During the studies of rainwater chemistry in industrial centers in England and Scotland in 1852, Scottish scientist Robert Angus Smith coined the phrase acid rain for the first time. His work, Air and Rain: The Beginnings of a Chemical Climatology, was heavily influenced by this occurrence (1872).
It was not identified as a major environmental hazard impacting significant regions of western Europe and eastern North America until the late 1960s and early 1970s, though. Acid rain occurs in Asia, Africa, South America, and Australia, among other places. It is sometimes overshadowed by climate change as a worldwide environmental problem.
Individuals may question what they can do in their daily lives to mitigate the catastrophic repercussions of our climate emergency as more scientists grow frightened about the approaching, apocalyptic effects of our climate emergency.
●⫸ What is Acid Rain?
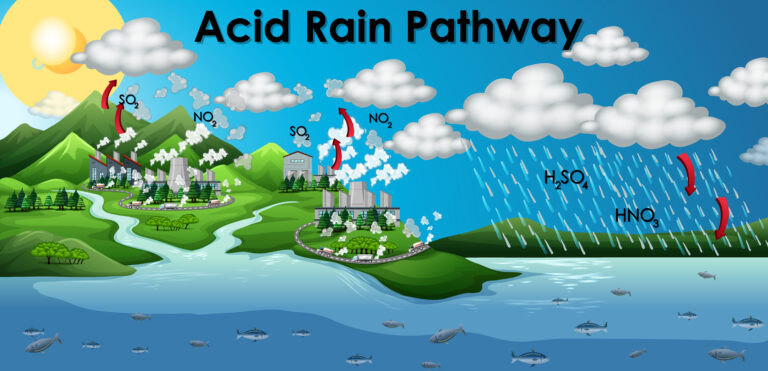
Acid rain, also known as acid deposition, is any type of precipitation that contains acidic components such as sulfuric or nitric acid and falls to the earth from the sky, wet or dry. This may be seen in acidic rain, snow, fog, hail, and even dust.
●⫸ Why does Acid Rain occur?
Acid rain is caused by the emission of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOX) into the atmosphere, which is transported by wind and air currents. SO2 and NOX combine with water, oxygen, and other molecules to produce sulfuric and nitric acids. After that, they’re combined with water and other components before being discharged into the environment.
While some of the SO2 and NOX that cause acid rain originate from natural sources such as volcanoes, the bulk comes from fossil fuel burning. The main sources of SO2 and NOX in the atmosphere are as follows:
◉ Fossil fuels are burned to create power. Electric power plants are responsible for two-thirds of SO2 and one-fourth of NOX emissions in the atmosphere.
◉ Vehicles and heavy machinery.
◉ Manufacturing, oil refineries, and other industries are only a handful of the many.
It is an issue for everyone, not just those who live near these sources, because the wind may carry SO2 and NOX across great distances and borders.
●⫸ What are the effects of Acid rain?
In acid-sensitive environments, acid deposition can harm biodiversity and reduce the pH of surface waters. It weakens trees and makes them more vulnerable to other stresses such as drought, harsh cold, and pests.
Acid rain depletes the soil of key plant nutrients and buffers, such as calcium and magnesium, in acid-sensitive locations, and can liberate aluminum in its deadly dissolved form, which is bonded to soil particles and rock.
It causes the degradation of limestone and marble structures and monuments by contributing to the corrosion of surfaces exposed to air pollution. Although Acid rain has been greatly decreased in certain locations, it continues to be a serious environmental hazard within and downstream of major industrial and agricultural sectors across the world.
●⫸ How does Acid Rain affect Climate change?
Climate change and Acid rain are both caused by anthropogenic emissions. When we evaluate the total amount of gases and pollutants generated by automobiles or coal-fired power plants, we can see that climate change and Acid rain are becoming more severe.
◉ Climate change is exacerbated by acid rain, which pollutes the environment:
Acid rain-producing coal-fired power plants, for example, also generate large amounts of carbon dioxide, which hastens climate change. The coal industry released 65 percent of CO2 emissions in the electric sector in 2018, according to the US Energy Information Administration…1,150 that’s million metric tonnes of CO2 spewed in a single year.
As a result, shifting to renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydropower will reduce harmful GHG emissions while also reducing Acid rain deposition.
◉ A lake that has been impacted by acid rain is more vulnerable to climate change:
According to a study released by an aquatic scientist at Oregon State University and co-authors from Syracuse and Cornell Universities, clean lakes with low levels of plankton and dissolved organic matter in the water as a result of Acid rain rendered trout populations more vulnerable.
Trout, on the other hand, found sanctuary from warming consequences in lakes that had recovered from Acid rain damage, with darker waters where sun rays couldn’t reach as deep.
◉ Acidification is caused by climate change, so it’s a double whammy:
Scientific models and analysis were used in a 2012 publication published by the National Science Foundation (NSF) to illustrate how climate change was increasing and will continue to increase the acidity of northeastern streams and forests.
According to the article, “scientists have determined that today’s higher atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) level and associated air fallout is influencing the hydrology and water quality of forested watersheds in a similar manner to Acid rain.”
Climate change’s effects are already being seen; but, based on scientific evidence and estimates, we should expect much greater changes in the future.
For example, if present emissions levels are maintained, New York would see an 11°F increase in temperature and a five-inch increase in annual precipitation (rainfall) by the end of the century. Winters will be shorter and warmer as a result of these predicted changes, and spring floods will be more severe.
●⫸ How to Prevent Acid Rain?
Limiting the quantity of sulfuric dioxide and nitrous oxide emitted into the atmosphere is the most effective strategy to prevent the occurrence of Acid rain. Since 1990, the Environmental Protection Agency has forced firms that release these two pollutants (namely, those that burn fossil fuels to generate electricity) to reduce their emissions significantly.
Although Acid rain may appear to be a major issue, there are numerous things you can do as an individual to help avoid it. Any action you do to preserve energy reduces the number of fossil fuels used to generate that energy, lowering the amount of Acid rain produced.
What can you do to save energy? Purchase energy-efficient appliances; carpool, take public transit, walk, or bike wherever feasible; set your thermostat to a low temperature in the winter and a high temperature in the summer; insulate your home; and switch off lights, computers, and appliances when not in use.
●⫸ Conclusion:
Stopping Acid rain caused by humans can be accomplished in several ways. According to the EPA, regulating emissions from automobiles and buildings is a critical step. This may be accomplished by limiting the usage of fossil fuels and focusing on more environmentally friendly energy sources like solar and wind power.
Additionally, each individual may contribute by lowering their automobile usage. According to the EPA, taking public transit, walking, riding a bike, or carpooling are all smart places to start. People may also cut back on their consumption of energy, which is often generated from fossil fuels or converted to a solar-powered system. Many electrical providers offer solar packages to their consumers that do not require installation and are rather inexpensive.





Thank you for the very informative article. I found a lot of new and useful information on this topic.
I really like your writing and the way you convey information. This article is truly engaging and easy to understand.
I completely agree with the author’s perspective on this topic. This article provides a fresh and useful point of view.
Wow, this is such an incredible post! I love the valuable insights you’ve shared here. I think my followers would really appreciate this too, so I’ll be sure to share it with them.
Thank you so much for your enthusiastic response! I’m glad that you found the post valuable and insightful. It’s wonderful to know that the content resonated with you and that you consider it share-worthy with your followers.
Your support in spreading the word is greatly appreciated, as it helps us reach and engage with a broader audience. If there are any specific topics or areas you or your followers are particularly interested in, please feel free to let us know. We’re always looking to tailor our content to our readers’ interests and needs.
Thanks again for your kind words and for being a part of our community. Happy sharing! 🌟📚🤝
This article has been very helpful in deepening my understanding of this topic. Thank you for providing such valuable information.
You’re very welcome, and I’m delighted that the article was helpful in deepening your understanding of the topic. It’s always gratifying to know that the information we provide is valuable and beneficial to our readers. If you have any more questions or need further clarification on this topic or any other, please don’t hesitate to reach out. We’re here to help and provide as much insight as we can. Thank you for your feedback, and I’m looking forward to assisting you in your continued learning journey! 🌟📚🙏
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here.
The sketch is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish.
nonetheless, you command get bought an edginess over that you wish be delivering
the following. unwell unquestionably come further formerly again since exactly the
same nearly very often inside case you shield this
hike.
Thank you for your kind and thoughtful feedback! I’m delighted to hear that you appreciate the style and presentation of the content. It’s always a goal to blend informative material with an engaging and tasteful approach, so it’s wonderful to know this resonates with you.
Your encouragement for the continued delivery of content with a unique edge is greatly valued. It’s feedback like yours that inspires me to keep exploring new ideas and perspectives, ensuring that the content remains fresh and relevant.
I’m looking forward to your continued engagement, and please feel free to share any specific topics or areas you’d like to see covered in the future. Your input is invaluable in guiding the direction of our content. Thanks again for your support, and here’s to many more insightful and enjoyable posts! 🌟📚🎨
Good way of describing, and good article to take information concerning my presentation topic, which i am going
to present in school.
I’m delighted to hear that you found the article helpful for your school presentation! It’s great to know that the information was presented in a way that resonated with you and will assist in your academic endeavors. If you have any questions or need further details on the topic, please don’t hesitate to reach out. Best of luck with your presentation – I’m sure you’ll do a fantastic job! 🌟📚
WOW just what I was searching for. Came here by searching
for check my reference
I’m thrilled to hear that my blog post resonated with you! It’s always rewarding to know when the content we share sparks interest and proves useful to our readers. If you have any specific aspects of the post that you found particularly enlightening or if there are other topics in geography you’re curious about, feel free to share! Your feedback is invaluable in helping us create more engaging and informative content. Looking forward to hearing more from you! 🌍✨
Today, I went to the beach front with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it to my
4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She put
the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab
inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back!
LoL I know this is entirely off topic but I had
to tell someone!
Oh, what an unexpected turn of events at the beach! While we usually discuss the wonders of geography, your story certainly adds a unique and memorable twist to the experiences one can have while exploring nature. It’s one of those moments that, despite the surprise and discomfort for your daughter, can become a funny family story over time.
We’re sorry to hear about her little encounter with the hermit crab, though! It’s fascinating how even a simple sea shell can be a hidden home for marine life. It’s a good reminder of the surprises and diversity nature holds. Hopefully, this experience hasn’t put her off beach adventures for good. There’s so much beauty and learning to be had by the sea.
Thanks for sharing your story with us, even if it was a bit off-topic. It’s always a pleasure to connect with our readers over shared experiences in the great outdoors.
Pretty part of content. I just stumbled upon your blog and
in accession capital to claim that I acquire actually enjoyed account your
weblog posts. Anyway I will be subscribing for your feeds
and even I fulfillment you get entry to consistently rapidly.
We’re delighted to hear that you’ve stumbled upon our blog and are enjoying the content! It’s always exciting for us to welcome new readers into our community, especially those who share our enthusiasm for geography.
Thank you for deciding to subscribe to our feeds. We’re committed to regularly updating our blog with interesting and insightful posts, so you can look forward to a steady stream of engaging geography-related content. Our goal is to provide our readers with both enjoyment and knowledge, and your feedback is a wonderful affirmation that we’re on the right track.
If there are any particular topics within geography that you’re interested in, please feel free to let us know. We love incorporating our readers’ interests into our content planning.
Excellent goods from you, man. I’ve bear in mind your stuff prior to
and you’re just too fantastic. I actually like what you have acquired here, really like what you’re
saying and the way through which you say it. You are making it entertaining and you continue to take care of to stay it sensible.
I can not wait to learn far more from you. This is actually a terrific web
site.
Thank you so much for your enthusiastic feedback! We’re genuinely thrilled to know that you find our content not only informative but also entertaining. It’s incredibly rewarding for us to know that our passion for geography and the way we present it resonates so well with you.
Your encouragement motivates us to continue exploring and sharing more fascinating aspects of geography. We’re excited to bring you even more content that you’ll find engaging and insightful. Stay tuned for our upcoming articles and features – we believe you’ll find them just as captivating!
If there are any specific topics or regions you’re particularly interested in, please do let us know. We always welcome suggestions from our readers.
Thanks once again for your support and for being a part of our geography-loving community!
After looking at a number of the articles on your web page, I truly like your technique of writing a blog.
I book-marked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back in the near future.
Please check out my website too and let me know
what you think.
Thank you so much for your kind words and for bookmarking our blog! We’re thrilled to hear that you appreciate our approach to writing about geography. It’s always encouraging to know that our efforts resonate with our readers.
We’re definitely interested in exploring your website as well. Sharing insights and perspectives with fellow geography enthusiasts is something we value highly. Could you please provide the link to your site? We’d love to take a look and share our thoughts.
Looking forward to your reply, and thank you once again for your support!
This is a topic that is near to my heart… Cheers! Exactly where are your contact details though?
I’m glad to hear that this topic resonates with you!
Fine way of telling, and pleasant piece of writing to get data concerning my presentation subject, which i am going
to deliver in academy.
Thank you for your kind feedback. We’re delighted to know that you found our writing both informative and pleasant, especially as it pertains to your presentation subject. It’s wonderful to know that our content is being used as a valuable resource in academic settings.
We’re curious and excited to learn more about the subject of your presentation. If it’s related to geography or any of the topics we cover, we’d love to hear how our content has contributed to your work. Additionally, if you need further information or have specific questions as you prepare for your presentation, feel free to reach out. We’re here to help!
Wishing you the best of luck with your presentation at the academy. It’s always inspiring to see the application of knowledge in educational and professional environments, and we’re honored to be a part of your journey.
I think the admin of this website is really
working hard in support of his site, as here every material is quality based material.
Dear Reader,
Thank you so much for your kind words and recognition of our efforts. It’s truly heartening to hear that our commitment to providing quality material is noticed and appreciated by our readers.
Our team indeed works diligently to ensure that every piece of content on ‘Let’s Talk Geography’ is informative, accurate, and engaging. We believe that quality is key when it comes to educational resources, and we’re glad that this resonates with you.
Your encouragement serves as a great motivator for us to continue our work and to constantly strive for improvement. It’s feedback like yours that reminds us why we’re so passionate about geography and sharing knowledge with others.
If there are any topics or types of content you would particularly like to see more of on our site, please don’t hesitate to let us know. We’re always looking for ways to better serve our readers’ interests and curiosity.
Thank you once again for your support. We hope to keep meeting and exceeding your expectations with our future content!
Warm regards,
The ‘Let’s Talk Geography’ Team
I’ve been exploring for a little bit for any high-quality articles or blog posts on this sort of area
. Exploring in Yahoo I ultimately stumbled upon this site.
Studying this information So i am happy to show that I’ve an incredibly good uncanny feeling I found out exactly what I
needed. I most definitely will make certain to don?t omit this website and
give it a glance regularly.
Dear Reader,
We’re glad to know that your exploration led you to ‘Let’s Talk Geography’ and that our content has resonated so strongly with you. It’s always rewarding to learn that our articles and blog posts are not just being read but also providing the exact information and insights our readers are seeking.
Your description of having an ‘incredibly good uncanny feeling’ upon finding our site is truly motivating for our team. We strive to create high-quality, informative, and engaging content about geography and related areas, so knowing that we’ve hit the mark with you is fantastic.
Thank you for making a note to regularly visit our site. We’re continually updating our content with new and interesting articles, so there will always be something fresh and intriguing for you to explore.
If there are specific topics within geography or related fields that you’re particularly interested in, please feel free to let us know. We value reader input and are always looking for ideas to broaden the scope of our content.
Once again, thank you for your kind words and for choosing to engage with ‘Let’s Talk Geography’. We look forward to having you as a regular reader and to continuing to provide content that piques your interest and curiosity.
Warm regards,
The ‘Let’s Talk Geography’ Team
Howdy! I know this is kinda off topic however I’d figured I’d ask.
Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest authoring a blog article or vice-versa?
My website addresses a lot of the same topics as yours and I believe we could
greatly benefit from each other. If you are interested feel free to shoot me an e-mail.
I look forward to hearing from you! Terrific blog by the way!
Dear Reader,
Howdy! Thank you for reaching out and for your kind words about our blog. It’s always great to connect with fellow enthusiasts who share a passion for similar topics.
We are certainly open to the idea of link trading and guest authoring, as collaborations like these can be mutually beneficial and enriching for both our audiences. Your proposal to share expertise and insights aligns well with our goal of fostering a community of knowledge-sharing in the realm of geography and related subjects.
Could you please provide more details about your website? We’d love to explore the content you offer and see how our platforms can complement each other. Once we have a better understanding of your site and the topics you cover, we can discuss the potential for collaboration more concretely.
Please feel free to send us an email with the details, and we can take it from there. Our email address is ([email protected]). We’re looking forward to the possibility of working together and to the opportunity of expanding our respective audiences.
Thank you once again for your interest in collaborating with ‘Let’s Talk Geography’. We’re excited to hear more about your website and ideas for potential partnership.
Warm regards,
The ‘Let’s Talk Geography’ Team
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own blog and was curious what all
is needed to get set up? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a
pretty penny? I’m not very web smart so I’m not 100% sure. Any recommendations or advice
would be greatly appreciated. Thank you
Hi there, yeah this post is really pleasant and
I have learned lot of things from it regarding blogging.
thanks.
There’s certainly a great deal to learn about this subject.
I love all of the points you made.
Why users still use to read news papers when in this technological world the whole thing is available on net?
You’re so interesting! I do not believe I have read anything like this before.
So great to discover another person with a few unique thoughts
on this issue. Seriously.. thanks for starting this up. This website is something that’s needed on the web, someone with a little originality!
That’s so kind of you to say! I’m thrilled my thoughts resonated with you.