Introduction
Have you ever gazed at the night sky and wondered which planet reigns supreme in size? The biggest planet in our solar system dominates in mass and in sheer wonder and mystery.
Jupiter is the biggest planet in our solar system. It is a colossal gas giant that dwarfs all other planets. With its mesmerizing bands of clouds and the iconic Great Red Spot, Jupiter has fascinated astronomers and casual stargazers alike for centuries.
Understanding Jupiter, the massive planet in our solar system, is crucial for grasping the dynamics of our cosmic neighborhood. Jupiter’s immense size and gravitational pull play a vital role in shaping the orbits of other planets and protecting Earth from potential comet and asteroid impacts.
Read also: Planet Size Comparison – Epic Battle among 8 Planets of the Solar System
Moreover, studying Jupiter helps scientists learn about the formation and evolution of our solar system.
This article discusses the characteristics, significance, and mysteries of the biggest planet in our solar system. It explores the planet’s characteristics, its role within the solar system, and the ongoing scientific missions to uncover its secrets.
Appreciating the biggest planet in our solar system enhances our understanding of planetary science and the protective nature of the planet. This knowledge is essential for scientific advancement and fostering a sense of wonder about our universe.
We will explore Jupiter’s physical characteristics, moons, and atmospheric phenomena. The article will also discuss historical and current space missions, compare Jupiter with other planets, and present fun facts highlighting its unique attributes.
Read also: What is the Order of the Planets in the Solar System?
Understanding the Biggest Planet in Our Solar System
General Characteristics of Jupiter
- It is the largest in our solar system and is twice as massive as other planets.
- It is regarded as the most primitive planet.
- It mainly consists of dust and gases that remained from the formation of the Sun 4.5 billion years ago.
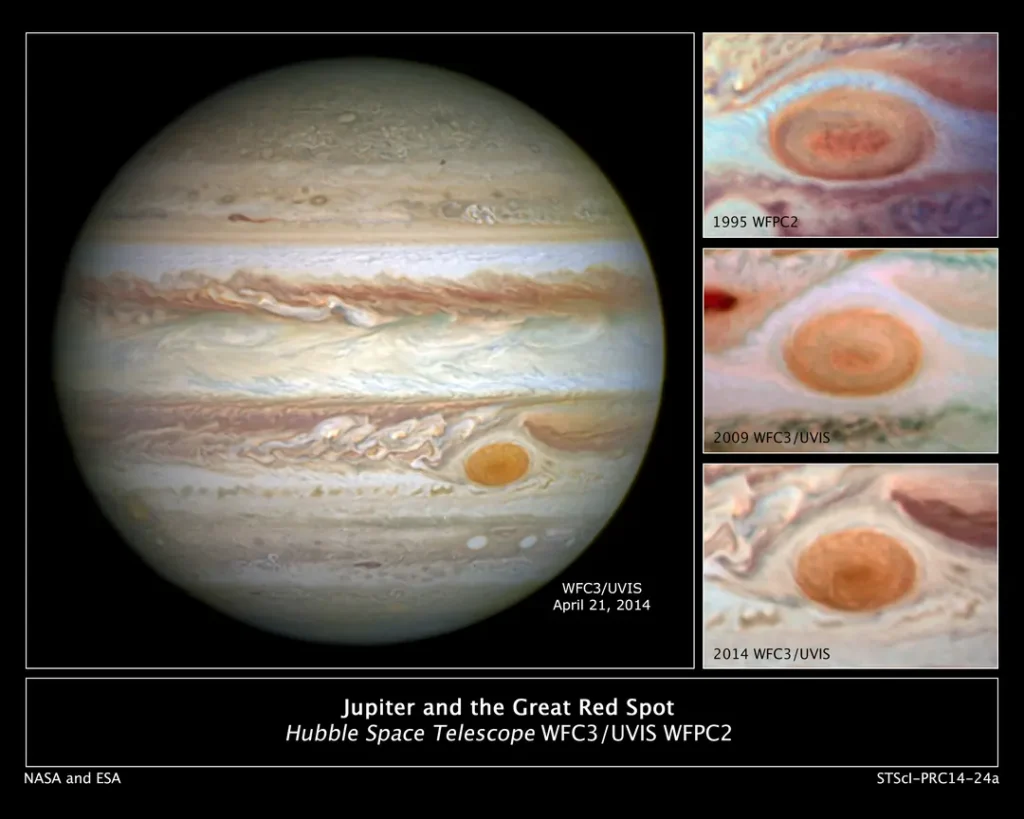
- Its most vivid and particular storm is known as the Great Red Spot and is twice Earth’s width.
- This gas giant has an immense volume of more than 1300 times that of Earth.
- The planet revolves around the sun once every 11.86 Earth years at an average speed of 29,236 miles per hour.
- Since 2021, NASA’s spacecraft Juno has been looking into Jupiter and its moons.
Jupiter’s Position in the Solar System
Jupiter is the biggest planet in the solar system. It is currently in the constellation of Taurus, and the right ascension is 3 hours 50 minutes 3 seconds. The planet could be seen looking in the right direction at 58 degrees above the horizon from Greenwich, United Kingdom. It stands out as one of the most illuminating objects in the night sky.
Read also: 3 Most Important Theories to Explain How the Solar System Formed?
Jupiter’s Physical Features
Atmosphere and Weather
Even a small telescope can reveal significant information about the biggest planet in our solar system. Jupiter’s atmosphere consists of many clouds positioned vertically and horizontally. These clouds have a chain of forms consisting of many elliptical features that remind us of Earth’s cyclonic and anticyclonic storm systems.
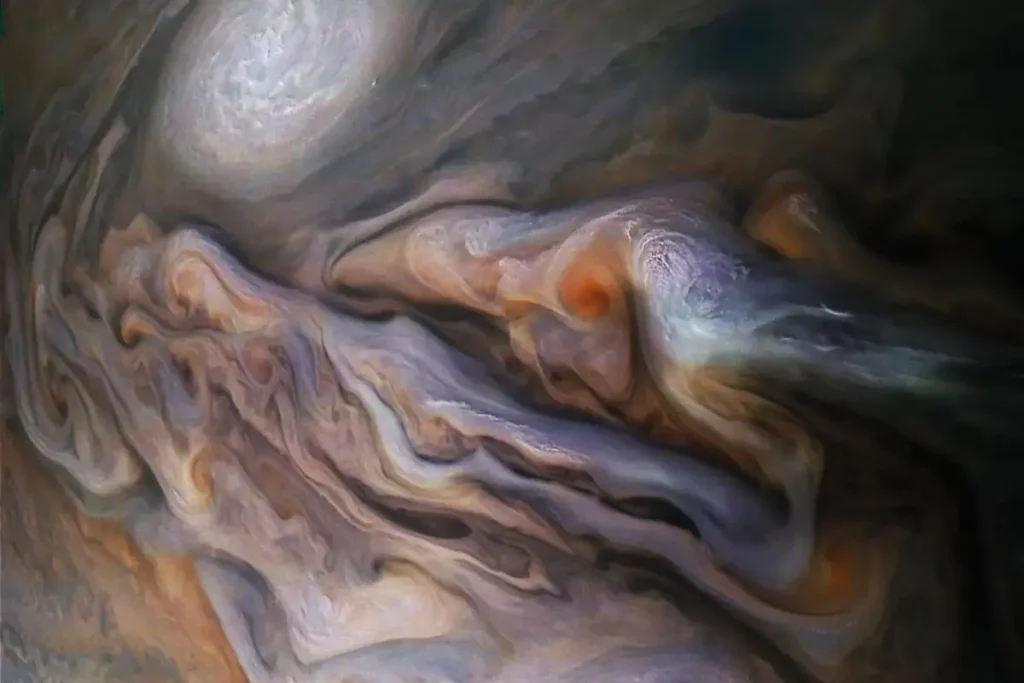

Situated among the Milky Way Galaxy, Jupiter’s atmospheric structure closely matches the other celestial bodies, for instance, Venus, the hottest one in the solar system, and other moons that revolve around the solar system.
Read also: How many solar systems are in the milky way galaxy
Storms and weather patterns
Jupiter’s thrilling atmosphere is due to its clouds and colorful bands, which flow east and west. The atmosphere is mainly hydrogen and helium, but the clouds are ammonia. Under this are water clouds; the winds remain unaffected even after a certain point.
Its cloud levels vary in pastel colors from light yellow to browns and blue grays, making it the renowned Great Red Spot. These huge colors make it the biggest planet in our solar system, and its atmosphere is unique compared to other celestial bodies.
Read also: When will the Andromeda and Milky Way Galaxy Collide
Magnetic Field and Gravity
Being the biggest planet, Jupiter’s massive magnetic field is about 16 to 54 times as powerful as Earth’s. It revolves around other planets and traps particles that consist of electric charge. Closer to Earth, the magnetic field traps many charged particles and accelerates them to a higher energy level, creating high radiation that explodes the innermost moons and can degrade spacecraft.
Rings and Moons
Rings

- Halo light, the wide doughnut-structured ring, is near Jupiter.
- The main ring moves out of the halo ring.
- It has two moons, Adrstea and metis, which revolve around the main ring and are considered the primary source of dust.
- Gossamer rings are very light and expansive and contain tiny debris from the moons Amalthes and Thebe.
Moons
The number of moons is increasing daily as new ones are added daily. According to the latest updates, the solar system has over 200 moons, and these moons are massive in size, composition, and characteristics. Jupiter and Saturn have a huge number of moons.
The largest moon in our solar system is Ganymede and revolves around Jupiter. It has a diameter of about 5268 km and a magnetic field.

Major Moons
The largest moons of Jupiter are four Galilean moons: Lo, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. They were introduced in 1610 by Galileo Galilei and Simon Marius. They were the initial items discovered around the orbit of a particular body that is neither closer to Earth nor the Sun.
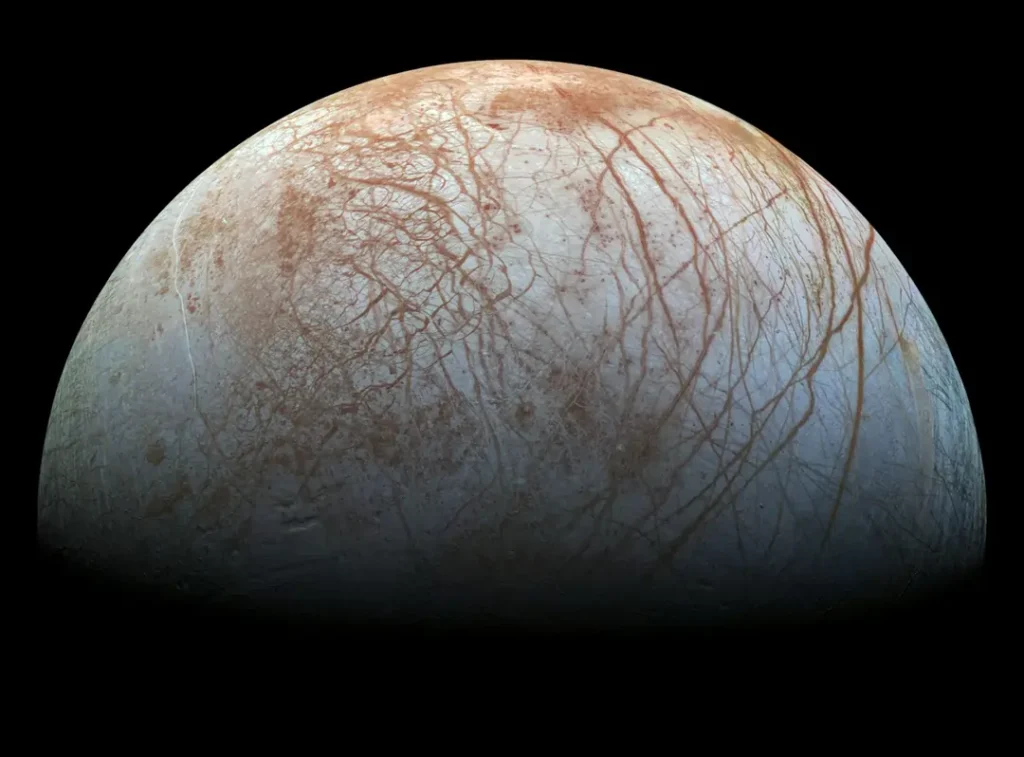
The Potential for Life on Europa: Jupiter’s radiation emits radiation on Europa’s surface, which is unsuitable for supporting life on the surface. However, the radiation may produce fuel below the ocean’s surface, dividing water molecules.

Scientific Exploration of Jupiter
Historical Missions
- Voyager 1 was launched on September 5, 1977, and passed in March 1979. The spacecraft took 18000 pictures of Jupiter, the biggest planet.
- In 2012, Voyager 1 entered interstellar space, making the first human-created object that ever did that.
- Voyager 2, launched on August 20, 1977, permitted NASA to significantly compare Jupiter and its Moons.
- The Galileo spacecraft was initially launched on October 18, 1989, and took place there in December 1995.
- The Ulysses spacecraft was first introduced on October 6, 1990, as part of a joint venture of NASA and ESA.
Current and Future Missions
NASA’s upcoming mission is to launch the Clipper mission on October 6, 2024, and it will reach Jupiter on April 11, 2030.
Jupiter in Comparison
- Venus and Jupiter can beat any planet in the solar system regarding brightness. Venus, a rock planet, and Jupiter, a giant gas planet, are very different but have a similar reflective atmosphere. Despite being hundreds of miles away, they are still the brightest in our solar system. Due to its size, Jupiter is the second-brightest planet in our solar system.
- Compared to Earth, Jupiter has a radius of 69,911km and a mass of about 1.8986X1027 kg, whereas Earth has an average radius of 6,371km and a mass of 5.97X1024 kg. Earth mainly comprises minerals and metals, whereas Jupiter comprises gases and particles, making it the biggest planet.
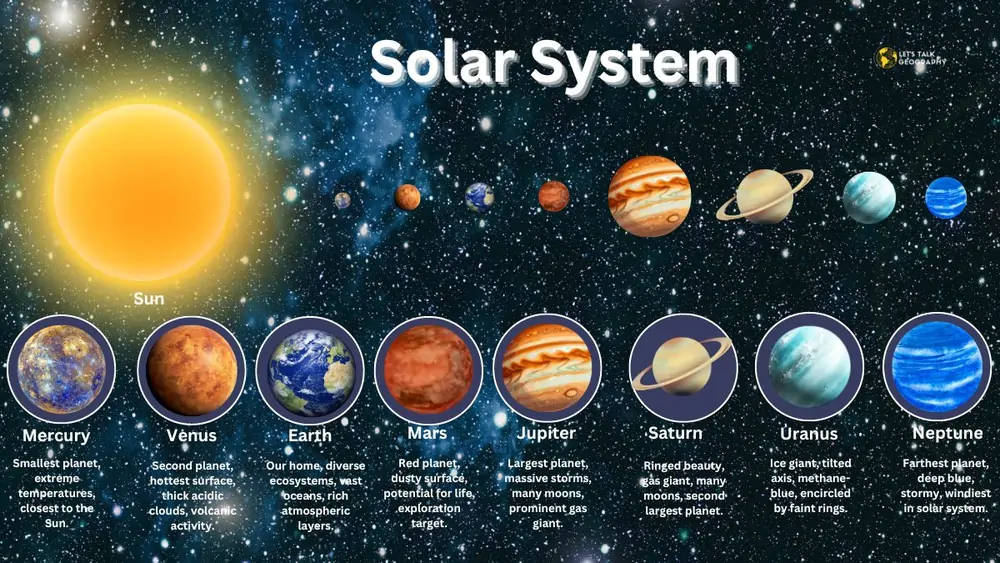
- While Jupiter is the biggest planet, Saturn is the second largest, with a diameter of about 120536 kilometers and a mass of 5.683*1026. Jupiter has 79 moons, while Saturn has 83 rings. Uranus has a diameter of about 50724 kilometers and 27 rings, while Neptune has 14 moons.
- The inner planets include Mercury, Venus, Mars, and Jupiter, among which Jupiter is a gas giant. The other terrestrial planets comprise rocky cores, metallic cores, silicate crusts, nickel, and sulfur. The inner planets have weak magnetic fields, while Jupiter has a high magnetic field. Jupiter comprises hydrogen and helium, while the other terrestrial planets comprise rocky cores, metallic cores, silicate crusts, nickel, and sulfur. They have very weak magnetic fields, while Jupiter has a high magnetic field.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the introduction to our exploration of the biggest planet in our solar system, Jupiter, has set the stage for a fascinating journey into the marvels of this colossal gas giant. We began with an intriguing hook, capturing the wonder surrounding Jupiter’s immense size and striking features, such as the Great Red Spot.
The background information provided a brief yet comprehensive overview, highlighting Jupiter’s prominence in the solar system. We then delved into the relevance of studying Jupiter, emphasizing its crucial role in protecting Earth and influencing planetary orbits. Our thesis outlined the article’s main focus, promising an in-depth look into Jupiter’s characteristics, significance, and ongoing scientific explorations.
Lastly, we underscored the importance of understanding Jupiter and appreciating its unique contributions to our knowledge of the cosmos. This introduction prepares readers for a detailed and engaging exploration of Jupiter, the biggest planet in our solar system.
FAQs
1. What is the biggest planet in our solar system?
Jupiter is the biggest planet in our solar system. It’s a gas giant with a mass more than twice that of all the other planets combined. Jupiter’s enormous size is evident in its diameter, roughly 11 times wider than Earth’s.
2. How big is Jupiter compared to Earth?
Jupiter dwarfs Earth in size. If Earth were the size of a nickel, Jupiter would be about as big as a basketball. In numerical terms, Jupiter’s diameter is about 140,000 kilometers, while Earth’s is a mere 12,742 kilometers.
3. What is Jupiter made of?
Unlike rocky planets like Earth, Jupiter primarily comprises hydrogen and helium gases. It’s believed to have a dense core of heavier elements, but its vast atmosphere makes it so massive.
4. Does Jupiter have any rings or moons?
Yes, Jupiter has a faint ring system, much less prominent than Saturn’s. More notably, it boasts a vast collection of moons, with 79 confirmed so far. The four largest, known as the Galilean moons, are Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. Each has its unique features and potential for harboring life.
5. What is the Great Red Spot on Jupiter?
The Great Red Spot is a colossal storm raging on Jupiter for at least 350 years. It’s so large that two or three Earths could fit inside it! Scientists are still studying this massive storm to understand its dynamics and longevity.
6. Could humans ever live on Jupiter?
Jupiter’s environment is incredibly harsh, with crushing atmospheric pressure, extreme temperatures, and a lack of solid surfaces. As of now, it’s not considered habitable for humans. However, some of Jupiter’s moons, particularly Europa, are of interest to scientists due to the potential presence of subsurface oceans that could support life.
7. How long does it take Jupiter to orbit the Sun and rotate on its axis?
Jupiter takes approximately 12 Earth years to complete one orbit around the Sun. However, it has the shortest day of all the planets, rotating on its axis in just under 10 hours. This rapid rotation contributes to its flattened shape and powerful storms.
8. Has Jupiter been explored by spacecraft?
Yes, several spacecraft have visited Jupiter. Pioneer 10 and 11, Voyager 1 and 2, Galileo, Cassini, and Juno are just a few missions that have provided valuable data and stunning images of this giant planet. The Juno mission, launched in 2011, is currently studying Jupiter’s atmosphere, magnetic field, and internal structure in detail.
References
- Educator guide: Modeling the structure of the solar system. (2018, December 18). NASA/JPL Edu. https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/edu/teach/activity/modeling-the-structure-of-the-solar-system/
- Solar system. (2020, November 20). Toppr-Guides. https://www.toppr.com/guides/physics/stars-and-the-solar-system/solar-system/
- What is the order of the planets in the Solar System? (n.d.). Cool Cosmos. Retrieved May 23, 2024, from https://coolcosmos.ipac.caltech.edu/ask/193-What-is-the-order-of-the-planets-in-the-Solar-System-
- The weather on Jupiter. (n.d.). Mission Juno. Retrieved May 25, 2024, from https://www.missionjuno.swri.edu/jupiter/atmosphere?show=hs_jupiter_atmosphere_story_the-weather-on-jupiter
- Jupiter – Gas Giant, Moons, Orbit. (n.d.). In Encyclopedia Britannica.
- Conjunction of Venus and Jupiter. (n.d.). Moas.org. Retrieved May 23, 2024, from https://www.moas.org/Conjunction-of-Venus-and-Jupiter-1-5548.html
- Jupiter. (2023, May 31). Nasa.gov. https://science.nasa.gov/jupiter/
- Choi, C. Q. (2022, July 21). Jupiter: A guide to the largest planet in the solar system. Space.com; Space. https://www.space.com/7-jupiter-largest-planet-solar-system.html
- Where is Jupiter? How to Find Jupiter in the Sky. (n.d.). Theskylive.com. Retrieved May 25, 2024, from https://theskylive.com/where-is-jupiter





