spurred by this wandering giant contribute to a deeper understanding of Earth’s dynamic systems and highlight the urgency of addressing climate change and its global consequences.
The Fascination with A23a
There’s an undeniable aura of wonder surrounding Iceberg A23a on the Move. Here’s a look into the reasons behind its captivating nature and the value it holds for future research:
- Awe-Inspiring Scale: The sheer size of A23a is difficult to comprehend. Visualizing a floating chunk of ice larger than many cities naturally evokes fascination and reminds us of nature’s immense power. The scale of A23a allows us to grasp the colossal forces at work in the Antarctic’s ice dynamics.
- The Drama of an Unfolding Journey: The sudden movement of A23a after decades of being stationary has added a sense of drama and anticipation to its story. Where will it end up? Will it pose threats to ecosystems or simply melt away in obscurity? Much like a thrilling adventure, its open-ended trajectory keeps observers engaged.
- A Symbol of a Changing World: While iceberg calving is natural, A23a’s story resonates in the context of climate change. It becomes symbolic of the larger picture of melting ice caps and potential threats related to rising sea levels, making it both alarming and intriguing.
◉ Future Insights into Iceberg Behavior
Beyond its spectacle, Iceberg A23a on the Move provides a valuable research opportunity for scientists:
- Long-Term Observation: With the ability to track and monitor A23a from its release to eventual breakdown, researchers can gather a long-term dataset on a single iceberg. This will offer insights into iceberg behaviors that shorter studies or simulations may need to capture.
- Calving and Grounding Studies: Observing how and why A23a broke free and data about the ocean floor structure where it was trapped will advance knowledge of calving events and grounding mechanics.
- Micro-Ecosystems: Icebergs become temporary habitats for microscopic life and even larger organisms. With ongoing documentation of A23a, scientists can examine how icebergs may alter their immediate environments during their lifespan.
- Ocean & Climate Studies: Melting icebergs impact surrounding water temperature and salinity, affecting ocean currents and regional climate. Researchers studying A23a have a rare opportunity to collect detailed data on how a massive iceberg interacts with a dynamic ocean environment.
Iceberg A23a on the Move transcends mere curiosity. It’s a natural marvel that ignites imaginations, stimulates vital research, and reminds us of the interconnectedness between the planet’s remote polar regions and our time’s shared global issues.
Conclusion
There’s an undeniable aura of wonder surrounding Iceberg A23a on the Move. Here’s a look into the reasons behind its captivating nature and the value it holds for future research:
◉ Key Takeaways:
- Iceberg A23a is a colossal reminder of the power and scale of nature, and its size has captured global attention.
- After remaining grounded for decades, A23a’s sudden movement underscores the dynamics of polar environments and the potential for large-scale ice events.
- Scientists closely monitor A23a’s trajectory, with potential implications for ecosystems if it grounds again and potential dangers as it melts into smaller fragments.
- Data gathered from A23a provides invaluable insights for improving our understanding of iceberg behaviors and ice dynamics.
◉ The Uncertain Future:
Whether it becomes grounded near islands or eventually fades into the open ocean, A23a’s uncertain future highlights the need for careful observation. Further research into this magnificent icy wanderer helps scientists address complex climate-related issues.
◉ The Bigger Picture:
- A Symbol of Change: Beyond its journey, Iceberg A23a on the Move symbolizes accelerating ice shelf instability. Its story underscores the consequences of climate change for Antarctica and our world.
Call to Action:
Were you fascinated by the story of Iceberg A23a on the Move?
Share this post with your friends to spread awareness about this incredible natural phenomenon and the broader implications for our planet! We’d love to hear your thoughts in the comments below.