Water is the driving force of all nature.“— Leonardo da Vinci.
However, water quality faces mounting threats today, particularly in coastal regions. One of the most pressing dangers to drinking water is saltwater intrusion, where seawater encroaches into freshwater aquifers, contaminating the sources we rely on for drinking, irrigation, and industry. This issue is becoming increasingly severe as climate change accelerates, especially for U.S. coastal cities. But how does saltwater intrusion into drinking water occur, and what can be done to safeguard our supplies?
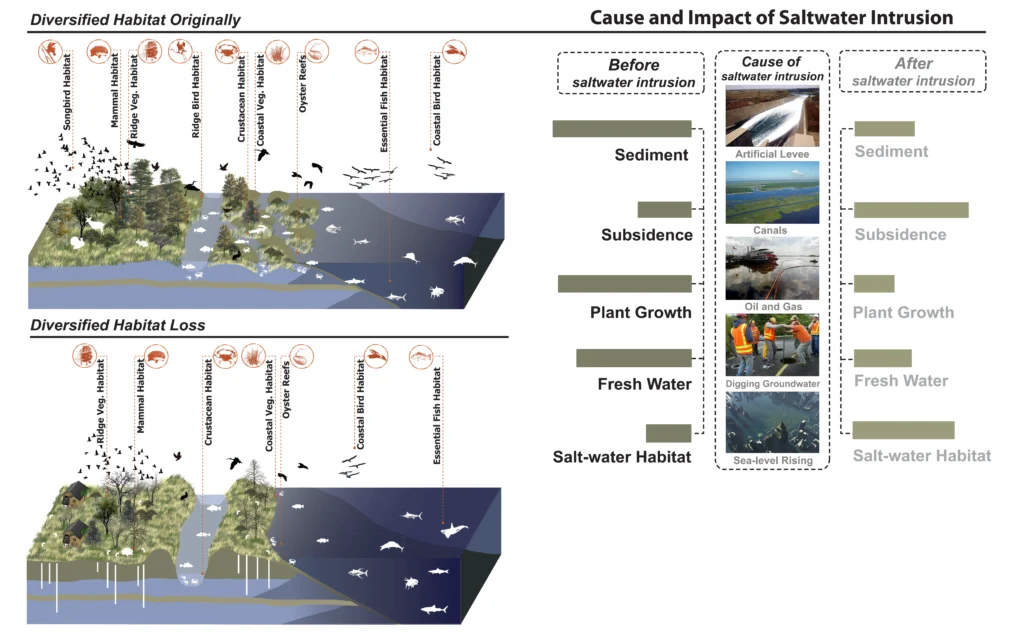
Understanding Saltwater Intrusion and Its Causes
What is Saltwater Intrusion?
Saltwater intrusion into drinking water happens when seawater infiltrates freshwater aquifers and wells, typically supplying drinking water to coastal communities. As the salty seawater mixes with freshwater, it contaminates the water, making it unsuitable for consumption without costly treatment.
Natural Causes of Saltwater Intrusion:
- Rising Sea Levels: One of the most significant factors driving saltwater intrusion in U.S. coastal cities is the rising sea levels caused by melting glaciers and polar ice caps. As seawater rises, it pushes inland, penetrating freshwater reserves.
- Drought: Droughts reduce the amount of freshwater in aquifers, making them more susceptible to being overtaken by saltwater.
- Over-pumping of Groundwater: As populations grow, the demand for water increases. Overpumping freshwater from underground aquifers lowers water levels, weakening the natural barrier that keeps saltwater at bay.
Man-Made Factors Contributing to Saltwater Intrusion:
- Urban Development: Coastal cities are expanding, often without considering the delicate balance between fresh and saltwater. Construction activities can disrupt the natural hydrological cycle and lead to saltwater encroachment.
- Climate Change: Global warming exacerbates both natural and man-made causes of drinking water salinization by climate change. For example, storms’ increased frequency and severity can push seawater further inland while human activities continue to stress water supplies.
| Cause of Saltwater Intrusion | Impact |
| Rising sea levels | Increases seawater pressure on freshwater aquifers, leading to contamination. |
| Over-pumping of groundwater | Reduces freshwater levels, allowing seawater to infiltrate aquifers. |
| Urban development and infrastructure | Disrupts natural water cycles, contributing to saltwater encroachment. |
Health Issues Stemming from Saltwater Intrusion
Saltwater intrusion poses severe health risks to affected communities, particularly those reliant on groundwater for drinking water. Contaminated water sources can cause a range of health issues:
1. Hypertension
When saltwater intrusion into drinking water occurs, the elevated sodium levels in water supplies can contribute to high blood pressure or hypertension, especially in vulnerable populations like the elderly and those with preexisting heart conditions.
2. Kidney Disease
High sodium levels due to drinking water salinization by climate change can worsen existing kidney conditions or lead to new kidney problems. Over time, the kidneys may struggle to filter excess salt from the bloodstream, leading to potential long-term damage.
3. Gastrointestinal Issues
Water contaminated with salt can lead to gastrointestinal problems such as nausea, diarrhea, and dehydration. Prolonged exposure to salty water may also irritate the stomach lining.
Symptoms of Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Areas
Saltwater intrusion is often invisible to the naked eye, but there are telltale signs that communities should be aware of. Identifying these symptoms early can help mitigate the damage:
1. Salty Taste in Tap Water
One of the most noticeable indicators of saltwater intrusion into drinking water is tap water’s salty or briny taste. If residents begin to detect an unusual taste, it could be a sign that their freshwater supply is compromised.
2. Corrosion of Pipes and Appliances
Saltwater is highly corrosive, and when it infiltrates freshwater systems, it can damage plumbing infrastructure. Rusting pipes, appliances, and water heaters are signs of saltwater intrusion in U.S. coastal cities.
3. Dying Vegetation
Saltwater contamination can also be detected in agriculture. Plants and crops that depend on freshwater may wilt, die, or produce lower yields when irrigated with saline water. This is an indirect but significant sign that local water supplies are being affected.
How Coastal Communities Can Combat Saltwater Intrusion
Residents of coastal areas have a vital role in addressing the hazards of saltwater intrusion into drinking water. While government and local authorities implement measures, individual actions can also have a substantial impact.
1. Water Conservation
By reducing water consumption, communities can help alleviate the strain on freshwater supplies. Water-efficient appliances, shorter showers, and responsible irrigation practices all contribute to maintaining aquifer levels.
2. Support Sustainable Infrastructure Projects
Residents should advocate for and support local policies that prioritize sustainable development. Projects that reduce over-extraction of groundwater and enhance the natural barriers between saltwater and freshwater, such as wetland restoration, can help mitigate the risk of saltwater intrusion.
3. Participation in Water Monitoring Programs
Many cities encourage residents to participate in local water quality monitoring efforts. Being informed about drinking water quality and reporting unusual changes can help local authorities address contamination issues more promptly.
Government Strategies to Address Saltwater Intrusion
As the threat of climate change and saltwater intrusion in the USA grows, local, state, and federal governments have recognized the need for proactive strategies to address the issue.
1. Groundwater Management and Protection Plans
Many U.S. states have developed Groundwater Management Plans to control over-pumping, a key contributor to saltwater intrusion. These plans include water rationing during droughts, improved well regulation, and the development of desalination technologies.
2. Restoration of Natural Barriers
To counteract the effects of saltwater intrusion in U.S. coastal cities, efforts are underway to restore natural ecosystems that act as barriers. For instance, marshland and mangrove restoration projects help create a buffer between saltwater and freshwater sources.
3. Desalination Plants
Some coastal cities are investing in desalination plants, which convert seawater into freshwater. Although this technology is expensive and energy-intensive, it is a reliable solution in areas where saltwater intrusion into drinking water is becoming increasingly common. California, for example, has made significant strides in desalination to address its water scarcity problems.
Future Plans to Prevent Saltwater Intrusion
Looking ahead, the U.S. government is exploring several long-term strategies to minimize the threat of saltwater intrusion.
1. Climate Change Mitigation
Addressing the root cause of drinking water salinization by climate change is critical. Efforts to reduce carbon emissions and limit global warming are part of broader initiatives to prevent future sea-level rise and the worsening of saltwater intrusion.
2. Managed Aquifer Recharge
Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) is an emerging technique where excess water, often from storm runoff or wastewater treatment, is intentionally stored in underground aquifers. This can help balance the freshwater levels in aquifers and prevent seawater from advancing inland.
Conclusion
The threat of saltwater intrusion into drinking water in U.S. coastal cities is growing due to climate change, urban development, and over-pumping. Left unchecked, this issue poses significant health risks, including hypertension and kidney disease, and can lead to costly infrastructure damage. The government and local communities must take action through sustainable water management, restoration of natural barriers, and technological advancements like desalination plants to ensure the safety and reliability of drinking water supplies.
In conclusion, addressing the impact of saltwater intrusion into drinking water requires a collective effort. By understanding the risks, implementing strategic actions, and being vigilant about water quality, we can protect our precious freshwater resources from the encroaching sea.
What is saltwater intrusion?
Saltwater intrusion occurs when seawater moves into freshwater aquifers, contaminating drinking water supplies and making them unsafe for consumption.
How does climate change affect saltwater intrusion?
Climate change contributes to rising sea levels, pushing saltwater further inland and exacerbating the risk of saltwater intrusion in coastal areas.
What are the health risks associated with saltwater intrusion?
Health risks include hypertension, kidney disease, and gastrointestinal issues due to elevated sodium levels in drinking water.
What can residents do to prevent saltwater intrusion?
Residents can conserve water, support sustainable development, and participate in local water monitoring programs to help reduce the risk of saltwater intrusion.
How is the U.S. government addressing saltwater intrusion?
The government is implementing strategies such as groundwater management plans, natural barrier restoration, and desalination projects to combat saltwater intrusion.





