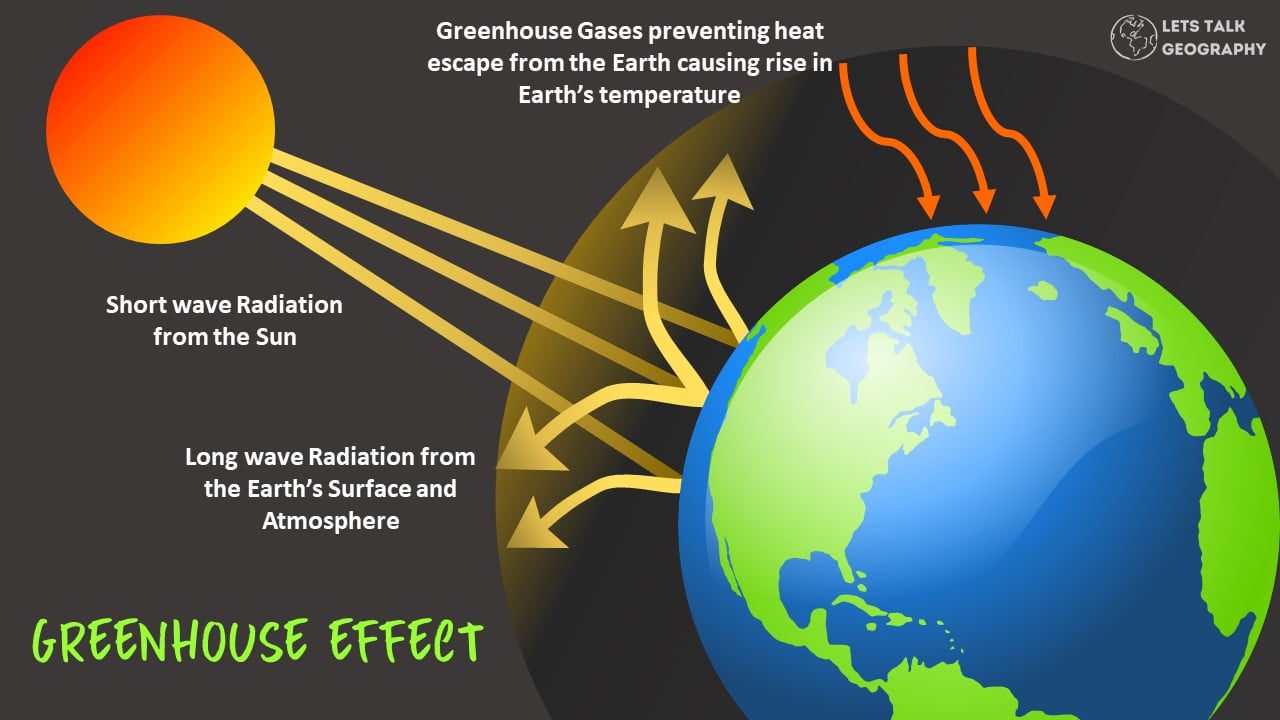
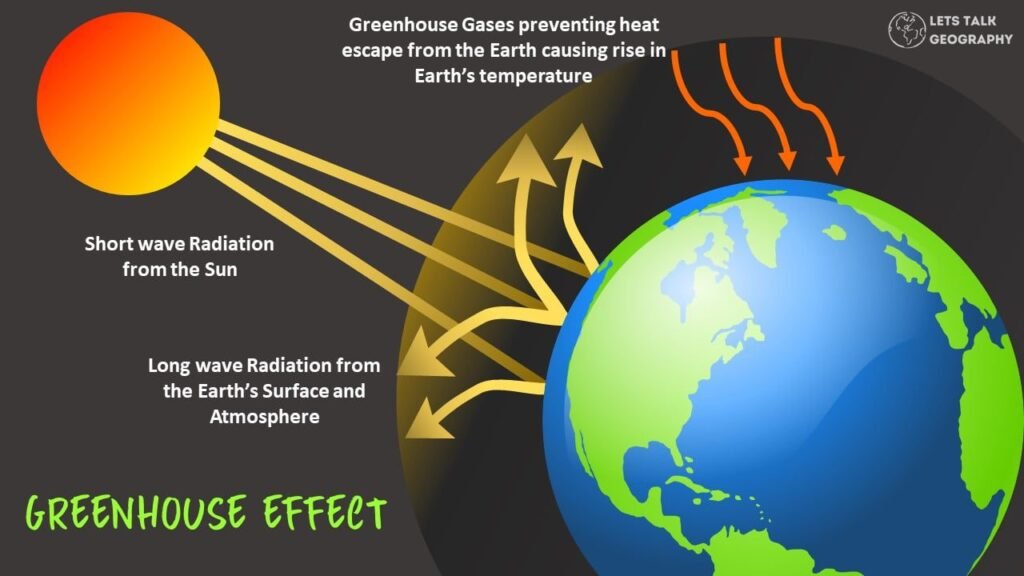
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that helps to keep our planet warm. However, human activities are strengthening the effect, leading to global warming. In this blog post, we will explore the causes and effects of global warming and discuss possible solutions. Stay tuned!
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
The greenhouse effect is a phenomenon that contributes to the earth’s temperature increase through radiation from the atmosphere, ultimately raising the temperature above the standard expected temperature if this atmosphere is absent.
In other words, the greenhouse effect is the inborn warming of the globe resulting from atmospheric gases entrapping the heat from the sun that would otherwise escape outer space.
Greenhouse gases absorb infrared radiation in the form of heat from the sun. They also boost the absorption rate of radiation from the sun with a short wavelength, but this has a feeble impact on the global temperature.
In other words, the greenhouse effect is the inborn warming of the globe resulting from atmospheric gases entrapping the heat from the sun that would otherwise escape outer space.
The Causes of the greenhouse effect:
◆ Greenhouse Gases:
A greenhouse gas’s role in producing the greenhouse effect depends on how much heat it absorbs. The amount of heat it re-radiates and the amount released into the atmosphere also determine the contribution of greenhouse gases to the greenhouse effect.
The greenhouse gases which contribute to the global greenhouse effect are as follows:
- Ozone (O3)
- Methane (CH4)
- Nitrous oxide (N2O)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Water vapour (H2O)
Concerning the GWP or global warming potential (the heat quantity these greenhouse gases absorb and re-radiate), methane is twenty-three times, and nitrous oxide is two hundred and ninety-six times more effective than carbon dioxide. Anyhow, the amount of carbon dioxide in the earth’s atmosphere is far more than that of nitrous oxide and methane.
◆ Accumulation of Carbon dioxide:
Not every greenhouse gas that is emitted into the atmosphere stays there for an indefinite period. For instance, the amount of carbon dioxide diffused in the oceans’ surface waters and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere remain at equilibrium because the water and air mix well on the sea’s surface. By adding more carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, some of it diffuses to the oceans.
◆ Industrialization:
Following the Industrial Revolution in the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, the release of greenhouse gases increased manifold. However, the past century has seen a quicker rise.
From 1970 to 2004, greenhouse gas emissions rose to 70%. Moreover, the release of the most effective greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide, increased by 80% in that duration. The current atmospheric carbon dioxide level far exceeds the natural level seen over the past 650,000 years.
Most of the CO2 that people contribute to emitting in the atmosphere is caused by burning fossil fuels, such as natural gas, coal, and oil. Planes, trains, trucks, and cars all burn these fossil fuels, and many electric powerhouses also burn fossil fuels.
◆ Deforestation:
Another way to release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere is by cutting down forests. People do deforestation for two reasons: degrading plant material and trees emit tons of CO2 into the atmosphere. On the contrary, living trees take in carbon dioxide. The gas stays in the atmosphere by decreasing the number of living trees that would have absorbed carbon dioxide.
◆ Animal Husbandry:
Most of the methane in the atmosphere originates in landfills, livestock farming, and the production of fossil fuels, such as natural gas processing and coal mining. Nitrous oxide comes from burning fossil fuels and using agricultural technology.
◆ Animal Husbandry:
Fluorinated gases such as hydrofluorocarbons, hydrochlorofluorocarbons, and chlorofluorocarbons emitted from refrigerators and aerosol cans also contribute to the greenhouse effect.
All of the human activities mentioned above contribute to the greenhouse effect, capturing and trapping more heat energy than average and ultimately causing global warming.
Impacts of the greenhouse effect on global warming
Even a minute increment in average atmospheric temperature can cause massive effects. Perhaps the most apparent and considerable effect is that ice caps and glaciers melt more rapidly than expected. The meltwater flows into oceans, raising sea levels and lowering ocean salt levels.
◆ Melting of Glaciers and Ice Caps: Glaciers and ice sheets retreat and advance naturally. It doesn’t take the earth to be oven-hot for the glaciers to melt. As the global temperature has altered, the ice sheets have shrunk and grown, and the sea levels have risen and fallen.

Primitive corals on land in the Bahamas, Bermuda, and Florida indicate that the sea level was about 5 to 6 meters higher some 13,000 years ago than the current level. Northern summers used to be around 3 to 5 degrees Celsius higher than now during those primitive fossils.
However, global warming is rising at a faster rate than ever before, and the impacts are yet to be determined.
◆ Rise in Sea Level: Global Sea levels are also rising due to the regular glacial melt. Anyhow, scientists have discovered other ways that cause the melting of glaciers even faster. For instance, Chacaltaya has uncovered dark rocks by melting the Bolivian glacier. These rocks absorb radiation from the sun, boosting the melting action.
◆ Recurrent Flood: Increasing Sea levels could cause flooding in coastal regions, displacing an alarming number of people in Florida, the Netherlands, Bangladesh, etc. Such forced displacement affects the people displaced and the areas where these displaced people flee for temporary shelter.
Millions of people depend upon glacial water for irrigation, drinking, and hydroelectric power supply in India, Peru, and Bolivia. A speedy decrease in the glaciers would significantly impact their lives.
◆ Climate Change: Some environmentalists interpret “global warming” as “climate change.” They do so, keeping in mind that the greenhouse effect impacts more than just temperature.
Another impact is the alteration in precipitation, such as snow and rain. Resultantly, precipitation patterns might change and appear more extreme with the advancement of the twentieth century, with rainfall enhanced in the eastern regions of South and North America, central and northern Asia, and northern Europe. However, it has diminished in some parts of southern Asia, the Mediterranean, and Africa.
The way forward
We should take steps to control greenhouse gas emissions and minimize the greenhouse effect to a considerable level. In that case, we can protect our environment from the terrible effects of rapidly increasing global warming.
- Calculating Carbon footprint to estimate annual greenhouse gas emission.
- Changing our diet to prevent forest loss.
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions in industrial and transportation sectors.
- Shift to Non-conventional sources of energy to avoid burning fossil fuels.
- Controlling the use of air conditioners and refrigerators to reduce CFC emissions.
- Daily practice of Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Renew, Recycle.
- Using energy-efficient products.
- Arranging an afforestation program to increase greenery.
- Reducing environmental pollution.
- Traveling with green means of transport, like – bicycles, etc.
⫸ FAQs:
1. What is the Greenhouse Effect?
The Greenhouse Effect occurs when greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, raising the Earth’s temperature. Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane can come from natural sources like volcanoes, but most come from human activities like burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests.
2. How does the Greenhouse Effect work?
The Greenhouse Effect occurs when greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, raising the Earth’s temperature. Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane can come from natural sources like volcanoes, but most come from human activities like burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests.
3. What are greenhouse gases?
Greenhouse gases are gases in the atmosphere that trap heat. The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. Greenhouse gases come from natural sources like volcanoes and human activities like burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests.
4. What is the difference between weather and climate?
Weather is the day-to-day conditions of the atmosphere, such as temperature, precipitation, and wind. Climate is the average weather conditions over a long period. Climate change is a long-term shift in average weather conditions.
5. How do we know the Earth is getting warmer?
There are many ways to measure the Earth’s temperature, including ground-based thermometers, weather balloons, and satellites. Scientists use these measurements to create a global temperature record, which shows that the Earth’s average temperature has risen by about 1.5 degrees Fahrenheit since 1880.
6. How does climate change affect people?
Climate change affects people in many ways, including changes in weather patterns, sea-level rise, and the availability of food, water, and other resources. Climate change can also lead to extreme weather events like hurricanes and floods.