Introduction:
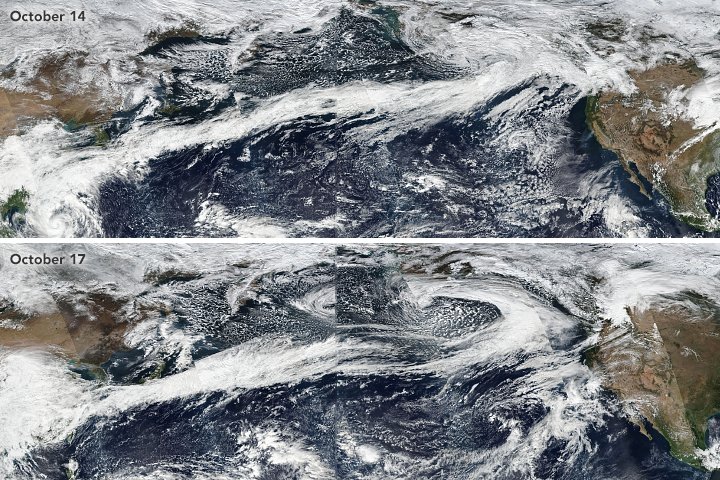
Imagine vast, flowing rivers in the sky, invisible to the naked eye but detectable through satellite imagery and meteorological observations. Atmospheric rivers (ARs) are relatively narrow regions in the Earth’s atmosphere that transport huge amounts of water vapor from the tropics toward the poles.
Despite their name, atmospheric rivers are not liquid water but instead are composed of moist air. They can carry an amount of water vapor roughly equivalent to the average flow at the mouth of the Mississippi River.
Atmospheric rivers are fascinating and complex phenomena that play a pivotal role in the global weather system, particularly in how they distribute precipitation across vast geographical areas.
Definition Atmospheric River:
These rivers are long, narrow regions in the atmosphere that transport most of the moisture from the tropics toward the poles. These ribbons of vapor can be thousands of kilometers long but are only a few hundred kilometers wide.
These corridors of concentrated moisture in the atmosphere are not just random occurrences but are integral components of the Earth’s hydrological cycle, significantly influencing rain and snowfall patterns.
Characteristics:
Atmospheric rivers (ARs) exhibit several distinctive characteristics-
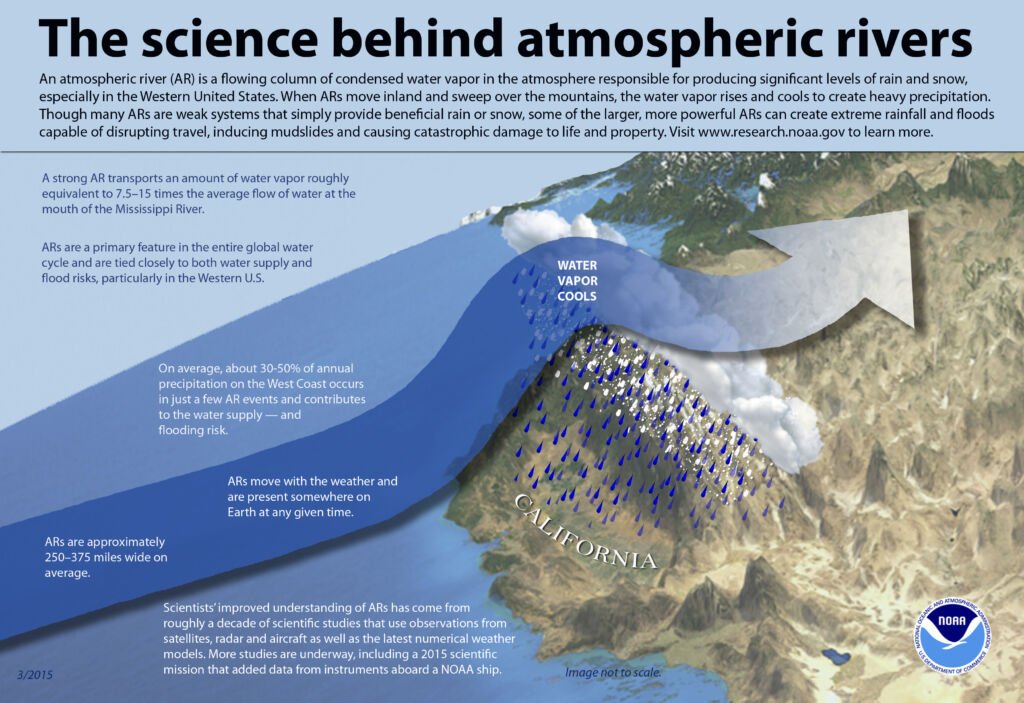
Moisture Content: Atmospheric rivers carry vast amounts of water vapor, equivalent to the flow of major rivers on Earth’s surface, making them critical in transporting moisture from the tropics to higher latitudes. It may sometimes be as high as 15 times that amount.
Size and Shape: They are relatively narrow, often only a few hundred kilometers across, but can extend for thousands of kilometers in length, resembling long, narrow bands of moisture in the atmosphere.
Formation Regions: ARs typically form over the ocean, especially in warm regions where the air can hold large amounts of water vapor, and are driven by global wind patterns.
Temperature Influence: They can be composed of warmer or cooler air masses, influencing their impact upon making landfall, such as causing snowfall or rainfall depending on their temperature profile.
Vertical Structure: Atmospheric rivers have a well-defined vertical structure, with the highest concentration of moisture found at altitudes up to 2.5 kilometers above the surface.
Types of Atmospheric River:
Cold Atmospheric Rivers: Associated with cooler air masses, often resulting in snowfall when they make landfall in colder regions.
Warm Atmospheric Rivers: Associated with warmer air masses, typically causing heavy rainfall and sometimes leading to flooding.
Origin:
Atmospheric rivers originate from the tropics or subtropical regions, where warm temperatures lead to a high rate of evaporation. This moisture-laden air is then transported towards higher latitudes by the prevailing winds. It is a worldwide event.
Impacts of Atmospheric Rivers:
● Impact on Weather Patterns:
The role of atmospheric rivers in shaping weather patterns, especially precipitation, is profound. When these moisture-laden air masses make landfall, they often encounter geographical features such as mountain ranges that force the air upward.
This upward motion causes the air to cool and the water vapor to condense into liquid or solid particles, resulting in precipitation in the form of rain or snow.
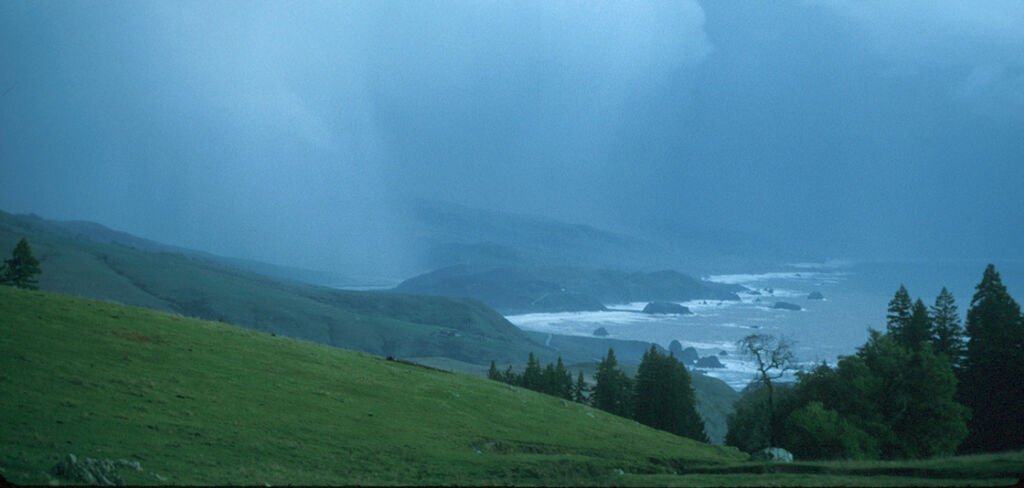

This process can lead to significant rainfall and snowfall events, contributing to the water supply in many regions, particularly the west coasts of North and South America, Europe, and Africa.
However, the intense precipitation associated with atmospheric rivers can also lead to extreme weather events, such as floods and landslides, especially in regions with saturated soils or steep terrain.
● Hydrological Significance:
Atmospheric rivers are vital for water resources, replenishing reservoirs and aquifers, and supporting ecosystems, especially in arid and semi-arid regions.
● Variability and Change:
The intensity, frequency, and paths of atmospheric rivers can vary significantly from year to year and are subject to changes under global climate change scenarios.
● Predictability and Monitoring:
Advances in satellite technology and atmospheric modeling have improved the ability to monitor and predict the movement and impact of atmospheric rivers, aiding in disaster preparedness and water resource management.
These characteristics underscore the importance of atmospheric rivers in the global climate system, influencing not just regional weather patterns but also water supply, ecosystem health, and disaster risk management.
The role of climate change on atmospheric rivers (ARs):
Climate change, driven by the increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, is expected to have significant impacts on the characteristics, frequency, intensity, and geographical distribution of atmospheric rivers.
● Increased Intensity:
Warmer temperatures lead to an increase in the amount of water vapor that the atmosphere can hold – approximately 7% more water vapor for every 1°C rise in temperature according to the Clausius-Clapeyron relation. This means that atmospheric rivers are likely to carry more moisture, potentially leading to more intense precipitation events when they make landfall.
● Altered Frequency and Distribution:
Climate change may alter the paths and frequency of atmospheric rivers. Some regions might experience an increased number of AR events, while others may see a decrease. This shift could significantly impact water availability and flood risk in affected areas.
● Greater Precipitation Extremes:
With atmospheric rivers becoming more intense, regions prone to ARs may face more extreme rainfall and snowfall events. This increase in extreme precipitation can exacerbate flood risks, strain flood management infrastructure, and increase the vulnerability of communities.
● Impact on Snowpack and Water Supply:
In regions where snowpack is a critical water source, warmer atmospheric rivers can lead to more rain-on-snow events, reducing snow accumulation and hastening snowmelt. This shift can alter seasonal water availability, impacting agriculture, water supply, and ecosystem health.
● Changes in Ecosystem Dynamics:
The changes in precipitation patterns and water availability due to more intense atmospheric rivers can affect ecosystem dynamics, plant and animal distributions, and the health of forests and wetlands.
● Increased Landslide and Erosion Risk:
Intense precipitation events associated with stronger atmospheric rivers can lead to an increased risk of landslides and erosion, particularly in steep and vulnerable terrains.
What is the Pineapple Express?
The Pineapple Express is a well-known example of an atmospheric river (AR) that significantly impacts the weather patterns, particularly along the Pacific coast of North America.
It is characterized by a strong and persistent flow of moist air that originates from the Hawaiian region, near the tropics, hence the name “Pineapple” Express. This flow brings warm, moist air from the Pacific Ocean toward the western coast of North America.
Regions affected by the Pineapple Express, such as California, Oregon, Washington, and parts of British Columbia, can experience substantial rainfall over a short period. This can lead to flooding, landslides, and other hydrological impacts.
The warm air associated with the Pineapple Express can lead to higher-than-average temperatures during its events, influencing local climate conditions and potentially leading to early snowmelt in mountainous regions.
The Pineapple Express serves as a vivid example of the dynamic and powerful nature of atmospheric rivers and their significant impact on weather, climate, and hydrology.
Conclusion:
Understanding atmospheric rivers is vital for weather forecasting, water resource management, and preparing for and mitigating the impacts of extreme weather events.
As our climate changes, the behavior of atmospheric rivers may also change, potentially altering their frequency, intensity, and impact on ecosystems and human societies.
Therefore, ongoing research into atmospheric rivers is critical for enhancing our ability to predict and respond to the challenges posed by these dynamic features of our atmosphere.