“Whoever sails the North Sea must respect its moods, or the sea will write its own ending.”
The North Sea is often described as unpredictable, unforgiving, and deceptively familiar. We may picture its steel-blue surface stretching quietly toward the horizon, but beneath that seemingly calm façade lies a dynamic marine environment shaped by shallow basins, narrow continental shelves, shifting sandbank formations, dangerous storm surges, and occasional rogue waves capable of slamming into vessels without warning.
So, why do centuries of mariners—from Vikings to modern shipping crews—speak of this sea with a mix of awe and caution? Why do these waters continue to claim lives even in an age of advanced forecasting technology? And how has global climate modeling reshaped our understanding of the North Sea threat profile?
Let’s dive into the science, the history, and the modern implications behind this legendary and dangerous body of water.
Introduction
The North Sea is not the deepest ocean basin on Earth, yet it remains one of the most treacherous maritime zones in Europe. Its complex geography, sudden storm development, and intense tidal range patterns create the perfect cocktail for maritime hazards.
Every year, thousands of shipping routes crisscross the region. And despite modern navigation systems, accidents persist.
- The North Sea hosts over 400 million tons of cargo transport annually.
- Storms in the region can whip wind speeds beyond 60 mph in winter.
- Short-period waves make ship maneuvering extremely difficult.
As we examine what makes the North Sea so deadly, we uncover a story that blends natural science with historical events, human error, and the limits of technology.
Read Also: Why Are the Oceans Blue? The 3 Secrets Behind the Color of the Sea
Where the North Sea Actually Lies
The North Sea occupies a uniquely hazardous geographic position, sandwiched between the United Kingdom, Norway, Denmark, the Netherlands, Germany, and Belgium. Though technically connected to the greater Atlantic Ocean system, the North Sea behaves like a self-contained basin—shallow, semi-enclosed, and structurally constrained by continental shelves. This limited depth prevents wave energy from dispersing properly, creating short, steep wave patterns that challenge navigation and increase the likelihood of rogue waves.
Its southern sector is especially shallow, with large expanses measuring only 20–40 meters deep. These geological characteristics are compounded by sprawling sandbank systems, especially across the Dogger Bank, where depths reduce dramatically. As Atlantic swells push into these shallower regions, the seabed interaction intensifies wave height and accelerates turbulence. The result is a sea where even moderate storms generate hazardous surface conditions.
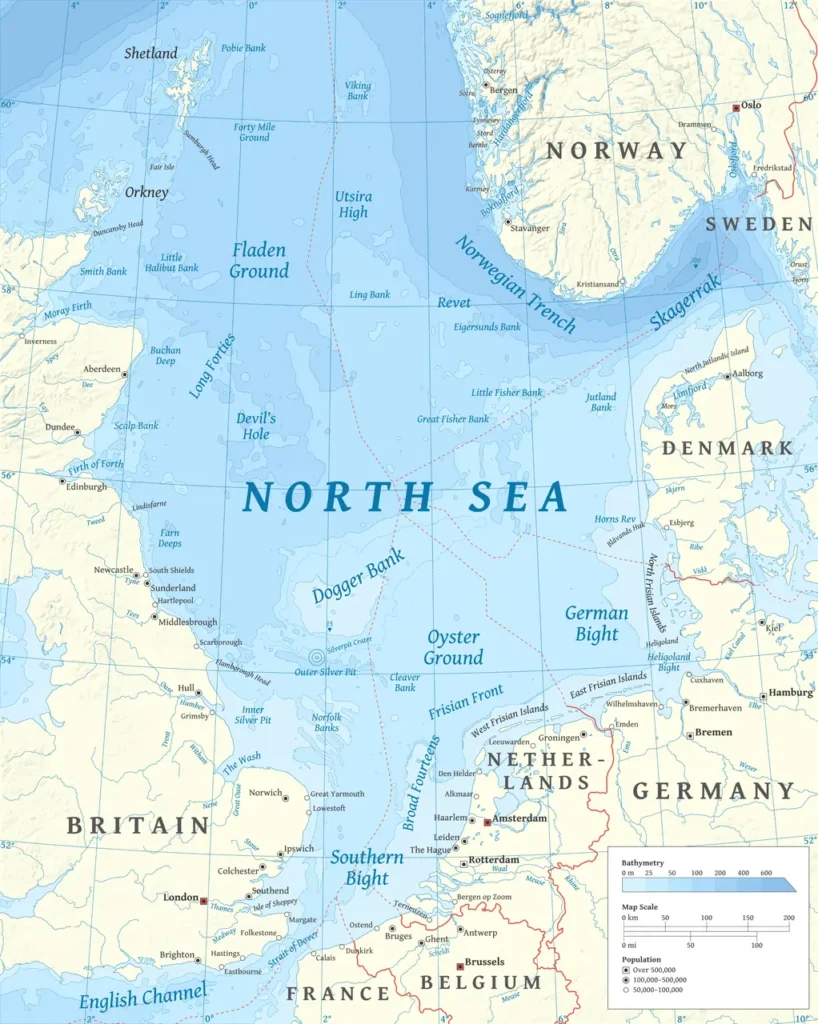
Adding to this complexity is the pronounced tidal range. In areas along the UK and Dutch coasts, tides can reach 5–6 meters, creating strong hydraulic forces and rapidly shifting currents. When powerful storms from the North Atlantic combine with these tidal dynamics, the North Sea becomes highly vulnerable to destructive storm surges. Historical records show that severe surges have reshaped coastlines, breached defenses, and inundated low-lying communities.
This geographical setup—shallow waters, constricted shaping by coastlines, large tidal range, unpredictable swell transfer, and sandbank disruptions—makes the North Sea one of the most scientifically fascinating and operationally dangerous maritime environments in the Northern Hemisphere.
Read Also: 10 Amazing Facts about the Earth’s Oceans
Why Geography Makes the Sea Dangerous
1. Shallow Basin + Narrow Continental Shelves
The North Sea has a unique underwater structure that makes it especially hazardous during high-energy weather events. Unlike deep-ocean basins that absorb wave energy efficiently, the North Sea averages only about 300 feet in depth, and some southern sections drop to less than 100 feet. This shallow structure compresses incoming waves, forcing them to steepen and break more aggressively. When storm surges form, the reduced depth acts as a multiplier: the water has nowhere to disperse, so tide-driven energy intensifies.
The narrow continental shelves around the North Sea further complicate this system. As waves approach land, the water column narrows drastically, leading to increased friction and rapid wave transformation. This is one reason the region experiences unpredictable turbulence and localized rogue waves during winter storms.
Key factors that make this geography dangerous:
- Shallow depth intensifies wave energy during storm surges
- Short wave period makes vessel stabilization difficult
- Narrow shelves amplify turbulence near coastlines
- Steepened waves increase structural impact on ships
The combined effects mean that even moderate atmospheric disturbances can turn dangerous quickly. Every meter of sea-level pressure drop can raise water levels by 10 centimeters, which significantly affects the North Sea because of its shallow basin and tight shelf boundaries.
Read Also: Ocean Relief: 7 Spectacular Features That Shape Our Oceans
2. The Dogger Bank Factor
The Dogger Bank is one of the most important geological features in the North Sea, but it is also one of the most treacherous. This extensive sandbank, stretching roughly 160 miles across the central basin, rises close to the surface—sometimes to depths as shallow as 50–100 feet. While this region was once dry land thousands of years ago, today it acts as a natural wave disruptor.
When waves passing through deeper areas hit the Dogger Bank, their speed changes abruptly due to reduced depth. As a result, turbulence increases, and waves shorten, creating steep, aggressive waveforms that challenge both modern vessels and fishing boats. This can influence rogue wave development because conflicting currents meet above the sandbank, amplifying chaotic patterns.
Why the Dogger Bank is so influential in the North Sea:
- Massive sandbank alters current direction
- Steep wave faces increase capsize risk
- Mixing zones heighten turbulence
- Wind-driven surges interact with shallow slopes
Weather systems frequently funnel through this central zone, meaning storm surges passing over the Dogger Bank often intensify locally. For mariners, radar and sonar tools sometimes misread the changing seabed contour, contributing to sudden instability. In essence, the Dogger Bank turns the North Sea into a dynamic, constantly shifting marine battlefield.
Read Also: Battle Lines for the Blue: COP14 Guidelines Confront Devastating Fishing Practices
3. Depth Variation Across the North Sea
Depth variation across the North Sea plays a critical role in determining how waves behave and how coastal areas respond to extreme weather.
| Region of the North Sea | Average Depth (ft) | Notes |
| Northern Basin | 600–2,000 | Deepest zone, influenced by the Norwegian Trench |
| Southern Basin | 60–200 | Highly navigated, shallow, storm-prone |
| Dogger Bank Area | 40–100 | One of the largest sandbanks causes wave-shortening |
| Coastal Margins | 20–60 | Affected by tides, surges, and sediment shifts |
When deep-water waves travel southward, they encounter shallower terrain, causing rapid energy compression. This leads to short, steep waves that can destabilize vessels. The presence of multiple sandbank systems—including the Dogger Bank, Fladen Ground, and Oyster Grounds—further complicates wave behavior by redirecting currents and increasing turbulence.

Depth-related hazards in the North Sea:
- Southern basin extremely shallow ⇒ higher storm amplification
- Northern basin deeper ⇒ wave energy transfers toward shallow zones
- Sandbanks disrupt flow ⇒ increased rogue wave events
- Variable tidal range interacts differently at different depths
Depth variation also influences sediment transport, making parts of the North Sea prone to sudden seabed shifts. These shifts affect navigation charts and cargo routes. Combined with a strong tidal range, depth variability contributes to unexpected surges, undercurrents, and wave amplification, proving that the North Sea is shaped by both its surface storms and its complex underwater landscape.
Read Also: Square Wave Formation – 6 Facts about the Rare and Dangerous Cross Waves
4. A High Tidal Range That Drives Chaos
The North Sea is notorious for its dramatic tidal range, which can reach 10–20 feet in many coastal zones. This wide swing between high and low tide creates a highly dynamic marine environment that amplifies risk for ships, offshore platforms, and coastal settlements. When storm pressure drops rapidly, the water level in the North Sea rises even higher than predicted, pushing seawater into vulnerable regions. Pair that with shallow basins and shifting sandbank systems, and the result is a volatile combination that can escalate from manageable waves to chaotic surges within hours.
The physics behind this is simple but terrifying. A large tidal range increases the volume of water being displaced every cycle, so any meteorological disturbance—especially winter depressions sweeping across the North Sea—can raise water much faster than evacuation times allow. As the tide peaks, incoming waves shorten and steepen over sandbanks like the Dogger Bank, creating localized turbulence and dangerous wave interference patterns. These sudden shifts increase the risk of rogue waves and unmanageable crosscurrents.
Important Points:
- The North Sea experiences extreme tidal variation between 10–20 ft.
- Shallow basins intensify water displacement.
- Storm surges hit hardest during peak tides.
- Sandbank formations increase unpredictability.
Read Also: How Miami is Battling Sea-Level Rise Due to Climate Change: 6 Strong Strategies
How Tidal Range Interacts With Weather Systems
The tidal range of the North Sea does not operate in isolation—it interacts continuously with prevailing atmospheric systems. When a low-pressure weather front sweeps into the region, it reduces atmospheric pressure on the ocean surface. The resulting “inverse barometer effect” causes the North Sea water level to rise, often by several feet. Add southwest winds pushing water toward the coast, and the heightened tidal range accelerates storm surge formation. Over shallower areas—especially around the Dogger Bank—the incoming water cannot disperse vertically, so it surges horizontally with increased force.
This phenomenon creates hazardous interactions that maritime vessels struggle to stabilize against. Even large cargo ships experience unpredictable lift and drag patterns. When strong wind fields collide with tidal currents, rogue waves become more likely, forming abruptly and violently. The combined influence of weather and tides transforms an already dangerous North Sea into a chaotic system capable of overwhelming even modern engineering.
Key Interaction Factors:
- Low atmospheric pressure magnifies water height.
- Strong winds compress water into narrow channels.
- Shallow water increases lateral wave acceleration.
- Sandbank topography disrupts wave energy distribution.
In summary: Weather instability + wide tidal range = intense storm surges and unpredictable wave patterns in the North Sea.
Read Also: Beyond the Blue: Exploring the 5 Astonishing Layers of the Atmosphere That Protect Our Planet
Why the North Sea Is So Treacherous
1. Storm Surges: The Silent Killer
We often imagine walls of water moving toward shore, but storm surges are more complex. When strong winds push water inland while atmospheric pressure drops, water levels can rise several feet above normal tides.
Historical Surge Events
The North Sea has produced some of Europe’s deadliest coastal disasters:
| Year | Name of Event | Estimated Deaths | Countries Affected |
| 1362 | Grote Mandrenke | 25,000+ | Germany, Denmark |
| 1953 | North Sea Flood | 2,551 | Netherlands, UK |
| 1825 | February Flood | Thousands | Denmark |
These events reshaped coastlines, destroyed villages, and initiated centuries of flood-defense engineering.
Read Also: How Does Climate Change Impact Coastal Ecosystems In The U.S.- 5 Shocking Threats
2. Rogue Waves: Sudden and Unforgiving
Rogue waves are large, spontaneous walls of water that appear without warning. They are particularly dangerous in the North Sea, where wind angles collide unpredictably.
Why Rogue Waves Happen Here
- Short, choppy wave patterns
- Conflicting wind directions
- Interaction with sandbank structures
- Shallow depth amplifying wave energy
Crews often describe being struck by “a house of water” before instruments even detect the event.

3. Winter Storm Season—A Maritime Nightmare
During winter, deep Atlantic depressions sweep into the North Sea, turning it into a hyperactive wave factory.
Windstorms + Narrow Channels = Disaster
- Winds from the southwest force water toward constricted coastlines.
- Pressure drops create setup surges.
- Waves shorten and steepen across the Dogger Bank region.
Read Also: Giants of the Sky: Atmospheric Rivers – Rainfall Heroes or Flood Villains?
Historical Perspective & Human Consequences
Vikings and Early Sailors
To Vikings, the North Sea was a road of opportunity—and a path of danger. Historical sagas describe sudden storms sweeping away entire fleets.
Why Early Navigation Struggled
- No forecasting tools
- Limited hull design
- Heavy reliance on sky visibility
- Primitive understanding of tides
The Middle Ages and Coastal Tragedies
Medieval towns along Germany and the Netherlands were repeatedly wiped out by storm floods. Many simply disappeared from maps.
Land Loss and Cultural Memory
The North Sea swallowed entire settlements, leaving folklore and ghost-town remains embedded in coastal identity.
Modern Shipping & Offshore Risks
Today, tankers, fishing vessels, offshore oil rigs, and wind farms populate the North Sea. Yet danger persists.
High Human Exposure Means High Accident Probability
- Heavy shipping congestion
- Complex wave physics
- Equipment fatigue
- Sudden fog events
Read Also: Mysteries of the Deep: Recent Discoveries from Ocean Expeditions
The Future of the North Sea
Changing Climate Patterns
The North Sea is entering a transformative era, and emerging climate models suggest patterns that demand our full attention. As global temperatures rise, the North Sea is projected to experience stronger storm systems, even if the overall number of storms remains consistent. Warmer oceans feed atmospheric instability, increasing wind intensity and producing more violent wave action. This creates a higher likelihood of rogue waves, especially in areas shaped by shallow depths and shifting sandbank formations such as the Dogger Bank.
Amplified Storm Surges
Amplified storm surges are another critical concern. A NOAA-backed study indicates that even a one-foot rise in baseline sea level can triple the risk of damaging coastal floods in shallow regions like the North Sea. When combined with its naturally high tidal range, these surges can push water several miles inland, affecting millions living in nearby coastal communities.
Impact on Fishing and Shipping Routes
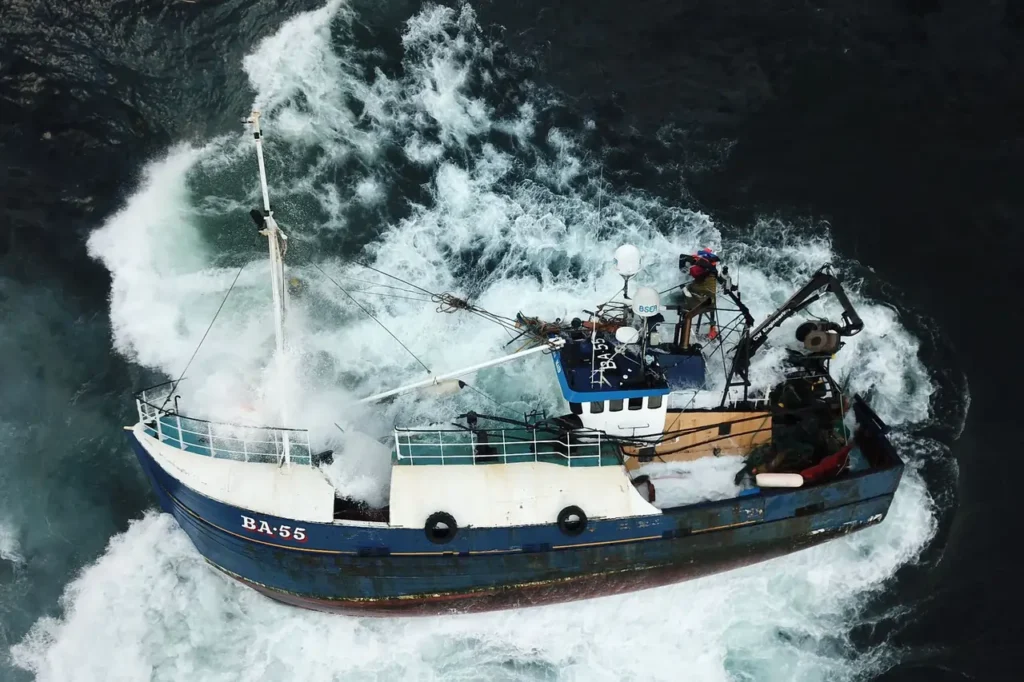

Economically, the implications are far-reaching. Fishing fleets operating across the North Sea will increasingly face shortened weather windows and unpredictable wave patterns. Shipping routes may require rerouting during winter months, leading to higher operational costs. Offshore wind farms—now essential to regional energy supply—will need reinforced structural designs to withstand future North Sea conditions defined by stronger winds, higher tides, and more volatile wave behavior.
Respecting the Sea: What We Can Learn
Respecting the North Sea begins with acknowledging how its physical structure and shifting conditions shape risk. When we study the North Sea, we recognize that shallow depth, wind-driven turbulence, and the presence of major sandbank systems—especially near the Dogger Bank—combine to produce unstable surface patterns. Strong winds interacting with limited depth intensify wave energy, while a wide tidal range increases water movement along coastal margins. These elements create the perfect environment for dangerous storm surges and unexpected rogue waves, both capable of overwhelming vessels and coastal defenses.
Read Also: Dark Oxygen Discovered below 10,000ft: An Oceanic Secret Revealed
Key Takeaway
The North Sea is not hazardous because of its overall size, but because its geography and atmospheric behavior intersect in ways that amplify risk. Understanding these factors allows navigators, engineers, and communities to assess hazards with greater clarity and plan safer maritime operations across the North Sea.
Conclusion
The North Sea stands as one of the most scientifically fascinating and historically impactful bodies of water on Earth. We’ve watched it shape coastlines, influence economies, claim ships, and challenge every era’s technology. Its waters may appear calm on a summer morning, but its true nature lurks beneath: shallow, volatile, wind-whipped, and shaped by thousands of years of atmospheric and geological interaction.
As we continue to study weather systems, ocean physics, and coastal risk, we gain deeper respect for what early mariners already knew: an underestimation of the North Sea can be fatal.
Understanding this sea—its past, present, and future—is our best strategy for staying safe and honoring the lives and stories woven into its turbulent waters.
FAQs
1. Why is the North Sea considered one of the most dangerous seas?
The North Sea has shallow depths, strong winds, short wave periods, and volatile weather systems. These combine to generate unpredictable, hazardous conditions that challenge ships and coastal communities.
2. What causes storm surges in the North Sea?
Storm surges form when low atmospheric pressure and high winds push water toward coastlines. The North Sea’s shallow structure and narrow basin amplify these impacts, creating dangerous flooding.
3. Can rogue waves occur in the North Sea?
Yes, rogue waves occur when opposing wind directions, short-period waves, and sandbank interactions collide. This makes spontaneous, large waves more likely to form without warning.
4. What is the Dogger Bank, and why is it important?
The Dogger Bank is one of Europe’s largest sandbank systems. It affects wave dynamics, causing waves to steepen and shorten, making navigation risky for vessels passing over it.
5. How is climate change affecting the North Sea?
Climate change is intensifying storms, altering tides, and increasing sea levels. These shifts worsen storm surges and coastal flooding throughout the North Sea region.





