“The universe is under no obligation to make sense to you.” ― Neil deGrasse Tyson
That brevity captures the awe we feel as we peer across billions of light-years. But every so often, the universe unloads a surprise so striking it forces us to rewrite cosmic history. The Alaknanda Galaxy is one such surprise.
Introduction — Could the Early Universe Build Milky Way-Like Galaxies So Quickly?
What if I told you that a spiral galaxy nearly identical to the Milky Way existed when the universe was barely 10% of its current age? That’s not a hypothetical — that’s the reality posed by the Alaknanda Galaxy. Astronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) recently identified this mature, grand-design spiral galaxy as it appeared roughly 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang — a time when most models forecast only small, irregular, and disordered star systems.
This discovery challenges long-held beliefs about galaxy formation and the timeline of cosmic structure development. In this article, we explore five shocking reasons why Alaknanda is more extraordinary than scientists expected — and what that means for our understanding of the early universe.
Read Also: Top 10 Latest Astronomical Discoveries in March 2025
What Is the Alaknanda Galaxy?
Alaknanda Galaxy is a massive, well-formed spiral galaxy identified using JWST data by researchers at the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics (NCRA–TIFR) in Pune, India.
Key facts:
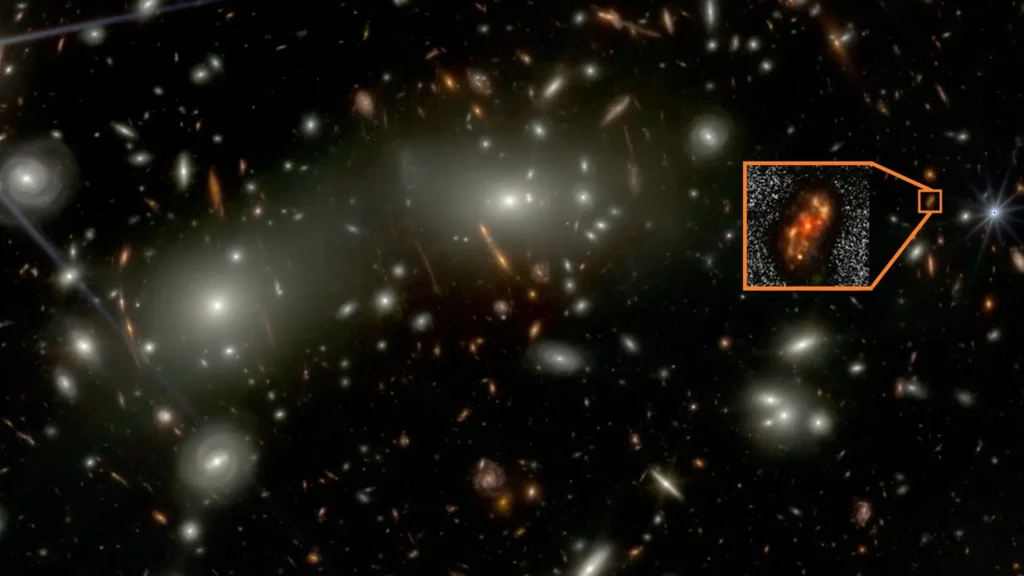

- Its photometric redshift corresponds to a time when the universe was only about 1.5 billion years old — much younger than the present age of ~13.8 billion years.
- It shows a grand textbook spiral structure: two sweeping spiral arms wrapping around a bright central bulge, strikingly similar to our own galaxy.
- Its diameter is roughly 30,000 light-years — smaller than the Milky Way’s ~100,000 light-year span, but large enough to signal a mature, well-organised disk.
Given these characteristics, Alaknanda stands out as one of the earliest known large spiral galaxies — essentially a cosmic baby version of the Milky Way.
Read Also: Mysterious Phenomenon at the Heart of the Milky Way Hints at a New Dark Matter Suspect
5 Shocking Reasons Why Alaknanda Defies Expectations
1. It’s Archaeologically Ancient — Yet Structurally Mature
Conventional wisdom held that early galaxies — especially those forming soon after the Big Bang — would be chaotic: irregular clumps of stars and gas, unsettled and turbulent. It was assumed that large spiral galaxies require billions of years to assemble, cool, rotate, and settle into a stable disk.
But Alaknanda flips that assumption — showing a textbook spiral galaxy structure at a very early cosmic epoch. Its well-defined arms and central bulge suggest that large-scale structural organization was possible far sooner than most models allowed.
This alone forces astronomers to reconsider when and how the first “mature” galaxies emerged.
Read Also: Ghost In The Cosmos: The Challenging Discovery of Nube, the Dwarf Galaxy
2. Rapid Star Formation — A Stellar Factory in Overdrive
One reason Alaknanda’s disk could form so quickly is its high star-formation rate. Observations indicate it was producing stars at a rate far higher than typical galaxies we see in the present-day universe.
Moreover, much of its stellar population may have formed in a relatively short timeframe — meaning Alaknanda didn’t just assemble mass slowly over eons: it experienced intense, rapid stellar birth cycles that filled its disk early. This rapid formation helps explain how a stable, rotating spiral could arise so soon after the Big Bang.
Read Also: How Many Stars Are In Our Solar System? 1, 2, or More? Discover the Cosmic Mystery!
3. Size & Mass — A Grand Spiral With Significant Stellar Mass
Despite its youth, Alaknanda appears to be massive. The published research estimates a stellar mass of the order of log(M∗/M⊙)≈10.2.
Translated, that means billions of Suns worth of stars — forming a galaxy with real heft. Its diameter (~30,000 light-years) is modest compared to the Milky Way, but it is still large for such an early epoch. The combination of a well-built disk, decent mass, and coherent structure implies a fully mature, settled system — not a transient clump.

This defies the expectation that early universe galaxies would be small, immature, or chaotic — instead showing that sizeable, disk-dominated, spiral-galaxy scale systems already existed when the universe was young.
4. Disk Stabilization & Spiral Arms — Incredibly Efficient Galactic Physics
Forming a grand-design spiral — with symmetric arms and a rotating disk — requires certain physical conditions: a stable, rotating disk; efficient cooling of gas; enough angular momentum; relatively low disturbance from major mergers; and a gradual build-up so that density waves can impose spiral patterns.
That such a configuration could emerge when the universe was only 1.5 billion years old means galactic physics operated far faster and more efficiently than our models predicted.
Essentially, the processes of gas accretion, cooling, disk formation, angular momentum conservation, and density wave propagation must have aligned perfectly — and early. Alaknanda’s structure suggests that under the right conditions, galaxy formation pathways can accelerate.
Read Also: Recently Identified Nebula by NASA – 10 Amazing Discoveries
5. Revision of Galaxy Formation Theory: The Cosmic Timeline Needs Rewriting
Perhaps the most sweeping consequence is theoretical. Alaknanda forces a rethink of when and how spiral galaxies — and by extension, disk galaxies — emerged in the universe. If such a mature spiral existed only ~1.5 billion years after the Big Bang, then the timeline for galaxy formation and galactic evolution must be adjusted.

Early-universe conditions — once thought too chaotic for orderly structures — might have permitted rapid formation of large, stable, disk-dominated galaxies. This may imply that there are many more such galaxies waiting to be discovered, hidden in the depths of cosmic time.
Read Also: How many solar systems are in the milky way galaxy
Table 1: Alaknanda vs What We Expected
| Property | Typical Expectation for Early Universe (≤2 Gyr post-Big Bang) | What Alaknanda Shows |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Irregular, clumpy, turbulent — no ordered disk or arms | Full grand-design spiral with two arms + central bulge (clear disk) |
| Stellar Mass | Relatively low mass — small proto-galaxy or dwarf-scale | Stellar mass ≈ 10^10.2 M⊙ — substantial galaxy-scale mass |
| Star Formation | High but chaotic and unsustained | Sustained, rapid star formation — efficient disk building |
| Disk Stability | Unlikely — too much turbulence & merging expected | Stable rotating disk, allowing spiral arms to form and persist |
| Timeline for Spiral Galaxy Emergence | Several billion years after Big Bang | Spiral present by 1.5 billion years post–Big Bang |
How Could Alaknanda Form So Fast? — Possible Explanations
When we ask how Alaknanda could achieve such maturity so early, a few ideas emerge, each with interesting implications for cosmic history:

- High Gas Accretion Rates + Efficient Cooling — If the early universe provided abundant cold gas inflows, a galaxy could accumulate mass fast, cooling and settling into a disk more quickly than typical models assume. This would speed up disk formation and enable spiral structure.
- Low Merger Environment / Calm Neighborhood — Perhaps Alaknanda grew in a region with fewer violent collisions. Without disruptive mergers, its disk could remain undisturbed long enough to stabilize.
- Early Angular Momentum Consolidation — The conservation and alignment of angular momentum (from inflowing gas and dark matter halo spin) might have been efficient, helping to build a smoothly rotating disk early on.
- Rapid Star Formation Triggered by Density Waves — Once a disk forms, density waves can organize star formation along spiral arms. If conditions allowed early disk formation, those processes could start soon after.
Each of these factors (or a combination) may explain Alaknanda’s unexpected maturity — but they also challenge and complicate existing galaxy formation models.
Read Also: Andromeda Galaxy: definition, Facts, distance, location
The Significance of Alaknanda Galaxy for Modern Astronomy
The discovery of the Alaknanda Galaxy has a ripple effect across how we interpret the early universe — touching on galaxy formation, cosmic evolution, and even the potential for early planet or star-system formation. Here’s why it matters:
- It pushes back the earliest epoch at which organized spiral galaxies could exist — meaning our cosmic timeline for galaxy formation must shift.
- It suggests that large, massive galaxies could have assembled far earlier than previously thought — reshaping statistics on galaxy population in the early universe.
- It offers a new window into disk dynamics, star formation, and galactic physics under early-universe conditions. Studying Alaknanda and similar galaxies may help refine models of galaxy formation and evolution.
- It raises the possibility that other mature galaxies from the early universe remain undetected — awaiting discovery with advanced telescopes like JWST.
In short: Alaknanda is not just a one-off oddity — it may be a sign that the early universe was more prolific and structured than we ever imagined.
Read Also: Surprising Secrets: Lesser-known facts about planets and moons
What Are the Unanswered Questions — Mysteries Still to Solve?
Despite its remarkable features, Alaknanda Galaxy leaves many questions open. Among them:
- What was the environment around Alaknanda? Did it live in a low-density region with few mergers, or was it shaped by interactions we can’t yet detect?
- How did its angular momentum evolve — was it inherited from the cosmic web, or built up via gas inflow?
- Are there many more such early spirals waiting to be found, or is Alaknanda a rare cosmic anomaly?
- What does its star formation history look like in detail — was its starburst early and rapid, or ongoing over hundreds of millions of years?
- Could such galaxies host planet formation and older chemical evolution — meaning planets (or at least metal-rich environments) might have existed far earlier than we generally assume?
Answers to these questions will shape the next generation of cosmic theories.
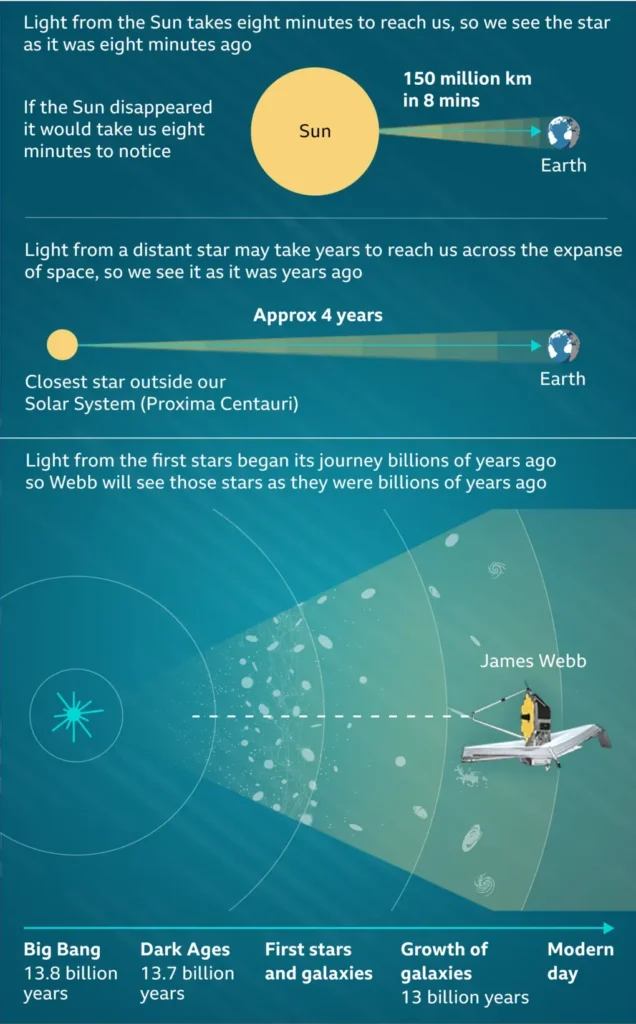
Read Also: When will the Andromeda and Milky Way Galaxy Collide
Key Takeaway
The discovery of the Alaknanda Galaxy shows that large spiral galaxies — complete with rotating disks and spiral arms — could form in just 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang. That overturns long-held assumptions about galaxy formation timelines, pushing astronomers to rethink how quickly cosmic structure evolved, and how many early-universe galaxies still await discovery.
Conclusion — A Cosmic Revelation Worth Watching
As a cosmic thought experiment: imagine finding a fully built cathedral in a newborn city — grand, complete, and fully functional — when everyone expected only huts. That’s what the Alaknanda Galaxy represents. It is a majestic, well-structured spiral galaxy that emerged far earlier than conventional wisdom allowed.
For us — astronomers, science communicators, cosmic dreamers — Alaknanda is a wake-up call. It reminds us that the universe still holds surprises, that our models are only as good as the data we feed them, and that with every leap in observational power, we must remain ready to be astonished.
It may turn out that Alaknanda is not alone — that deep in the cosmic past, the universe built more mature galaxies earlier than we imagined. As we scan the heavens with telescopes like JWST, we may soon find a population of such early spirals, forcing us to rewrite cosmic history yet again.
In the dance of stars, gas, gravity, and time — Alaknanda shows us that sometimes, the universe moves faster, builds stronger, and surprises harder than we ever dared hope.
References & External Links
- R. Jain, Y. Wadadekar, A grand-design spiral galaxy 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang with JWST, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2025).
- Press release: Alaknanda: JWST discovers massive grand-design spiral galaxy from the universe’s infancy, NCRA–TIFR.
- “Alaknanda: Galaxy that surprised scientists with its age”, UniverseMagazine.
- “Where is Alaknanda, Milky Way galaxy’s newly discovered twin sister?”, India Today Science Desk.
FAQs
1. Is the Alaknanda Galaxy a real observation or a theoretical model?
Yes — Alaknanda is a real astronomical observation, not a simulation or hypothetical model.
2. How far away is the Alaknanda Galaxy from Earth?
Alaknanda is located about 12 billion light-years away, meaning we see it as it was 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang.
3. Does Alaknanda resemble our Milky Way Galaxy?
Structurally, yes — it has a well-defined disk, central bulge, and two sweeping spiral arms, much like the Milky Way.
4. Why is Alaknanda’s discovery so significant for galaxy formation theories?
Because it demonstrates that a large, organized spiral galaxy could form far earlier than current models predict — forcing a re-evaluation of how quickly galaxies mature.
5. Could there be more galaxies like Alaknanda hidden in deep space?
Yes — the discovery implies that many more mature, early-epoch spiral galaxies may exist, possibly waiting to be unveiled by advanced telescopes.





