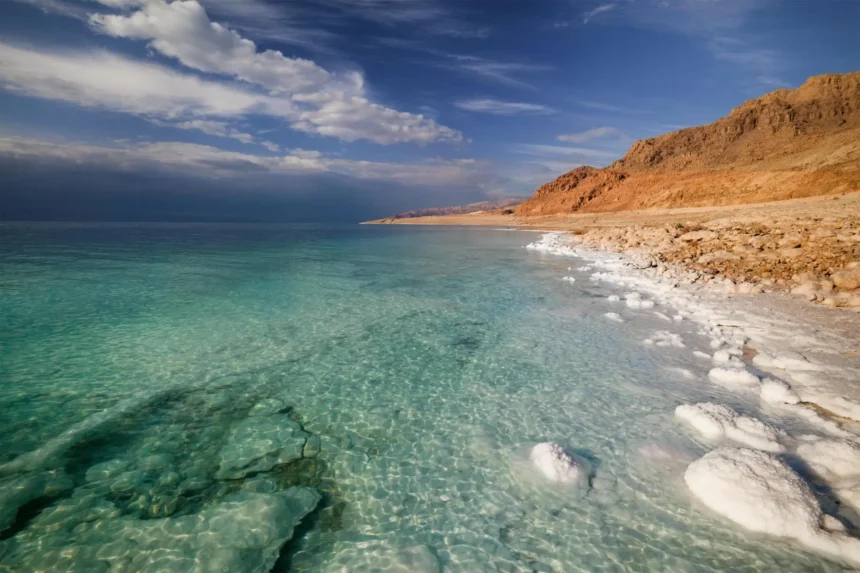
Forget expensive spa treatments. The Dead Sea, where you float effortlessly, where the mud heals your skin, and where no fish could ever survive with its mineral-rich waters and buoyant salinity, offers a unique and powerful wellness experience found nowhere else.
⫸ Introduction
The Dead Sea is a natural phenomenon that intrigues scientists and travelers alike. This hypersaline lake, located between Jordan and Israel, is Earth’s lowest point on land. But what exactly is the Dead Sea, and why does it have this unusual name?
What is the Dead Sea?
The Dead Sea is a landlocked salt lake with a nearly ten times higher salinity than the ocean. This extreme salt concentration prevents most aquatic life from surviving, leading to its name. Its unique location in the Jordan Rift Valley and hot, arid climate contribute to its extraordinary characteristics.

⫸ A Brief Overview of the Dead Sea's Unique Properties
The Dead Sea isn’t just a lake; it’s a phenomenon. This landlocked salt lake boasts a collection of characteristics that make it unlike any other body of water on Earth. Here’s a glimpse into what makes the Dead Sea so extraordinary:
- Hypersalinity: The Dead Sea’s salt concentration is about ten times higher than typical ocean water. This extreme salinity results from its closed basin, high evaporation rates, and mineral-rich inflows.
- Buoyancy: The Dead Sea’s high salinity makes it incredibly dense, allowing you to float effortlessly on the surface. This makes for a memorable and enjoyable experience.
- Mineral-Rich Composition: The Dead Sea isn’t just salty; it’s a concentrated cocktail of minerals like magnesium, calcium, potassium, and bromides. These minerals are believed responsible for many of the Dead Sea’s purported therapeutic benefits.
At what elevation is the Dead Sea?
The Dead Sea is the lowest land-based elevation on Earth. Its surface and shores are approximately 430 meters (1,412 feet) below sea level.
How deep is the Dead Sea?
The Dead Sea’s depth reaches a maximum of around 306 meters (997 feet), making it one of the world’s deepest hypersaline lakes.
Can you swim in the Dead Sea?
Traditional swimming isn’t possible in the Dead Sea due to its extreme buoyancy. However, you can’t sink! The high salt content allows you to float effortlessly on the surface, creating a unique and relaxing experience. Be cautious, as the high salt content can irritate eyes and open cuts.

⫸ Location and Geography
The Dead Sea has a unique geographical position, straddling borders and nestling within a fascinating geological formation. Let’s pinpoint its location and explore the natural forces that shaped it:
In which country is the Dead Sea?

The Dead Sea doesn’t belong to a single country. Its eastern shore borders Jordan, while its western shore is shared between Israel and the Palestinian West Bank.
Jordan Rift Valley Formation
The Jordan Rift Valley is a classic example of a continental rift zone. These zones form at the boundaries where tectonic plates, the giant slabs that makeup Earth’s crust, are pulling apart.
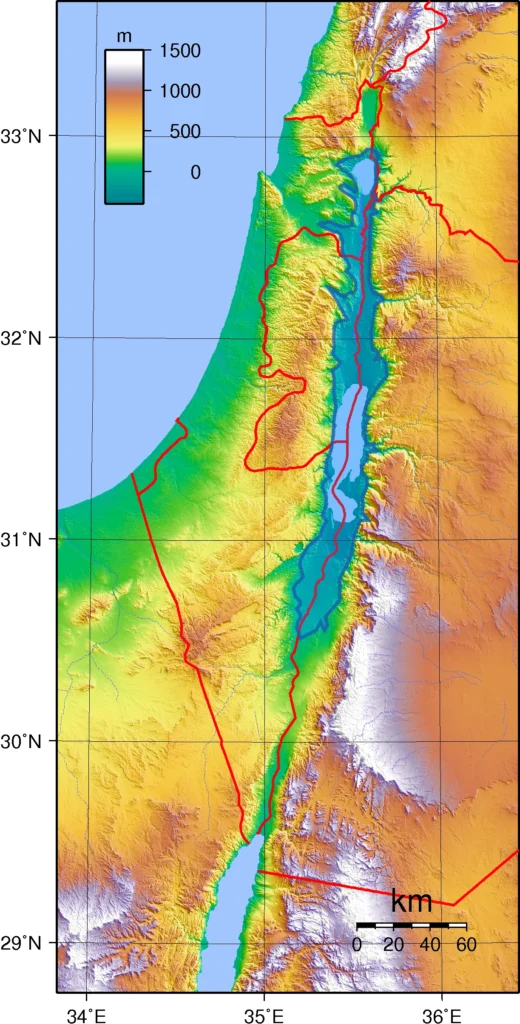
- In this case, the African and Arabian tectonic plates are slowly separating. The land between them subsides as they do, creating a long, deep depression.
- The Dead Sea Transform (DST) runs along the Jordan Rift Valley and is the specific fault line responsible for much of its creation. This is a strike-slip fault, where the plates primarily slide past each other horizontally.
- Over millions of years, this ongoing plate movement formed the Jordan Rift Valley. The Dead Sea sits in the lowest part of this rift, about 430 meters (1410 feet) below sea level, making it Earth’s lowest point on land.
⫸ Why is the Dead Sea so Salty?
The Dead Sea isn’t just salty; it’s one of the saltiest bodies of water on the planet. This extreme salinity arises from a unique combination of geography, climate, and geology.
Salinity Levels Compared to the Ocean
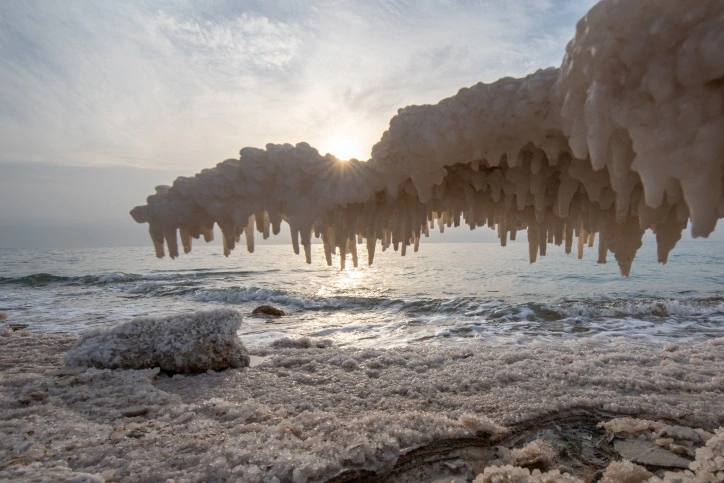
The Dead Sea’s salinity is about 34%—nearly ten times saltier than regular ocean water, with about a 3.5% salt concentration. This makes it almost impossible to sink into the Dead Sea!
Chemical Composition (Minerals)
The Dead Sea’s salt isn’t just regular table salt (sodium chloride). It contains a rich cocktail of minerals, including:

- Magnesium
- Calcium
- Potassium
- Bromides
- Sulfates
Factors Contributing to High Salinity
- Evaporation: The hot, arid climate surrounding the Dead Sea leads to high evaporation rates. As water evaporates, the salts get left behind, becoming increasingly concentrated.
- Lack of Outlet: Typical lakes and seas have rivers flowing out of them, carrying salts away. The Dead Sea is a terminal lake, meaning it has no outlet. The only way for water to leave is through evaporation, increasing salinity.
- Mineral-Rich Inflow: Rivers like the Jordan River carry dissolved minerals into the Dead Sea, replenishing its salt content.
Why is the Dead Sea Called the Dead Sea?
The Dead Sea gets its name because its extreme salinity makes it impossible for most fish or aquatic plants to survive. However, it does support unique extremophile microbes adapted to its harsh conditions.
⫸ Is there any life in the Dead Sea?
The Dead Sea’s name might suggest a barren wasteland, but the truth is more nuanced. While its extreme salinity creates harsh conditions, life still finds a way to persevere in surprising forms.
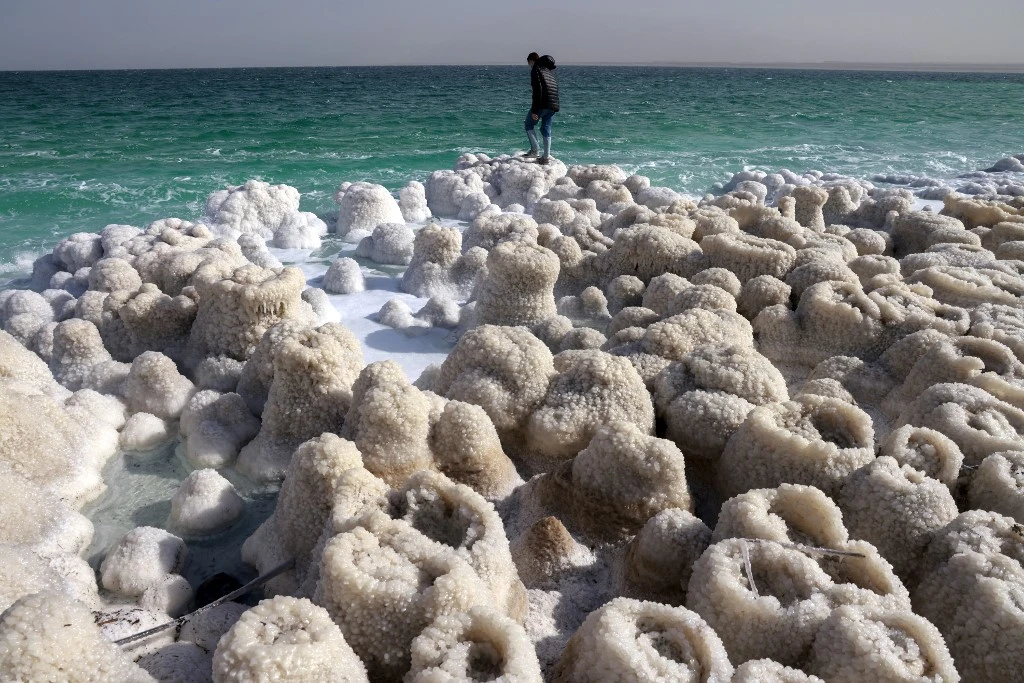

The Dead Sea animal
Traditional animals, as we know them, cannot survive in the Dead Sea. The high salt content puts immense stress on their bodies.
The Dead Sea fish
Fish are similarly unable to tolerate the Dead Sea environment. Any fish that stray in from the Jordan River or other freshwater sources quickly perish.
Lack of aquatic plants
The Dead Sea’s hypersaline water also prevents most aquatic plants’ growth. There won’t be fields of seaweed or other underwater vegetation here.
Unique extremophile microorganisms
Despite the challenges, the Dead Sea is still alive. Hardy microorganisms called extremophiles have adapted to extreme conditions. These include types of bacteria and archaea, single-celled lifeforms with unique survival strategies.
⫸ History and Cultural Significance
The Dead Sea isn’t just a geographical marvel – it’s a place steeped in history and echoes of ancient civilizations. Let’s delve into its rich past:
Biblical References
The Dead Sea is featured in various stories in the Bible. It’s associated with the cities of Sodom and Gomorrah, and many believe the caves near its shores were where the famed Dead Sea Scrolls were hidden. The prophet Ezekiel even foresaw the Dead Sea’s waters becoming fresh and teeming with life.
Historical Civilizations Surrounding the Dead Sea
Various civilizations, from the ancient Egyptians to the Nabateans and Romans, recognized the Dead Sea’s value. These groups built communities around it, drawn by its unique resources and strategic location. Remnants of fortresses, like Masada, still stand as testaments to the region’s turbulent history.

Ancient Uses (Mineral Extraction)
The Dead Sea has long been a source of valuable minerals and resources. The ancient Egyptians likely used its asphalt for mummification and harnessed the therapeutic benefits of Dead Sea salts and mud. The Nabateans traded these valuable resources along regional routes.
⫸ 5 Surprising Health Benefits of This Salty Wonder
The Dead Sea might have an uninviting name, but this incredibly salty lake offers many health and wellness benefits. Its unique mineral composition and high salinity work together to provide potential relief for various conditions. Let’s explore how the Dead Sea can be a natural health ally:
1. Skin Soother: The Dead Sea’s minerals, like magnesium, potassium, and calcium, are like balm for troubled skin. Research suggests Dead Sea mud and salt baths can significantly improve conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and atopic dermatitis. These elements reduce inflammation, boost skin hydration, and strengthen the skin’s natural barrier.
2. Arthritis Relief: The Dead Sea can offer relief to those who suffer from arthritis and related joint pain. Floating in its buoyant waters reduces joint stress, while the minerals help decrease inflammation and improve mobility.
3. Respiratory Aid: The air surrounding the Dead Sea is unique due to its low pollen count, high atmospheric pressure, and mineral-rich composition. This environment could benefit people with respiratory conditions like asthma, potentially reducing symptoms and aiding breathing.
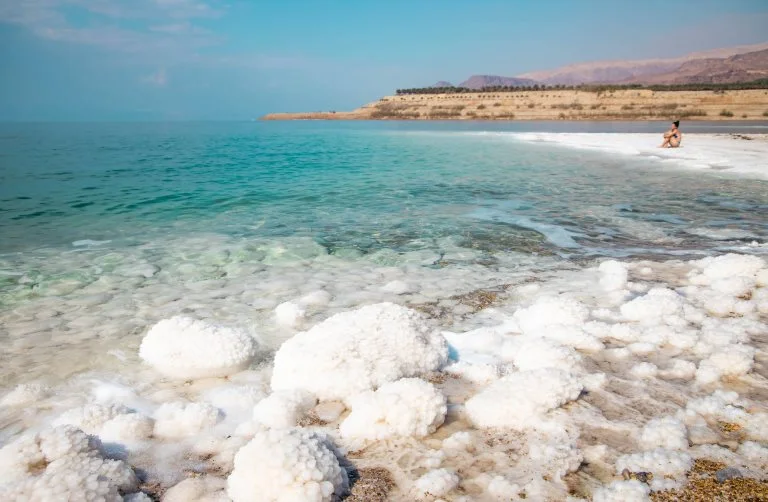

4. Stress Buster: The Dead Sea’s environment is inherently relaxing. The mineral-rich waters, effortless floating, and serene surroundings create a powerful stress-reducing effect. This can translate to better mood, decreased stress hormones, and improved sleep quality.
5. Anti-Aging Potential: The Dead Sea’s minerals are natural antioxidants that help protect against free radical damage, a significant factor in skin aging. Regularly using Dead Sea mud masks and skincare products might help minimize fine lines and wrinkles and promote a youthful complexion.
⫸ The Dead Sea Today
The Dead Sea remains a place of both wonder and concern. While it’s a major draw for tourism and wellness seekers, environmental challenges and conservation efforts underscore the need for a careful balance.
Tourism and Health Spas
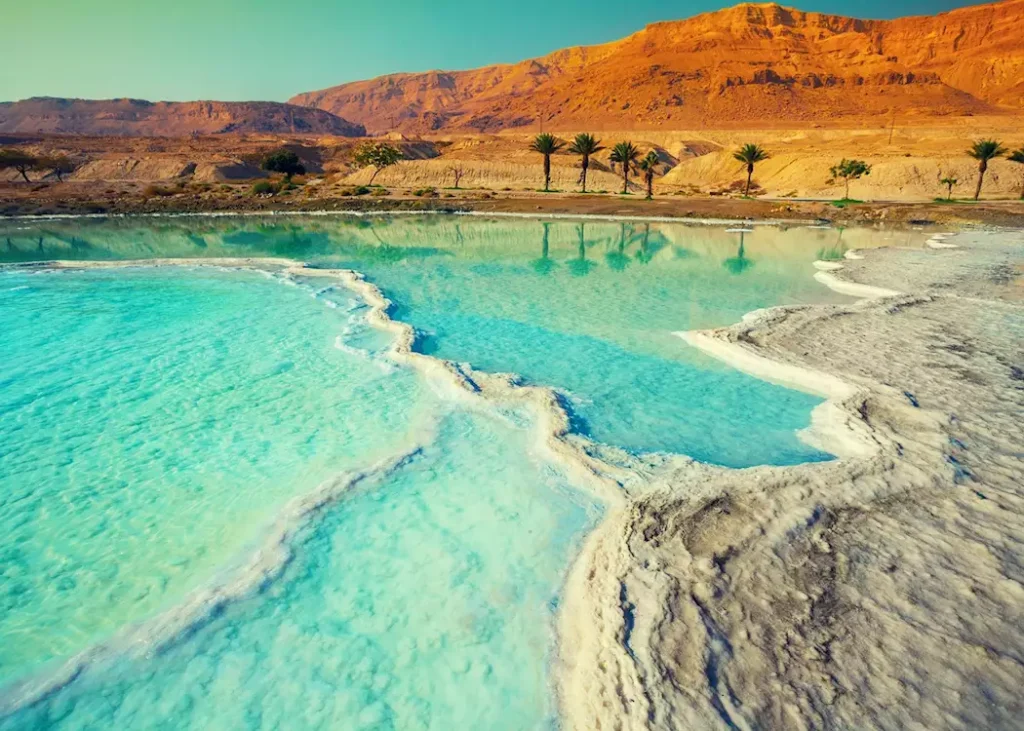

The Dead Sea has become synonymous with its health spas and resorts. People travel from all over the world to experience the therapeutic benefits of its mineral-rich waters and mud. The area offers luxury spas, clinics, and a variety of wellness treatments, capitalizing on the Dead Sea’s unique properties.
Shrinking of the Dead Sea (Environmental Concerns)
Unfortunately, the Dead Sea is shrinking at an alarming rate—roughly a meter yearly. Factors like diversifying freshwater from the Jordan River for agriculture, industry, and mineral extraction contribute to this decline. The shrinking Dead Sea has negative consequences, such as sinkholes, a disrupted ecosystem, and a potential impact on the area’s tourism.
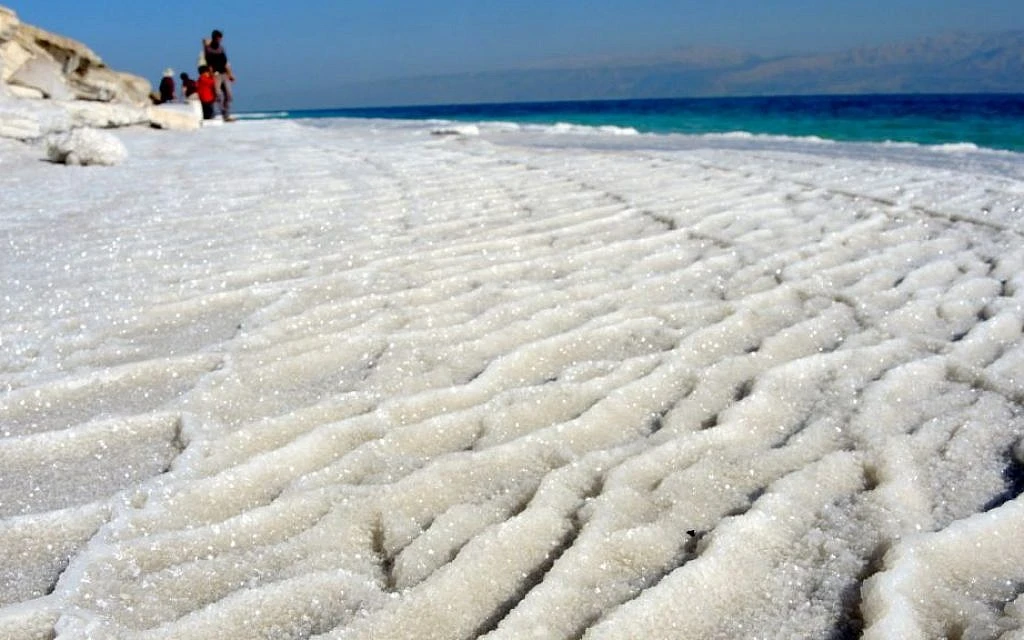

Conservation Efforts
Recognizing the severity of the situation, various conservation projects are underway. Efforts include:
- Water Replenishment: Plans exist for a potential canal linking the Red Sea and the Dead Sea, though these are complex due to cost and potential environmental impacts.
- Resource Management: Increased water use and mineral extraction regulation aims to limit further damage.
- Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public on the Dead Sea’s fragility is crucial for supporting conservation measures.
⫸ Conclusion
The Dead Sea, a place of stark beauty and remarkable properties, faces an uncertain future. Let’s consider what’s at stake and why understanding this unique ecosystem holds such importance:
The Future of the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea is shrinking at an alarming rate due to human activities like water diversion and mineral extraction. This decline risks severe environmental consequences, potentially altering the region’s climate and increasing sinkhole formation. While complete disappearance is unlikely, the Dead Sea faces significant changes.
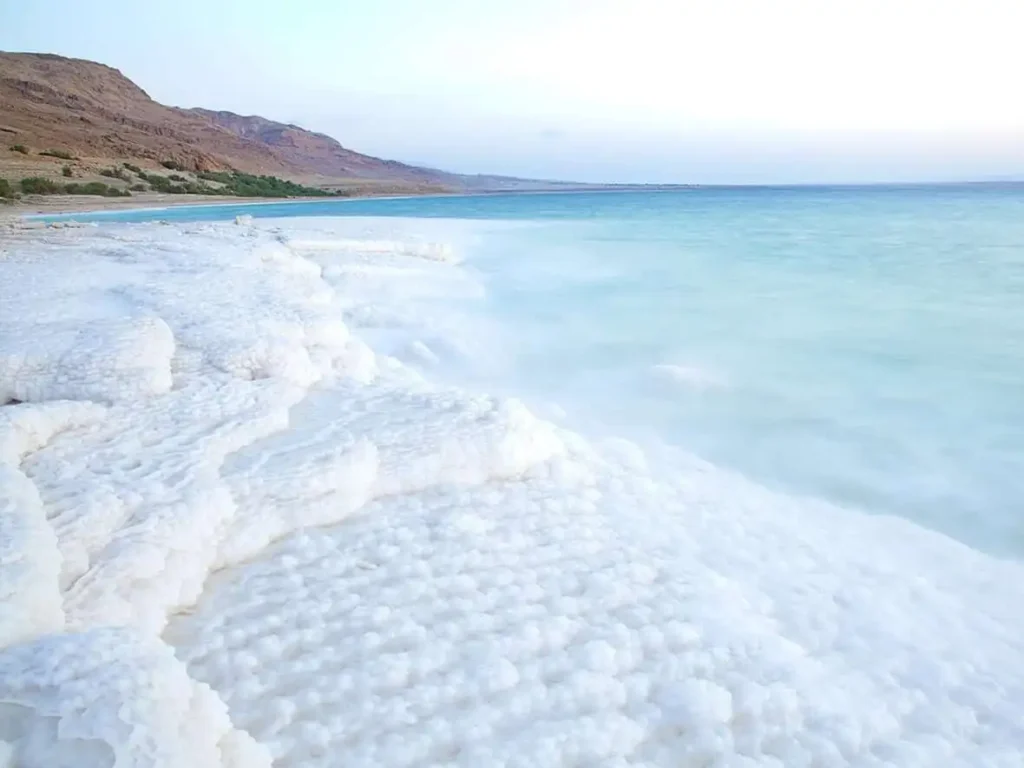

Importance of Understanding this Unique Ecosystem
The Dead Sea is a scientific treasure trove. Studying it can yield insights into extreme environments potential medical applications of its minerals, and even help us understand other seemingly inhospitable places in our solar system. Beyond science, preserving the Dead Sea is crucial for cultural heritage, tourism, and the region’s delicate balance.





