Introduction
The economic value of guano has been steadily rising over the last few decades, with its significance in agriculture and trade becoming even more pronounced. Guano, once a niche product derived from bird and bat droppings, is now a major component in global fertilizer markets. This natural substance, rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, is revered for enhancing soil fertility and boosting crop yields. In today’s environmentally conscious world, where sustainable farming practices are at the forefront, guano offers a unique, eco-friendly alternative to synthetic fertilizers.
However, the growing demand for guano is not only due to its agricultural applications. The guano industry also supports entire economies, particularly in regions where it is mined, such as Peru and Chile. The guano market is a vital part of global trade, contributing significantly to agricultural output worldwide.
In this article, we’ll explore eight key factors that underscore why the economic value of guano is more important than ever. From its ecological benefits to its economic impact, these factors reshape industries and offer solutions to modern agricultural challenges.
Read also: Extinct No More! Galápagos Rail Returns to Floreana After 200 Years—A Conservation Triumph!
What is Guano, and Why is it Valuable?
Before discussing the key factors, let’s first understand what makes guano valuable. Guano refers to the accumulated droppings of seabirds or bats. Over time, these droppings become rich in nutrients, particularly nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium—essential elements for plant growth. Because of its rich composition, guano is highly sought after as an organic fertilizer. Its historical use as fertilizer dates back centuries, but with the increasing shift toward sustainable farming, guano is once again gaining attention as an effective alternative to chemical fertilizers.
Read also: Circles of Life: Decoding the 5 Important Biogeochemical Cycles of the Ecosystem
8 Key Factors Behind the Economic Value of Guano
1. Natural Fertilizer for Sustainable Agriculture
- Essential Nutrients: Guano contains high levels of essential plant nutrients like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), which are key to plant growth. These nutrients support various vital processes in plants, including photosynthesis, root development, and the formation of flowers and fruits.
- Organic Farming Demand: With an increasing focus on organic farming, guano has become a preferred alternative to chemical fertilizers. It’s natural, sustainable, and doesn’t introduce harmful chemicals into the soil, making it an eco-friendly solution for modern agriculture.
- Soil Fertility: Guano doesn’t just provide nutrients—it also helps maintain soil fertility over the long term. Unlike synthetic fertilizers, which can lead to soil degradation, guano enhances soil structure by increasing microbial activity, promoting better aeration, and improving water retention.
- Slow Release of Nutrients: One of the key benefits of guano is its slow release of nutrients. This ensures that plants receive a steady supply of essential elements over time, preventing nutrient leaching and reducing the need for frequent reapplication.
Read also: UN New World Agenda 2030 – 17 Sustainable Development Goals

2. High Nutrient Content
- Rich Composition: Guano is packed with nutrients, particularly nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). In addition, it contains microelements such as calcium, magnesium, and trace minerals that are beneficial for plant growth.
- Optimal for Different Crops: Because of its balanced composition, guano can be used for a wide range of crops, from vegetables and fruits to flowers and trees. Its versatility makes it highly valuable for various agricultural sectors, including small-scale organic farms and large commercial growers.
- Improved Crop Yields: Studies have shown that using guano as a fertilizer can produce higher crop yields than conventional synthetic fertilizers. This makes it an attractive option for farmers looking to maximize productivity while keeping their practices sustainable.
- Nutrient Availability: Unlike chemical fertilizers that may cause nutrient imbalances or burn crops if applied incorrectly, guano’s natural composition ensures that the nutrients are readily available to plants in the right amounts, reducing the risk of damage.
Read also: The Power of Biological Control of Pests – 3 Proven Natural Solutions
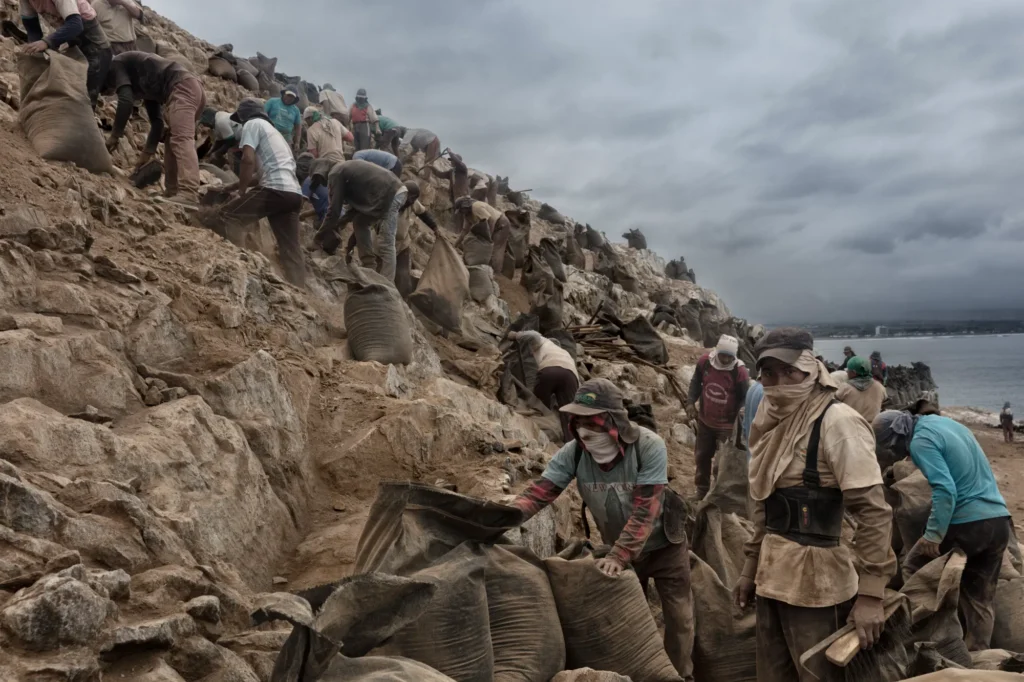
3. Economic Contribution to Local Economies
- Job Creation: The guano industry provides direct and indirect employment to thousands of people in guano-producing regions, such as Peru, Chile, and Indonesia. These jobs include mining, transportation, processing, packaging, and export activities.
- Revenue for Exporting Countries: Countries rich in guano deposits depend on this resource as an essential export commodity. Peru, for example, earns significant revenue from guano exports, contributing to its agricultural and national economic growth.
- Regional Economic Stability: The guano industry is a key economic driver in many rural areas. The local community benefits from direct employment and supporting industries that thrive around guano production, such as logistics, packaging, and retail businesses.
- Government Revenue: Governments in guano-producing countries often impose taxes or royalties on guano production, which provides additional funds for infrastructure development, public services, and other economic growth initiatives.
Read also: Top 10 Most Popular Cities In The World To Visit In 2025

4. Global Demand for Guano
- Rising Organic Farming Trends: As more countries and farmers shift towards organic farming practices, the demand for organic fertilizers like guano has surged. This increased demand is helping expand the global guano trade, driving up its economic value.
- High Demand for Eco-Friendly Alternatives: With growing environmental awareness, the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products has risen globally. As a natural, renewable resource, Guano is gaining popularity as a viable alternative to synthetic chemical fertilizers linked to environmental pollution.
- International Trade: The guano trade has become a significant part of international agricultural markets, with countries like Peru and Chile exporting large quantities to agricultural markets in Europe, North America, and Asia. The economic value of guano has thus extended beyond local production to global markets.
- Growth of Exporting Regions: As guano exports increase, producing countries benefit from trade relationships, foreign investments, and partnerships that contribute to the overall economic development of the region.
Read also: Animals of North America: 20 Astonishing Creatures You Must Discover
5. Long-Term Soil Health Benefits
- Improvement in Soil Structure: Guano is known to improve soil structure by enhancing aeration, increasing water retention, and promoting healthy root development. This, in turn, leads to better plant growth and stronger crops.
- Sustaining Soil Fertility: Over time, the use of guano helps restore depleted soils, ensuring they remain fertile for future generations. This is particularly important in regions where conventional farming practices have caused long-term soil degradation.
- Support for Microbial Life: The organic matter in guano fosters the growth of beneficial soil microbes that are essential for nutrient cycling. This leads to healthier soil ecosystems, which can naturally support plant growth without needing constant fertilization.
- Reduced Dependency on Chemical Inputs: Guano’s long-term benefits reduce the need for chemical fertilizers, which can harm soil health in the long run. Using guano as a sustainable option helps preserve and regenerate soil ecosystems.
Read also: Soil Formation Process: 1 Glimpse From Rock to Rich Earth
6. Reduced Environmental Impact
- Lower Carbon Footprint: The environmental impact of guano harvesting is relatively low compared to the production of synthetic fertilizers, which require energy-intensive processes and release greenhouse gases. Guano is a renewable resource that requires minimal processing.
- No Harmful Runoff: Unlike chemical fertilizers, which can cause nutrient runoff into nearby water bodies, guano’s slow-release properties minimize this risk. The nutrient-rich composition of guano ensures that plants absorb the fertilizer effectively without contributing to water pollution.
- Minimized Soil Erosion: Guano’s ability to improve soil structure reduces the likelihood of soil erosion. Well-structured soil is less prone to washing away during heavy rains, helping preserve topsoil and reduce sedimentation in waterways.
- Sustainable Harvesting Practices: When guano is harvested responsibly, it can provide a continuous and sustainable source of nutrients for agriculture without harming the environment. Ethical guano harvesting practices ensure that the ecosystem is not disrupted and that guano resources remain available for future generations.
Read also: Reduce Your Carbon Footprint Now! 10 Shockingly Simple Ways to Save the Planet
7. The Rise of the Organic Farming Movement
- Consumer Preferences: As consumer demand for organic food increases, organic farmers seek high-quality fertilizers that align with their values. Guano fits perfectly into this movement as an organic fertilizer by providing a natural, non-synthetic option for boosting crop production.
- Certification and Market Growth: The rise of organic certification programs has made it easier for farmers to access new product markets. Guano plays a key role in helping farmers meet the stringent requirements of these certifications, contributing to the growth of organic farming worldwide.
- Increased Focus on Health: As more consumers become aware of synthetic chemicals’ potential health risks, they opt for organic food produced with natural fertilizers like guano. This shift is helping fuel the growth of the organic farming sector and further boosting the demand for guano.
- International Organic Standards: The growing standardization of organic farming practices in various countries also contributes to the rising demand for guano. As the international market for organic products expands, so does the need for reliable and sustainable organic fertilizers.

8. Increasing Role in Global Trade
- Strategic Export Commodity: Guano has become a strategic commodity in international trade, with countries that produce guano establishing long-term relationships with global agricultural markets. Its trade value has increased as demand for organic and sustainable fertilizers continues to grow.
- Export Market Expansion: The global guano market has expanded significantly, increasing exports to Europe, North America, and Asia. This is due to the global shift toward organic farming and the increasing demand for eco-friendly products.
- Trade Policies and Regulations: As guano’s economic value grows, so do the regulatory measures surrounding its trade. Exporting countries are working to establish stronger trade agreements and regulations to ensure that guano continues to flow efficiently across borders, supporting global agricultural needs.
- Supply Chain Growth: With the growing global demand for guano, supply chains are becoming more sophisticated. This includes improved transportation logistics, storage facilities, and distribution networks that ensure guano reaches farmers worldwide at competitive prices.
These eight key factors illustrate why the economic value of guano is more important than ever. As a sustainable, nutrient-rich fertilizer, guano is vital in modern agriculture, contributing to environmental conservation and economic growth. The increasing demand for eco-friendly products and organic farming practices ensures that the future of the guano industry is poised for continued success.
Read also: 7 Controversial Famous Border Walls in the World You Need to Know About
Glimpse of Past and Recent Trends in the Guano Industry
Past Trends in the Guano Industry
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, the guano industry was one of the most significant fertilizer sources globally. During this time, guano was considered a “golden resource” due to its high nutrient content, especially nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. The initial discovery of guano’s fertility-enhancing properties led to its rapid commercial exploitation, especially in regions like Peru, where large deposits of seabird droppings were found.
- The “Guano Rush”: In the mid-1800s, guano became a valuable commodity. Nations like the United States and the United Kingdom aggressively sought guano for agricultural purposes, leading to what was known as the “Guano Rush.” Large quantities of guano were mined, and shipping companies built massive fleets to transport it to far-flung markets, especially to regions experiencing agricultural expansion.
- Economic Dominance: During this period, guano was seen as an essential resource in boosting agricultural production, particularly in countries that were building large-scale farming economies. Its economic value was so high that it became the foundation for many local economies, especially in countries like Peru, Chile, and other coastal nations in South America.
- Depletion and Decline: By the mid-20th century, the overexploitation of guano deposits, particularly in Peru, led to a significant decline in the industry. Large deposits were exhausted, and synthetic fertilizers gradually replaced the demand for guano. The rise of synthetic fertilizers, powered by the Industrial Revolution, made them cheaper and more accessible, thus reducing the reliance on guano.
Read also: Animals on the Brink: Updated Endangered Species List 2025
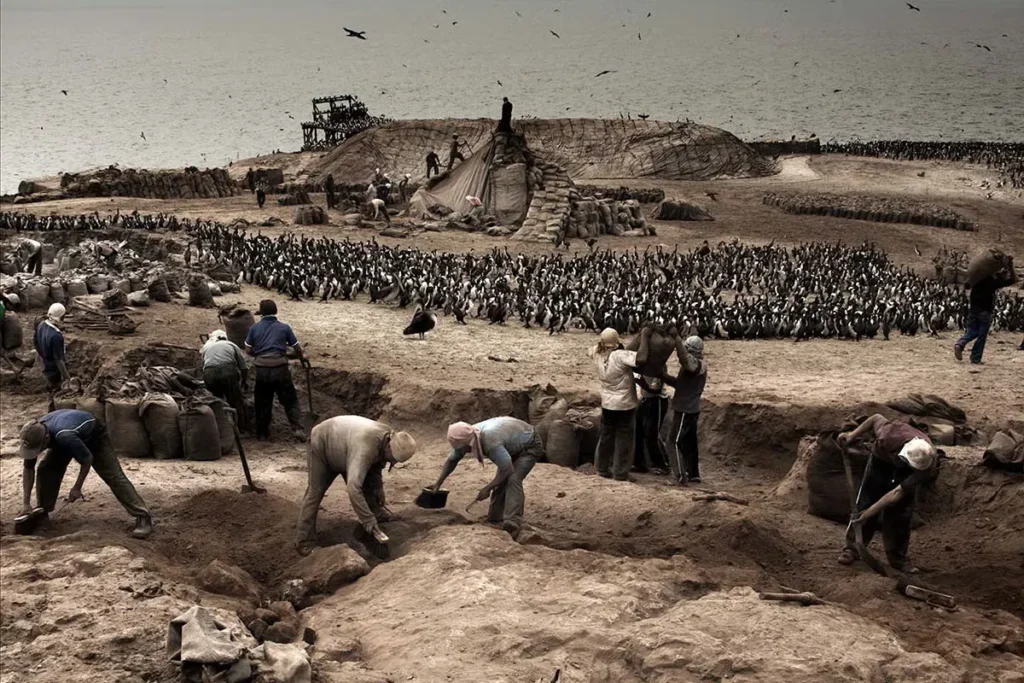

Recent Trends in the Guano Industry
In recent decades, the guano industry has experienced a resurgence, driven largely by growing concerns over the environmental impact of synthetic fertilizers and the rise of organic farming. As consumers and governments worldwide have become more focused on sustainable practices and reducing the environmental damage caused by chemicals in agriculture, the demand for organic fertilizers like guano has increased.
- Organic Farming Boom: The trend toward organic farming, which gained momentum in the late 20th century and accelerated in the 21st century, has revived interest in guano. With the rise of food safety concerns, health-conscious consumers are increasingly choosing organic products. This shift has created a significant market for natural fertilizers like guano, which is prized for its effectiveness and minimal environmental impact compared to synthetic fertilizers.
- Environmental Awareness: As awareness of the negative environmental consequences of chemical fertilizers (such as water pollution and soil degradation) has increased, there has been a global push toward more sustainable and natural farming inputs. With its slow-release nutrient profile, low carbon footprint, and ability to improve soil health, Guano has become a preferred choice for eco-conscious farmers.
- Guano Mining and Ethical Practices: With renewed interest in guano, there has been a push for more sustainable and ethical mining practices. In the past, overharvesting caused environmental damage and depletion of vital guano deposits. Today, many countries are focusing on responsible guano mining to ensure long-term sustainability. Regulations have been implemented to prevent overexploitation and protect bird habitats, particularly in Peru and Chile.
- Increased Global Trade: The global trade in guano has expanded in the last two decades. Countries that produce guano, like Peru and Chile, have seen their guano markets flourish due to the global shift toward sustainable and organic farming practices. This has led to the expansion of international trade routes, with countries in Europe, North America, and Asia increasingly importing guano for agricultural use.
Read also: 6 Strong Differences Between Primary and Secondary Ecological Succession
Changes in the Trend: A Shift Toward Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices
- From Synthetic Fertilizers to Organic Solutions: One of the most significant changes in the guano industry has been the shift from dependence on synthetic fertilizers to more sustainable, organic options. As chemical fertilizers became widely available, they supplanted natural fertilizers like guano for decades. However, environmental damage caused by excessive chemical fertilizer use, such as soil degradation and contamination of water supplies, has driven a resurgence in organic farming methods. This shift has led to an increased demand for guano and other organic fertilizers that are both sustainable and effective.
- Technological Advancements in Harvesting: Technological advancements have improved the efficiency of guano mining and processing, making it a more viable option for modern agriculture. New extraction methods ensure that guano is harvested responsibly, minimizing environmental damage and increasing the overall yield of usable guano from natural deposits.
- Emerging Markets and Ethical Sourcing: With the increasing demand for eco-friendly products, there is a greater focus on the ethical sourcing of guano. Many buyers, particularly in the organic farming sector, are now more concerned with how guano is sourced. This has prompted a change toward more ethical and sustainable mining practices, including limiting the impact on local ecosystems and ensuring the protection of bird and bat populations that are essential for guano production.
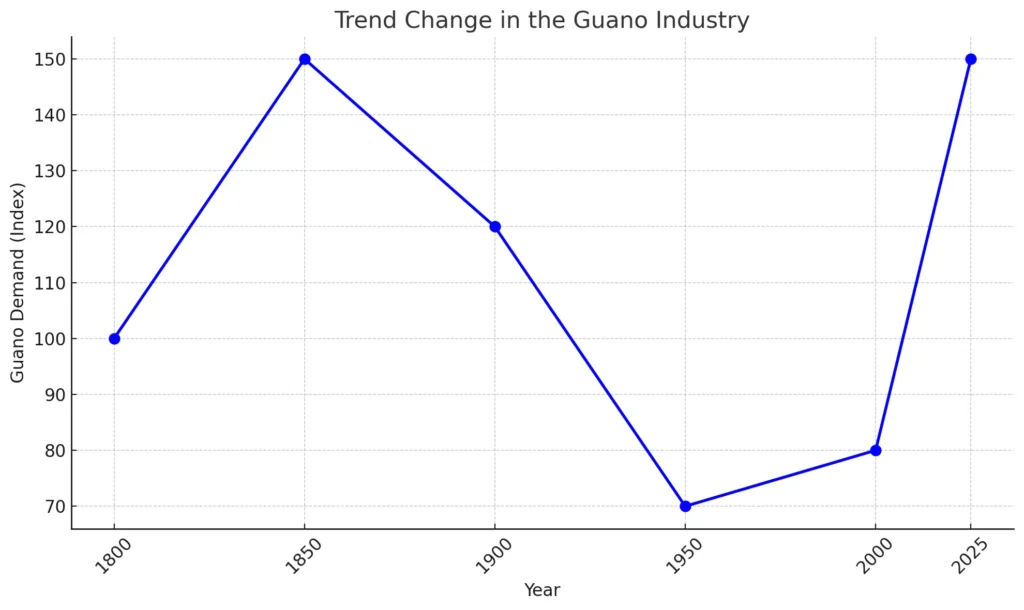
Here is a graph representing the trend change in the guano industry over time. The data shows the fluctuation of guano demand from the peak during the 1800s, a decline in the mid-20th century with the rise of synthetic fertilizers, and the recent resurgence due to the organic farming boom and sustainability trends. The increase in demand around 2000 and projected 2025 highlights the growing importance of guano in modern agriculture.
The Role of Guano in First-World Countries’ Economies
While guano has long been important in developing countries where it is mined, it also plays a crucial role in the economies of first-world countries, particularly in the context of sustainable agriculture and organic farming.
- Support for Organic Agriculture: First-world countries, including the United States and European countries, have seen a steady rise in organic farming. The demand for organic food has been consistently growing, driven by consumer preferences for healthier, chemical-free produce. As these nations move toward more sustainable farming practices, guano has emerged as a critical input for the organic farming sector. The demand for guano in these markets helps stimulate the trade and export of guano from producing countries like Peru.
- Export and Trade Benefits: First-world countries are significant guano importers, contributing to their agricultural sectors and economies. For example, countries in Europe, North America, and even parts of Asia have become key players in the global guano market. The import of guano contributes to these countries’ agricultural needs and stimulates economic activities related to trade, transport, and distribution, benefiting various industries.
- Innovation and Research: The economic role of guano in first-world countries is also seen in the growing investment in research and innovation related to its applications. As sustainable practices gain prominence, research is increasing into new ways of using guano, such as in biopesticides, soil amendments, and even pharmaceuticals. These countries invest in innovation to further boost guano’s agricultural and economic value.
- Environmental Responsibility: First-world nations have increasingly prioritized environmental sustainability, and using natural fertilizers like guano aligns with these goals. By promoting the use of guano, these countries are reducing their reliance on harmful synthetic fertilizers and supporting global efforts to mitigate the environmental impacts of industrial agriculture.
- Circular Economy and Local Agriculture: In some first-world countries, guano is also promoted as part of a circular economy strategy. Local farmers adopt sustainable fertilizers to meet organic certification standards and support small-scale, environmentally friendly agriculture. This contributes to the overall economic model by keeping the agricultural sector productive while reducing dependency on imported chemical inputs.
Read also: Green Infrastructure: How U.S. Coastal Cities Fight Climate Change and Protect Their Future
Guano Market Scope
- Growing Demand for Organic Fertilizers: The global demand for organic fertilizers, including guano, has steadily increased. This trend is driven by a rise in organic farming practices, consumer preference for organic food, and growing awareness of the environmental damage caused by synthetic fertilizers.
- Key Global Players: Peru, Chile, and Indonesia are major guano producers. These countries are responsible for a significant portion of global guano production, which is largely exported to Europe, North America, and Asia.
- Expansion of Organic Farming: As more farmers embrace sustainable practices, the use of guano is gaining popularity due to its rich nutrient content and environmental benefits. Expanding organic farming sectors, especially in first-world countries, fuels this demand.
- Rising Environmental Concerns: The growing awareness of the negative environmental impact of chemical fertilizers has shifted the agricultural industry towards more sustainable options like guano. As a result, guano has gained traction in global markets as a natural alternative.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in the guano harvesting process have made it more efficient and sustainable. Responsible sourcing and ethical harvesting practices are now being emphasized to protect ecosystems.
- Market Growth Projections: The guano market is expected to continue growing, driven by demand in agriculture and new applications in non-agricultural industries like pharmaceuticals.
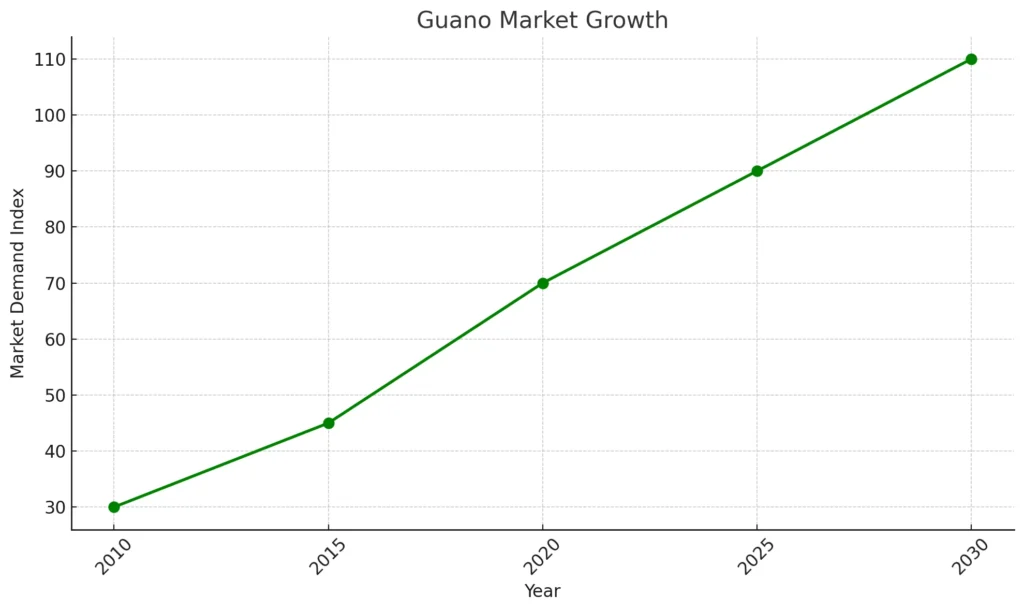
Here is the graph showing the growth in the guano market based on the increasing demand for organic fertilizers. The data highlights the projected market growth from 2010 to 2030, with a steady rise driven by the shift toward sustainable agricultural solutions:
Conclusion
The guano industry has undergone significant changes over the last century, from its peak use in the 19th century to a period of decline with the rise of synthetic fertilizers. However, recent trends show a renewed interest in guano as a sustainable and effective solution for modern farming practices. This shift is not only due to the growing demand for organic products but also because of the increasing focus on environmental sustainability and the negative impact of synthetic fertilizers.
In first-world countries, guano is critical in supporting the organic farming movement, stimulating trade-related economic activity, and helping farmers reduce their environmental footprint. The economic value of guano continues to rise, driven by consumer demand for sustainable agricultural solutions and a broader shift toward eco-conscious farming practices. As the global agriculture sector continues to evolve, guano will likely remain a key player in the search for sustainable, environmentally friendly agricultural solutions.
FAQs
1. What makes guano so valuable in agriculture?
Guano is rich in nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, making it an ideal organic fertilizer.
2. How does guano help improve soil health?
Guano improves soil structure, promotes microbial life, and enhances water retention, leading to better crop yields.
3. Where is guano primarily harvested?
Guano is mainly harvested in Peru, Chile, and Indonesia, where large bat and bird droppings deposits are found.
4. Is guano more sustainable than synthetic fertilizers?
Yes, guano is a natural alternative to chemical fertilizers, with minimal environmental impact and long-term soil health benefits.
5. Can guano be used in organic farming?
Absolutely! Guano is widely used in organic farming because it improves soil fertility and enhances crop growth.
6. What are the ethical concerns with guano harvesting?
Over-harvesting and destroying habitats can threaten bat and bird populations, necessitating sustainable and ethical harvesting practices.

