Introduction to Urbanization
Urbanization is the framework by which many people become habituated to stay in a small area that turns into a city. The definition constitutes a city that transforms from time to time, varies between places, and could be demonstrated more by demographics.
As cities expand at an unprecedented rate, the pressing question arises: Why is Urbanization Contributing to Pollution, and what are the long-term impacts on our environment?
Understanding Why Urbanization Contributing to Pollution involves exploring the rapid growth of urban areas and the accompanying increase in pollution levels. Urbanization leads to higher emissions from vehicles, industrial activities, and construction while also straining waste management systems and natural resources.
This article delves into why urbanization contributes to pollution and examines the environmental consequences. By addressing these critical issues, we can develop strategies to mitigate pollution and create more sustainable urban environments.
Factors of “Why Urbanization Contributes to Pollution“:
● Overpopulation:
- The ecosystem faces many challenges. There is a massive demand for land, which is being cleared up due to agriculture and urbanization. This is leading to endangered species and complications in natural cycles. In addition, overpopulation adds pollution that degrades the effects of climatic change.
- The vast consumption and generation of waste materials is linked to a larger population, destroying the waste management system and contributing to air, water, and soil pollution. The rising demand for energy leads to a massive amount of carbon release, adding to more global warming and its linked consequences. It also introduces several social and economic threats. Massive population levels lead to overcrowded cities and educational systems.
● Urban Slums and Squatter Settlements:
Slums face two challenges: two kinds of settlements. One of the new millenniums is rapid urbanization and urbanization of poverty. About one billion people, or 32 percent, live in slums, most of them in developing areas.
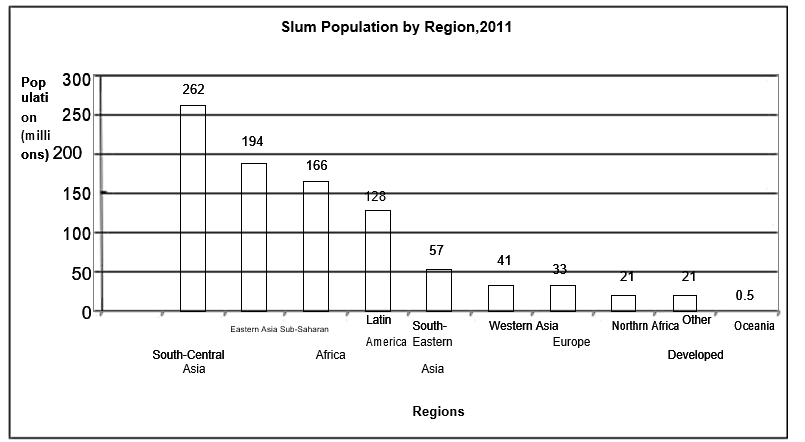
Most people in slums live under the threat of well-being and survival issues as they lack several benefits, including access to clean water, improved sanitation offerings, many living spaces, a framework of quality, and tenure security. In the upcoming period, the slum population will rise by about 2 billion globally.
Environmental Impacts of Urbanization:
● Land Use and Deforestation:
Urban areas are particular sectors of air pollution that include particulate matter, nitrogen, sulfur, and other organic substances; these pollutants are introduced into the environment by the emission of vehicles, industrial activities, and energy production.
Higher amounts of pollutants in urban areas destroy air quality, harm vegetation, destroy building materials, and influence climate change. They also degrade the quality of the soil by destroying waste management initiatives and other economic activities. Urban areas face deforestation due to land demands and challenges with safely managing and disposing waste.
● Fossil Fuels and Energy Consumption:
Another source of environmental destruction is fossil energy consumption. Due to urbanization, the demand for fossil fuels is increasing, and various nations depend upon these non-renewable energy sources.

According to the International Energy Agency, the total energy used per unit of economic activity in 2018 was calculated to be about 1.2 improvement. British Petro statistics recorded that coal consumption rose more than six times in Vietnam and around three to four times in other Southeast Asian nations.
Disease caused by urban pollution:
- Respiratory diseases: Air pollution affects the lungs and increases emphysema and other respiratory diseases. PM and nitrogen are associated with chronic bronchitis.
- Cancer: A large study of more than 57000 women who were found staying near major roads might increase the risk for breast cancer. Exposure to benzene, an industrial component, is associated with non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Fine particulate matter may harm the blood vessels and may pace up the calcification in arteries.
Solutions and Mitigation Strategies:
● Use Renewable Energy Sources:
Renewable energy sources, like solar, wind, hydel, geothermal, and tidal power, offer a cleaner, sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. These sources will never run out. They are natural and genuine but have primarily low or zero carbon footprints. Unlike fossil fuels, they have significant benefits, including a plentiful supply and no harmful emissions.

● Sustainable Urban Planning:
The main target of sustainable urban development is to maintain a balance between human development and environmental safeguarding. In doing so, cities can ensure people are healthy, safe, protected, and living in good conditions. The last decade has seen a change in urban planning, and proper decisions are being made.
● Addressing Climate Change:
Climatic changes caused by carbon emissions have drawn attention worldwide. The constant rise in temperature, the urban heat island effect, and water shortages affect urbanization.
Global warming has worsened extreme weather conditions, including heat waves. Multiple issues introduced by humans are causing climatic changes, degrading the air, water, and soil quality.
Conclusion:
Understanding why urbanization contributes to pollution is crucial as cities grow and evolve. The rapid expansion of urban areas increases emissions from vehicles, industrial activities, and construction, significantly contributing to pollution levels. Additionally, urbanization strains waste management systems and depletes natural resources, further exacerbating environmental issues.
We can identify key factors driving this trend by addressing why urbanization contributes to pollution and developing effective strategies to mitigate its impact. Sustainable urban planning, improved public transportation, and enhanced waste management practices are essential in reducing pollution. Recognizing these issues’ significance helps us create healthier and more sustainable cities, ensuring a better quality of life for future generations.
Call to action:
- Join the conversation on why urbanization Contributes to pollution.
- Raise awareness and support sustainable urban development.
- Advocate for green policies and innovative solutions to reduce pollution.
Together, we can build healthier, more sustainable cities for future generations. Let’s take action now!
FAQ’s:
What are the main ways urbanization contributes to pollution?
Urbanization contributes to pollution primarily through increased vehicular emissions, industrial activities, and construction. The growth of cities leads to higher energy consumption, resulting in more fossil fuel burning. Additionally, urban sprawl strains waste management systems, leading to improper waste disposal and increased air, water, and soil pollution.
How does urbanization affect air quality?
Urbanization affects air quality by increasing emissions from vehicles, industries, and construction activities. Concentrating these pollution sources in urban areas leads to higher levels of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and other harmful pollutants. Poor air quality causes respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and other health issues in urban populations.
What role does transportation play in urban pollution?
Transportation is a major contributor to urban pollution. The high density of vehicles in urban areas results in increased emissions of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons. Traffic congestion exacerbates the problem by causing idling and stop-and-go driving, which increases fuel consumption and emissions. Public transportation, cycling, and walking can help mitigate these effects.
How does urbanization impact water pollution?
Urbanization impacts water pollution through runoff from impervious surfaces like roads, sidewalks, and buildings, which carry pollutants such as oil, heavy metals, and chemicals into water bodies. Industrial discharges and untreated sewage also contribute to water pollution. This contamination can harm aquatic ecosystems, reduce water quality, and pose fatal health risks to humans and wildlife.
Can urbanization contribute to soil pollution?
Yes, urbanization can contribute to soil pollution. Construction activities, industrial processes, and improper waste disposal introduce contaminants like heavy metals, chemicals, and plastics into the soil. These pollutants can affect soil health, reduce agricultural productivity, and enter the food chain, posing risks to human health and the environment.
What measures can be taken to reduce pollution caused by urbanization?
To reduce pollution caused by urbanization, cities can implement several measures:
● Promote public transportation, cycling, and walking to decrease vehicular emissions.
● Adopt green building practices to minimize construction-related pollution.
● Implement regulations to control industrial emissions and promote cleaner production technologies.
● Increase green spaces and urban forests to improve air quality and provide environmental benefits.





