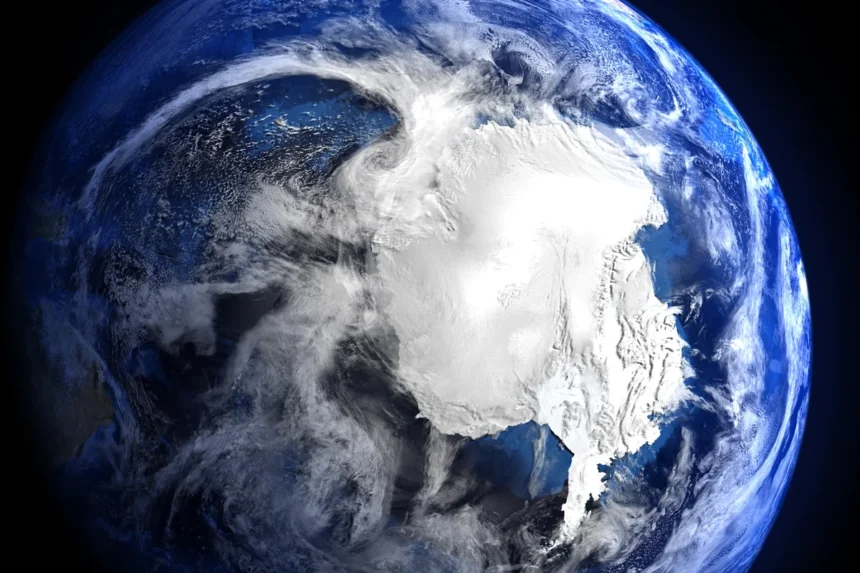
Antarctica was once an untouched wilderness. But from space, the icy continent reveals a different story. We see shifting glaciers, melting sea ice, and the subtle scars of human activity. This is Antarctica today, a place in urgent transformation.
⫸ Introduction
Antarctica, a land of extremes, captivates us with its pristine beauty and critical role in our planet’s health. We gain an unparalleled perspective on this icy realm from space, unlocking insights that ground-based observations cannot provide. This unique vantage point sheds light on Antarctica’s dynamic processes, hidden landscapes, and vulnerability in a changing world.

Brief overview of Antarctica’s unique geography and significance:
Antarctica is the Earth’s southernmost continent, a vast wilderness of ice sheets, glaciers, and mountains. It holds about 90% of the world’s freshwater ice and is crucial in regulating global ocean currents and climate. Antarctica’s unique ecosystems are home to iconic wildlife like penguins, seals, and whales, which are specially adapted to harsh conditions.
The value of observing Antarctica from space:
Satellites equipped with advanced sensors revolutionize our understanding of Antarctica from space. They monitor vast ice shelves, track the flow of glaciers, measure changes in sea ice extent, and even map hidden features beneath the ice surface. This data is essential for scientists to:

- Track climate change impacts: Antarctica is a bellwether; changes here indicate the health of our planet.
- Understand sea level rise: Melting Antarctic ice has global consequences.
- Protect fragile ecosystems: Space-based monitoring aids conservation efforts.
⫸ Antarctica’s Topography Through Satellite Imagery
Satellites orbiting Earth provide a breathtaking and uniquely informative perspective on Antarctica. We can analyze the icy continent’s topography from space with extraordinary detail. This data is fundamental to understanding Antarctica’s dynamic nature and response to a changing climate. Let’s explore some of the critical features revealed by satellite imagery.
Ice Shelves:
● Definition of ice shelves:
Ice shelves are massive floating platforms of ice that form where glaciers and ice sheets flow into the ocean. They play a crucial role in buttressing and slowing the flow of land-based ice.

● Major ice shelves in Antarctica:
Several major ice shelves fringe Antarctica. The largest is the Ross Ice Shelf, roughly the size of France. The Larsen Ice Shelf on the Antarctic Peninsula has famously experienced significant collapses in recent decades.

Glaciers:
● Types of glaciers found in Antarctica:
Antarctica harbors many glaciers, including outlet glaciers that drain the massive ice sheets, valley glaciers nestled within mountain ranges, and fast-flowing ice streams.

● Satellite monitoring of glacier flow and retreat:
Satellites track even subtle changes in glacier speed and extent. This data reveals clear trends of widespread glacial retreat across Antarctica, particularly in West Antarctica.
● The significance of glacier melt for sea level rise:
Glacier meltwater flowing into the ocean contributes to the global sea level rise. Antarctica’s ice holds enough potential to raise sea levels dramatically, making glacier monitoring critical for predicting future coastal impacts.
Sea Ice:
● Seasonal variations in Antarctic sea ice extent
Sea ice surrounding Antarctica expands dramatically during winter and shrinks during summer. This annual cycle is a vital part of the Southern Ocean ecosystem.
● Trends in sea ice coverage and thickness.
While there’s regional variability, satellite data reveals complex trends in Antarctic sea ice coverage and thickness. Understanding these changes is essential for modeling ocean circulation and the ecosystem it supports.

● The role of sea ice in the Antarctic ecosystem
Sea ice provides a platform for critical species like krill, the foundation of the Antarctic food web, and breeding grounds for penguins and seals.
Transantarctic Mountains:
● Formation and geological significance
The Transantarctic Mountains are one of the world’s longest ranges, dividing East and West Antarctica. They formed through complex geological processes, including uplift and faulting.
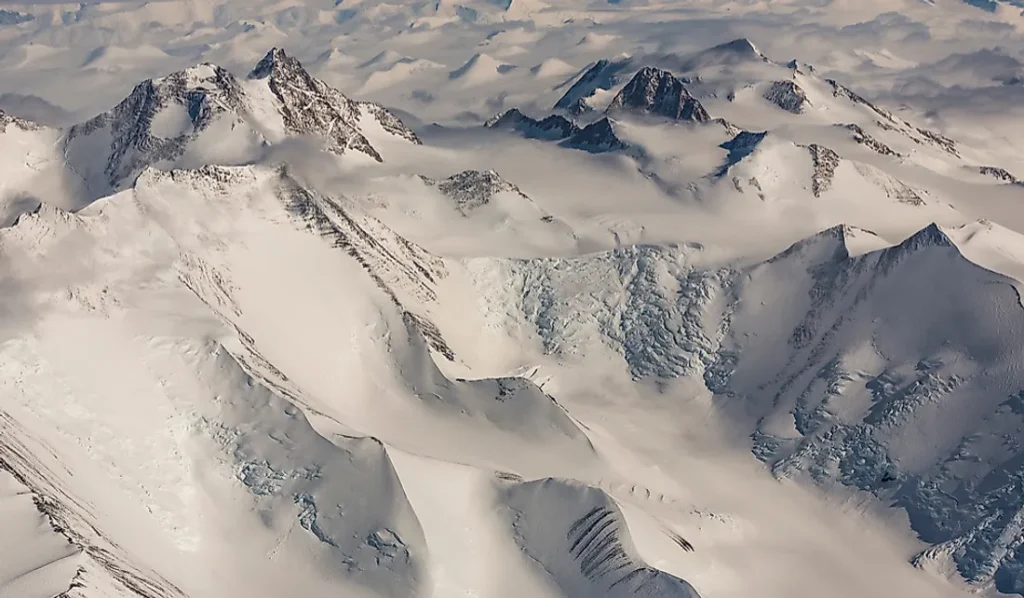

● Identifying the range from space
Satellite imagery delineates the Transantarctic Mountains, providing insights into their geological structure and the glacial systems they harbor.
Subglacial Features:
● How satellites detect hidden lakes and mountains
Antarctica from space reveals the surface and what lies beneath the ice. Scientists use specialized instruments like ice-penetrating radar to map a hidden world of subglacial lakes and mountain ranges.
● Examples: Lake Vostok
Lake Vostok is one of the largest subglacial lakes in the world, buried under kilometers of ice. It’s a potential harbor for unique life forms and clues about Antarctica’s ancient past.
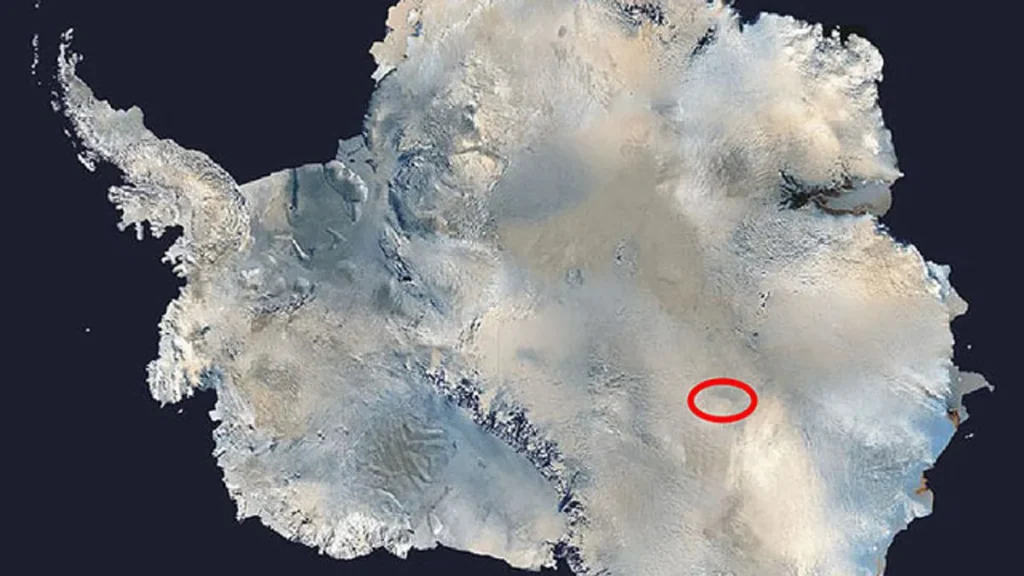

⫸ Satellite Imagery: Our Eyes on the Ice
Satellite technology has revolutionized our understanding of Antarctica from space. It provides a vantage point that unveils the icy continent’s grandeur, its fragility in the face of climate change, and the surprising resilience of life that thrives there. Let’s explore how satellites help us monitor this remote and vital region.
Types of satellites used to observe Antarctica:
A fleet of Earth-observing satellites gathers data about Antarctica. Some key missions include:
- Landsat is a long-running program that has provided high-resolution imagery for decades, tracking changes in coastlines, glaciers, and ice shelves.
- MODIS: This instrument is aboard NASA’s Terra and Aqua satellites. It captures wide-area views to study changes in sea ice extent and surface temperature.
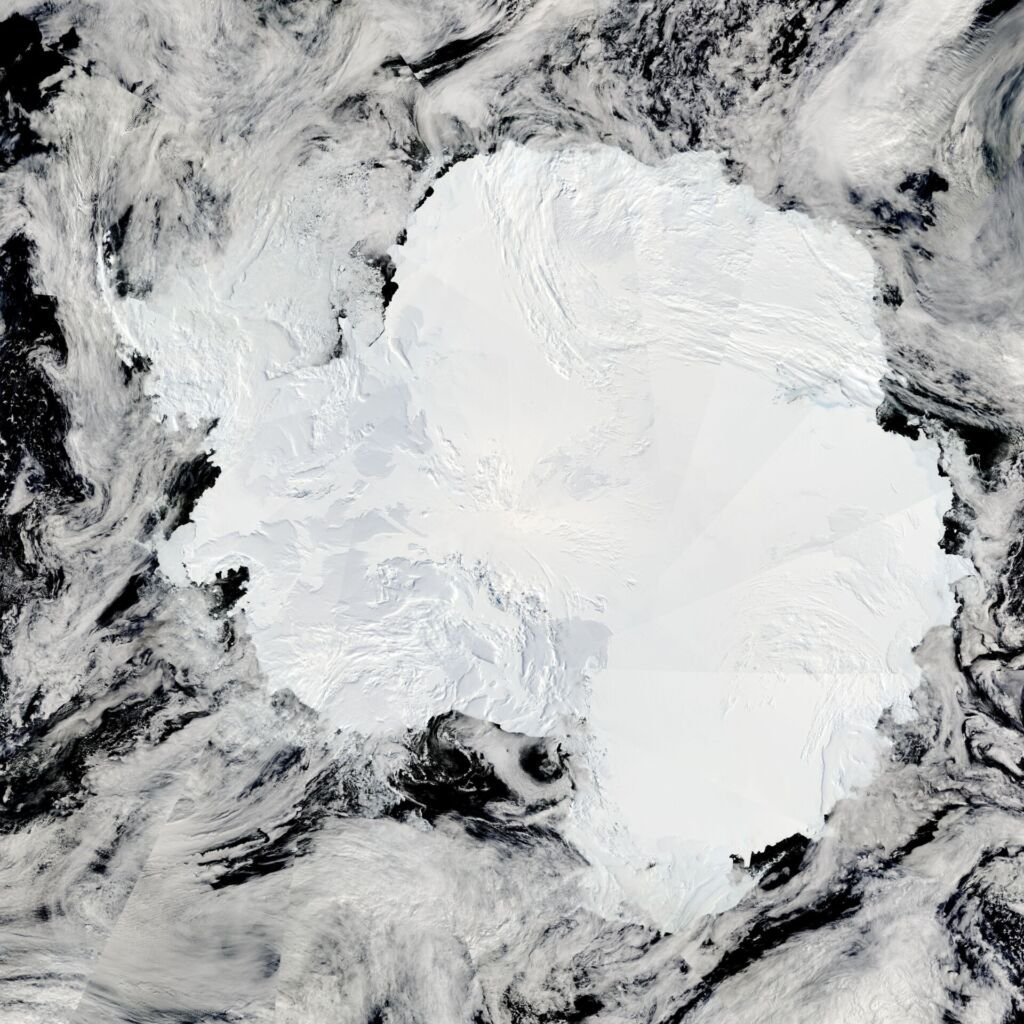

Key data collected by satellites:
Satellites collect a treasure trove of information about Antarctica from space:
- Surface Temperature: Reveals patterns of warming and cooling across the continent.
- Ice Thickness: Specialized instruments measure the height of ice sheets and sea ice, providing clues about melt rates.
- Sea Ice Extent: Mapping sea ice’s seasonal expansion and retreat is essential for understanding polar ecosystems.
Monitoring Ice Loss:
Antarctica from space tells a concerning story of accelerating ice loss. Satellites give us a front-row seat to these dramatic changes:
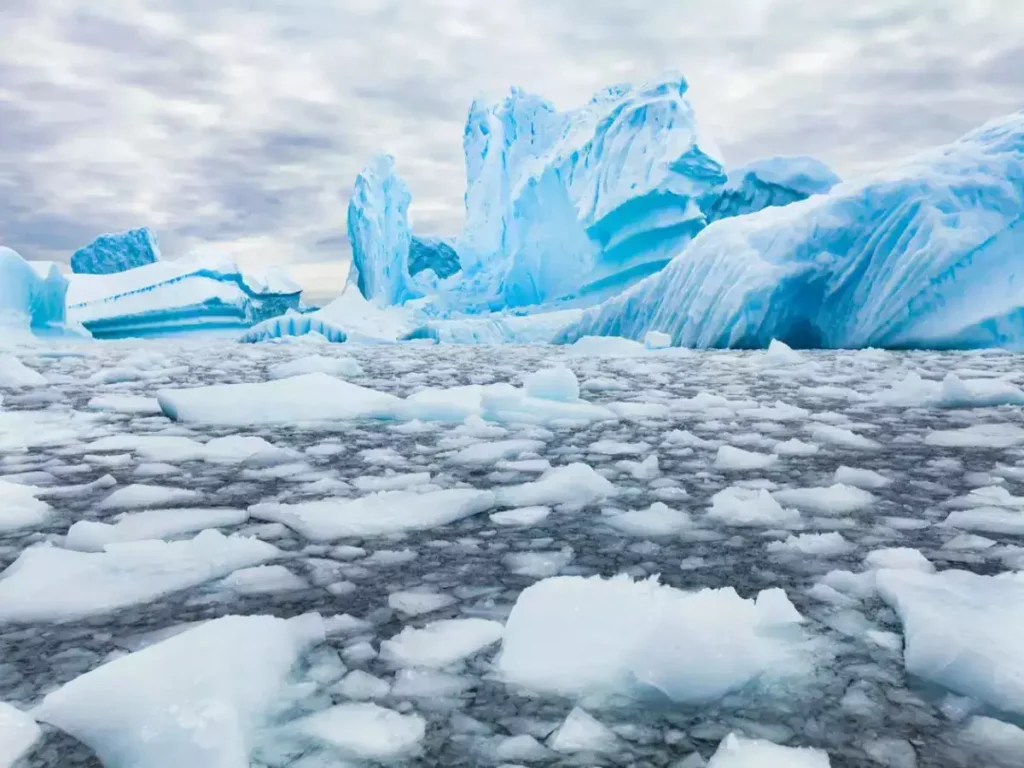

● Measuring ice sheet melt and ice shelf disintegration
Altimeters on satellites like ICESat-2 precisely measure ice sheet loss, revealing areas of rapid thinning, particularly in West Antarctica. Images track the break-up of massive ice shelves.
● Impact on global sea levels
The fate of Antarctica’s ice holds major consequences for our planet. Data on ice sheet melt directly informs projections of future global sea level rise, posing risks to coastal communities worldwide.

Wildlife Observation:
Satellites even illuminate Antarctica’s animal life from space.
● Penguin colony tracking
High-resolution images reveal the surprising extent of Emperor penguin colonies, aiding scientists in monitoring these iconic species.
● Identifying whale habitats
By observing ocean color and temperature, satellites help pinpoint important feeding grounds for whales and other marine life, which is crucial for conservation efforts.
⫸ Landmark Discoveries from Space
Satellites orbiting our planet have revolutionized our understanding of Antarctica. From the comfort of our laboratories and homes, we can now peer into the mysteries of this frozen continent. Let’s explore some of Antarctica’s most significant discoveries from space has made to science.
The Larsen B Ice Shelf Collapse:
In 2002, scientists witnessed a shocking event through satellite imagery – the disintegration of a massive section of the Larsen B Ice Shelf. Over 35 days, an area larger than Rhode Island crumbled into the ocean. This collapse highlighted the vulnerability of Antarctic ice formations to a warming climate.
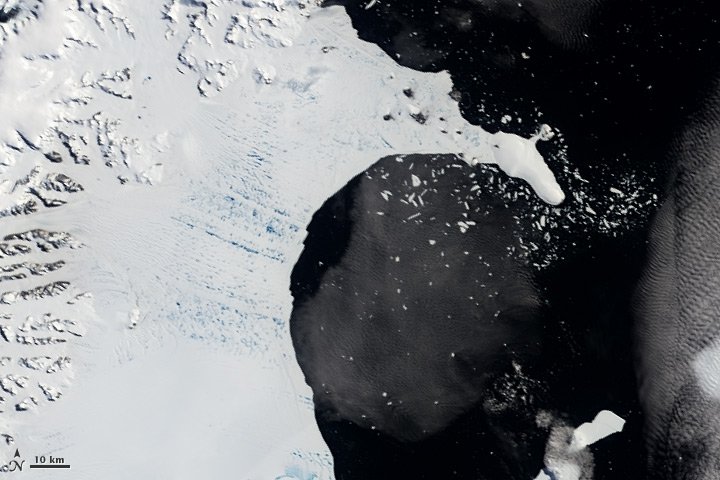

Hidden Subglacial Lakes:
Antarctica’s thick ice sheet hides a secret world. Scientists have discovered a whole network of subglacial lakes lurking beneath kilometers of ice. Lake Vostok, one of the largest, is a potential haven for unique life forms that have evolved in isolation for millions of years. Antarctica from space allows us to map and study these mysterious bodies of water.
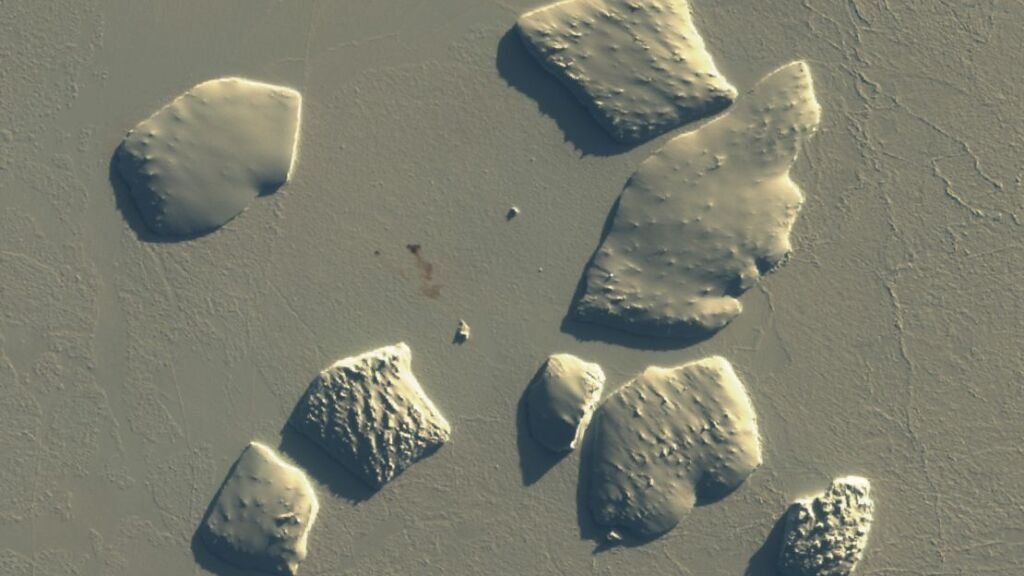
Mapping Emperor Penguin Colonies:
The iconic emperor penguin, a symbol of Antarctica’s harsh beauty, is relatively easy to track. However, satellite imagery has changed the game. Scientists can pinpoint previously unknown emperor penguin colonies by identifying the stains their droppings leave on the ice. This space-age monitoring helps us understand the population trends of this fascinating species.

⫸ The Future of Antarctic Observation
The view of Antarctica from space has revolutionized our understanding of this remote and crucial continent. As satellite technology advances and international cooperation expands, the future of Antarctic observation promises even more remarkable insights. Let’s dive into the key areas shaping this field:
New Satellite Technologies:
Emerging satellite technologies are pushing the boundaries of what we can observe in Antarctica. Higher-resolution imaging allows scientists to map even finer-scale changes in ice features. Advanced radar systems can penetrate the ice sheet, revealing the bedrock topography and providing clues to the continent’s long-term evolution.
International Collaboration for Data Sharing:
International collaboration is essential for maximizing the impact of Antarctic satellite data. Initiatives like the Polar Space Task Group coordinate the efforts of various space agencies, ensuring data is shared freely and analyzed effectively. This collaboration accelerates research and allows scientists to understand Antarctica’s changes comprehensively.
Climate Change Monitoring and Prediction:
The most urgent application of satellite observation is in understanding and predicting the impact of climate change on Antarctica. Tracking ice sheet melt, sea ice variability, and changes in ocean currents provides crucial data for climate models. This enables scientists to forecast future sea level rise and refine our understanding of how Antarctica’s changes might impact global climate patterns.

⫸ Experience Antarctica from Space
Antarctica from space reveals a world that is both awe-inspiring and fragile. Satellites provide a crucial vantage point for understanding this icy continent, giving scientists a bird’s-eye view of its immense ice sheets, hidden landscapes, and wildlife within this extreme environment. Let’s dive into the wealth of resources available to explore Antarctica from space —from the vast archives of NASA and the ESA to interactive tools and even opportunities to contribute to scientific research.
● NASA Resources:
- Earth Observatory: NASA’s Earth Observatory offers stunning imagery and informative articles on Antarctica from space, often highlighting changes and discoveries.
- NASA Worldview: This interactive tool lets you visualize recent and historical satellite data of Antarctica, including customizable views of sea ice, temperatures, and more.
● European Space Agency (ESA):
- ESA’s Earth Online features beautiful satellite images of Antarctica, news, and updates on ESA missions studying the continent.
- Polar View: This ESA-led initiative monitors sea ice and icebergs in the Arctic and Antarctic, providing crucial data for climate research and maritime safety.
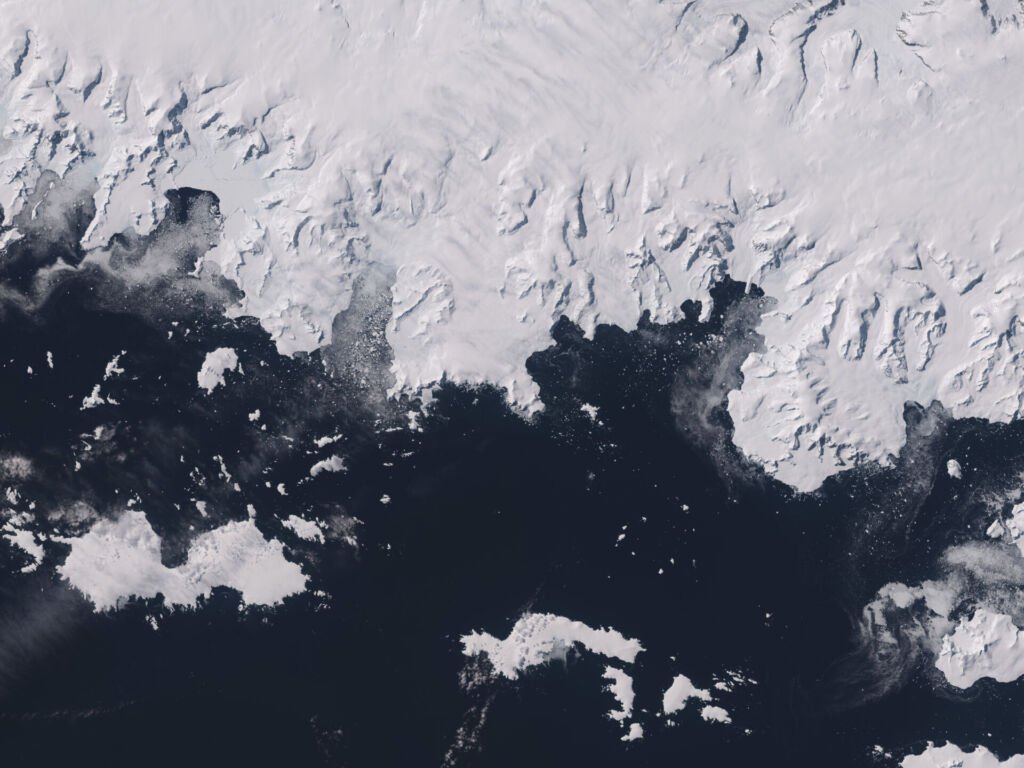

● Online Resources and Interactive Maps:
- The Landsat Image Mosaic of Antarctica (LIMA): This project provides a high-resolution, true-color satellite map of the entire continent.
- Google Earth: Zoom into Antarctica with Google Earth to explore research stations, geographic features, and 3D terrain views.
● Citizen Science Projects:
- Penguin Watch: Help scientists monitor populations by counting penguins in satellite images.
● Other Public Image Archives:
- US Geological Survey (USGS) EarthExplorer: Search for historical and current satellite data, including imagery of Antarctica.
⫸ Conclusion
Viewing Antarctica from space makes the full scale of its breathtaking beauty and worrying vulnerability startlingly clear. Satellite imagery paints a vivid picture, revealing how climate change and human activities reshape this fragile continent. This space-based perspective fuels scientific discovery and underscores the importance of global cooperation in protecting Antarctica for future generations. It’s a call to action that we cannot afford to ignore.





