Introduction:
Our planet is changing. From scorching heat waves to monstrous storms, the effects of climate change are no longer a distant threat – they’re a present reality impacting every corner of the globe.
Have you ever wondered what the future holds if we don’t curb climate change? This post dives deep into 7 of the most alarming effects we’re already witnessing, from rising sea levels swallowing coastlines to extreme weather events turning the familiar into the frightening. But fear not, knowledge is power! By understanding these effects of climate change, we can take action and fight for a healthier planet. So, buckle up and join us as we unveil the reality of climate change and the urgent need for solutions.
The Culprits Behind Our Changing Climate: Understanding the Major Causes of Climate Change
We’ve recently explored the alarming effects of climate change, from rising sea levels to intensifying weather patterns. But what’s driving these dramatic shifts in our planet’s health? Understanding the significant causes of climate change is crucial because knowledge empowers us to take action and mitigate these effects.
◆ The Greenhouse Effect: A Natural Process Gone Awry
Imagine a giant heat trap wrapped around Earth. That’s essentially the greenhouse effect. Certain gases, like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, act like a blanket, trapping the sun’s heat in our atmosphere. This natural process keeps our planet warm and habitable, allowing life to thrive.
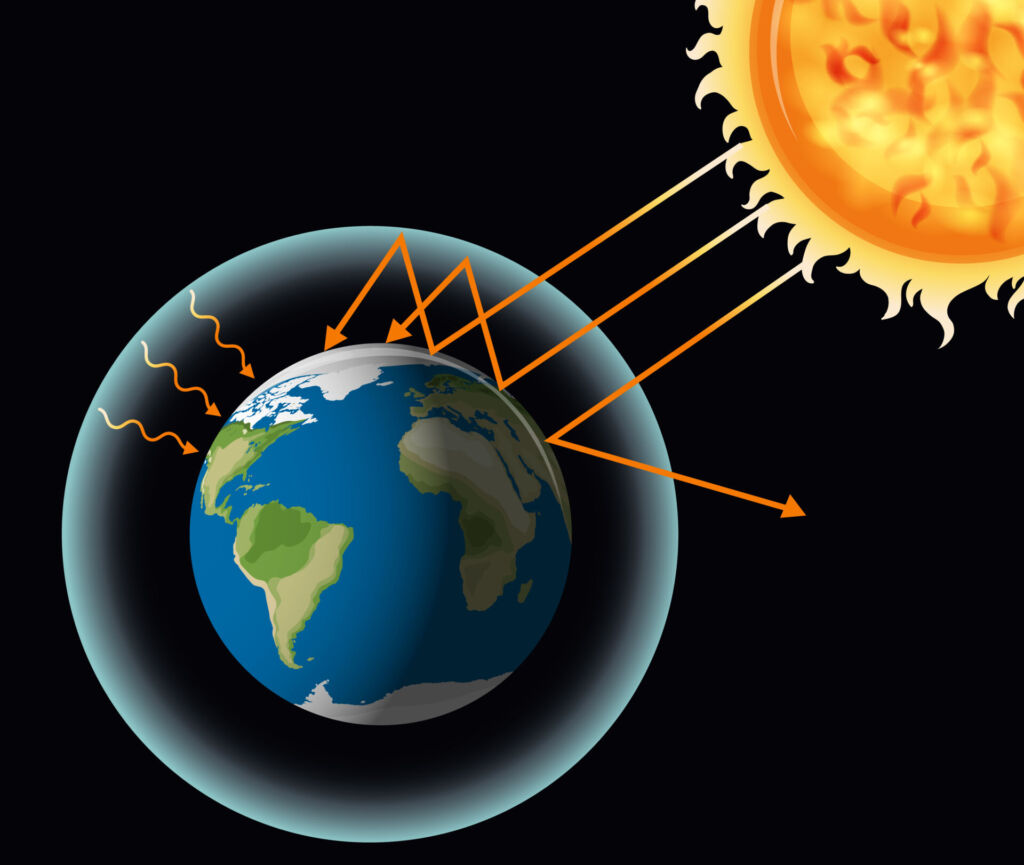
The problem lies in the increasing concentration of these greenhouse gases due to human activities. Here’s how:
- Burning Fossil Fuels: The primary culprit. Coal, oil, and natural gas release large amounts of carbon dioxide when burned for energy production. This CO2 traps additional heat, disrupting the natural balance of the greenhouse effect.
- Deforestation: Trees play a vital role by absorbing carbon dioxide. When we cut down forests for agriculture, development, or logging, this vital absorption process is disrupted, leading to more CO2 remaining in the atmosphere.
- Industrial Processes: Manufacturing releases various greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide. These emissions contribute significantly to the overall increase in greenhouse gas concentration.
The increased greenhouse gas concentration intensifies the natural greenhouse effect, trapping more heat and causing global temperatures to rise. This warming is the root cause of many climate change effects.
◆ Industrial Agriculture: A Hidden Contributor
Modern farming practices contribute to climate change in several ways:
- Fertilizers: Nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas 265 times more effective at trapping heat than carbon dioxide over 100 years, is released from fertilizers to boost crop yields.
- Deforestation: Clearing land for agriculture destroys forests, reducing Earth’s natural carbon sinks. Trees absorb and store carbon dioxide, so their loss disrupts this vital cooling mechanism.
- Livestock Emissions: Animals like cows release methane, another significant greenhouse gas, through their digestive processes. This methane contributes to the overall warming effect.
◆ Beyond the Big Three: Other Human Activities
While the above factors are major contributors, other human activities also play a role in climate change:
- Landfill Methane: Decomposing organic waste in landfills produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas significantly impacting warming.
- Urbanization: Cities generate heat due to concentrated infrastructure and activities like transportation. This “urban heat island effect” contributes to the overall warming trend.
- Black Carbon Emissions: Incomplete combustion of fossil fuels and biomass releases black carbon particles. These particles absorb solar radiation, further warming the atmosphere.

◆ The Takeaway: Knowledge Empowers Action
Understanding the causes of climate change is crucial because it empowers us to take action. Addressing these issues can create a healthier future for our planet. Here are some potential solutions:
- Transitioning to cleaner energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal reduces our reliance on fossil fuels and their associated greenhouse gas emissions.
- Sustainable forestry practices that promote reforestation and responsible logging can help restore lost carbon sinks.
- Innovation in agricultural techniques and manure management can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the farming industry.
- Implementing waste management solutions like composting and methane capture from landfills can decrease methane emissions.
- Urban planning that prioritizes green spaces, energy-efficient buildings, and sustainable transportation options can mitigate the urban heat island effect.
Climate change is a complex issue with many causes. However, by understanding these causes and taking action, we can strive to create a more sustainable future for ourselves and future generations. As we continue to explore the effects of climate change, remember that the solutions lie within our hands.
The Unequivocal Evidence: Proof of Climate Change and its Effects on Nature and Mankind
Climate change is no longer a distant threat on the horizon – it’s a reality impacting every corner of the globe. The scientific community overwhelmingly agrees that the Earth’s climate is changing at an unprecedented rate, primarily due to human activities. But beyond the scientific consensus, there’s a wealth of evidence in nature and its effects on humanity that paints a clear picture of a planet in flux.
◆ Nature's Cry for Help: Tangible Signs of Climate Change
Our planet is complex, and climate change disrupts its delicate balance. Here are some of the most evident signs of climate change observed in nature:
- Rising Global Temperatures: The average global temperature has increased by about 1 degree Celsius (1.8 degrees Fahrenheit) since the late 19th century, with the last decade being the warmest on record. This seemingly slight increase has significant cascading effects.
- Warming Oceans: Over 90% of the excess heat trapped by greenhouse gases is absorbed by the oceans. This warming disrupts ocean currents, marine ecosystems, and weather patterns.
- Melting Glaciers and Ice Sheets: Mountain glaciers and polar ice sheets are melting alarmingly, contributing to rising sea levels and disrupting freshwater supplies.
- Shrinking Sea Ice: Arctic sea ice extent has significantly declined, impacting polar ecosystems and altering weather patterns.
- Changes in Precipitation Patterns: Climate change leads to more frequent and intense extreme weather events, including floods, droughts, heat waves, and powerful storms. These events disrupt agricultural production, displace communities, and threaten human safety.
- Ocean Acidification: As the oceans absorb more carbon dioxide, they become more acidic. This acidification harms marine life, particularly organisms with calcium carbonate shells, disrupting food webs.
- Shifting Species Ranges: Plants and animals are moving to cooler regions in response to rising temperatures, impacting ecosystems and potentially leading to extinctions.
These are just some of the numerous ways nature responds to climate change. The effects are interconnected and far-reaching, highlighting the urgency of addressing this issue.
◆ The Ripple Effect: How Climate Change Impacts Mankind
The effects of climate change aren’t limited to the natural world. They have a profound impact on human societies across the globe:
- Food Security Threats: Changing weather patterns, rising temperatures, and extreme weather events disrupt agricultural production, leading to food shortages and price hikes. This impacts vulnerable populations the most and threatens global food security.
- Rising Sea Levels: Coastal communities face increasing threats from rising sea levels, including inundation, saltwater intrusion, and erosion. These displace populations, damage infrastructure, and disrupt livelihoods.
- Water Scarcity: Changing precipitation patterns and melting glaciers put pressure on freshwater resources. Droughts are becoming more frequent and severe, leading to water shortages for drinking, sanitation, and irrigation.
- Extreme Weather Events: More frequent and intense heat waves, floods, droughts, and storms are causing widespread damage to infrastructure, property, and lives. These events also disrupt economies and exacerbate existing social inequalities.
- Health Impacts: Climate change can exacerbate health problems like heat stress, respiratory illnesses, and waterborne diseases. Additionally, changing weather patterns can create suitable conditions for the spread of vector-borne diseases like malaria and dengue fever.
- Mass Migration: Climate change can force people to leave their homes due to rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and resource scarcity. This mass migration puts pressure on social services and international cooperation.
The effects of climate change are deeply intertwined with human well-being. Addressing climate change is not just an environmental issue; it’s a critical social and economic issue.
◆ Beyond the Evidence: Building a Sustainable Future
The evidence of climate change is undeniable. From the melting glaciers to the intensifying storms, nature sends a clear message. The good news is that we have the knowledge and technology to tackle this challenge. Here are some crucial steps towards a sustainable future:
- Transitioning to renewable energy: Shifting from fossil fuels to clean energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in buildings and industries can significantly reduce energy consumption and emissions.
- Sustainable Land Management: Reforestation, responsible land use practices, and soil conservation can enhance carbon capture and reduce deforestation emissions.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: Adopting agricultural practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote soil health can improve food security in a changing climate.
- Investing in Green Infrastructure: Building sea walls, flood-resistant infrastructure, and green spaces in cities can help communities adapt to the effects of climate change.
Addressing climate change requires a global effort – from individuals making conscious choices to governments implementing bold policies. By acting now, we can create a more sustainable future. Here are just some of the ways we can work together to limit the impacts of climate change:
- Support for Climate Policies: Engage with elected officials and advocate for policies that promote climate action, such as investing in renewable energy and implementing carbon pricing mechanisms.
- Climate Education: Spread awareness and educate others about the causes and effects of climate change, empowering individuals to take action in their communities.
- Personal Sustainability Efforts: Reduce your carbon footprint by choosing sustainable transportation options, conserving energy and water, and making mindful choices about food consumption.
Curtailing Climate Change: A Collective Effort for a Sustainable Future
Climate change is no longer a looming threat; it’s a reality impacting every corner of the globe. The good news? We have the knowledge and technology to tackle this challenge, but it requires a collective effort. Here, we explore ways to curtail climate change and build a more sustainable future.
◆ Shifting Our Energy Landscape
Burning fossil fuels is a primary contributor to greenhouse gas emissions and a significant driver of climate change. Here’s how we can shift our energy landscape:
- Embrace Renewables: It is crucial to invest in and adopt clean energy sources like solar, wind, geothermal, and hydropower. These technologies offer sustainable energy options with minimal environmental impact.
- Boost Energy Efficiency: Reducing energy consumption across industries and households lessens the reliance on fossil fuels. This can be achieved through energy-efficient appliances, building upgrades, and innovative energy management practices.
◆ Transforming How We Use Land
Land-use practices significantly influence the environment. Here are the steps we can take:
- Protect Existing Forests: Forests act as vital carbon sinks, absorbing and storing CO2. Protecting existing forests and promoting sustainable forestry practices are essential.
- Reforestation Efforts: Planting trees where possible helps restore lost carbon sinks and mitigate the effects of climate change.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Implementing practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, like improved fertilizer management and reduced reliance on animal agriculture, are essential.
◆ Individual Actions for a Collective Impact
While large-scale changes are crucial, individual actions can contribute significantly:
- Reduce Energy Consumption: Simple steps like turning off lights in unoccupied rooms, using energy-efficient appliances, and air-drying clothes have a cumulative impact.
- Embrace Green Transportation: Opting for public transportation, cycling, walking, or electric vehicles reduces reliance on fossil fuel-powered cars.
- Mindful Consumption: Choose sustainable products, reduce waste, and be aware of your purchases’ environmental impact.
- Support Sustainable Businesses: Seek out and support companies committed to sustainability practices.
◆ Investing in Innovation
Technological advancements play a crucial role in combating climate change:
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Technologies that capture and store carbon emissions from existing sources safely underground offer a promising solution.
- Climate-Smart Technologies: Investing in research and development of innovative technologies that can help us adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change is essential.
◆ The Power of Policy and Advocacy
Effective policies and global cooperation are vital:
- Carbon Pricing: Implementing carbon pricing can incentivize businesses and individuals to reduce emissions.
- International Agreements: Strong international agreements that hold countries accountable for reducing greenhouse gas emissions are crucial.
- Public Advocacy: Engaging with policymakers and advocating climate-friendly policies empowers individuals to create change.
Curtailing climate change requires a multifaceted approach. We can create a more sustainable future by implementing these solutions – from large-scale renewable energy projects to individual choices to invest in sustainable products. The effects of climate change are a stark reminder of the urgency to act. It’s time for collective action and a commitment to building a healthier planet for future generations.
Battling Climate Change: How WWF is Working to Restore Our Planet
The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) is a leading global conservation organization deeply concerned about the effects of climate change on wildlife and ecosystems worldwide. Climate change disrupts habitats, alters weather patterns, and threatens biodiversity. Recognizing this urgency, WWF has placed climate change at the forefront of its conservation efforts. Here’s how they’re working to restore the climate:
◆ Tackling Emissions at the Source:
- Renewable Energy Advocacy: WWF advocates for policies and investments that promote renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. This transition away from fossil fuels is crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Sustainable Forest Management: Forests play a vital role in absorbing carbon dioxide. WWF promotes sustainable forestry practices and protects existing forests to maintain these natural carbon sinks.
- Supporting Green Practices: WWF works with businesses and governments to implement climate-friendly practices, incentivizing sustainable land use and resource management.
◆ Protecting Vulnerable Ecosystems:
- Marine Conservation: WWF focuses on protecting vulnerable marine ecosystems like coral reefs. These ecosystems support diverse marine life and act as carbon sinks.
- Conservation Across Landscapes: WWF works on large-scale conservation projects that protect entire landscapes, ensuring habitat connectivity and resilience in a changing climate. This allows species to adapt and thrive even as some areas experience the effects of climate change.
- Community-Based Conservation: WWF empowers local communities to become stewards of their environment. This empowers them to implement sustainable practices and become guardians of natural resources.
◆ Investing in Innovative Solutions:
- Nature-Based Solutions: WWF promotes nature-based solutions, such as restoring coastal wetlands and mangroves. These ecosystems provide natural flood protection and act as carbon sinks, mitigating the effects of climate change.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: WWF supports sustainable agriculture practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions from farming activities. These practices promote soil health and can even sequester carbon.
- Renewable Energy Access: WWF supports initiatives that bring renewable energy access to remote communities. This reduces reliance on fossil fuels and promotes sustainable energy use.
◆ Raising Awareness and Advocacy:
- Education and Outreach: WWF educates the public about the effects of climate change and empowers individuals to adopt sustainable practices.
- Policy Advocacy: WWF advocates for strong climate policies at national and international levels. This includes lobbying governments to enact policies that promote renewable energy and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Public Engagement: WWF utilizes its platform to raise awareness and inspire public action on climate change. This includes campaigns and events that mobilize communities and call for climate action.
WWF’s multifaceted approach to climate change restoration recognizes the problem’s interconnected nature. By reducing emissions, protecting vital ecosystems, and fostering sustainable practices, WWF contributes significantly to building a more resilient future for our planet. While the task seems daunting, collective action guided by science and innovation offers a path toward mitigating the effects of climate change and safeguarding the natural world for generations to come.
Conclusion:
The effects of climate change are a stark reality, impacting everything from weather patterns to ecosystems to human societies. Rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions to food security are just a few of the alarming consequences we face.
However, amidst this challenge lies an opportunity. We can take action by understanding the major causes – primarily our reliance on fossil fuels and unsustainable practices. Transitioning to clean energy sources, adopting sustainable practices, and protecting natural resources are crucial to building a more resilient future.
The good news is that solutions exist. From large-scale renewable energy projects to individual choices to reduce waste and conserve resources, every effort counts. Let’s act collectively, driven by innovation and a shared responsibility for our planet. By taking action now, we can mitigate the effects of climate change and create a healthier, more sustainable future for future generations.
⫸ FAQs on Climate Change
Q: What is Climate Change?
A. Climate change refers to a broad array of environmental degradation predicted to result from increasing levels of atmospheric CO2, including global warming, alterations in precipitation, sea-level changes, and more extreme weather events.
Q: What are the major causes of Climate Change?
A. The major causes of climate change are emissions from human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Q: What is global warming?
A. Global warming is the gradual increase of the average temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere and oceans. It is caused by the increased levels of greenhouse gases that trap energy from the sun. This trapped energy makes the Earth’s atmosphere warm and disturbs the Earth’s climate.
Q: What will be the effects of Climate Change?
A. Climate change will have several serious effects, including increased drought, extreme weather events, food and water shortages, and mass extinctions.
Q: What can we do to stop Climate Change?
A. The main way to stop climate change is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by switching to clean energy sources and reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.





